Chapter 4 (Part A) : Eukaryotic Cells
description
Transcript of Chapter 4 (Part A) : Eukaryotic Cells

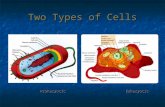
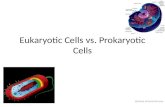
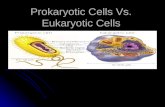
Eukaryot ic cel l structures:
•Eukaryote = organisms consist ing of one or more complex cel ls contain ing organel les
•Animals, p lants, fungi , prot ists are eukaryot ic
Chapter 4 (Part A) : Eukaryotic Cells

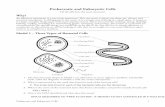
Parts --1. Cell walls: animal cells don’t have them; plants, fungi, some protists do

2. Plasma membrane: selectively-permeable barrier to environment; phospholipids and proteins

3. Nucleus: largest membrane-bound organelle in a cell; contains DNA + proteins (histones) in the form of chromosomes; covered by a double membrane with nuclear pores; where the genetic information is stored

4. Endoplasmic reticulum: 2 types – rough (with ribosomes) and smooth stacks of membranes from nucleus out into cytoplasm “factories” where many cellular molecules are made

5. Golgi apparatus:“packaging and shipping” areas of the cell; stacks of membranes with vesicles to the outside of the stacks; molecules are processed, packaged into vesicles, and moved to correct location in cell

Nucleus ER Golgi apparatus

6. Lysosomes: special vesicles that contain digestive enzymes and acid fuse with other vesicles functions: recycle old molecules and organelles lyse infecting bacteria, etc.; Mycobacterium tuberculosis prevents fusion of lysosome with vesicle in cell containing the bacteria; the bacteria then ride along with the immune system cell (macrophage)
bacterium
Macrophage
lysosome
nucleus


Macrophage now presenting bacterial antigens

Ribosomes:made of RNA and proteinshave no membranesite of protein synthesis80S in cells; 70S in mitochondria of cells
Ribosome sculpture at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, NY

8. Mitochondria: where aerobic respiration occurs; where much ATP is made; contains its own DNA and ribosomes (70S like bacteria); it is believed that mitochondria evolved from bacteria taken in by a bigger cell


9. Chloroplasts: In plants and some protists Site of photosynthesis Evolved from photosynthetic bacteria

10. Cytoplasm: about 75% water, used to absorb heat from many reactions in a cell; dissolved and suspended molecules in cytoplasm
11. Cytoskeleton: “scaffolding” of cell which holds it into a shape and attaches this cell to another loss of cytoskeleton components may lead to cancer– rounding up
Fibroblasts
Microtubule endings labeled

12. Flagella: move in a complex, whip-like motion
13. Cilia: hair-like appendages; move mucus.
Flagella video clip

A SEM of rabbit tracheal airway cilia http://users.umassmed.edu/michael.sanderson/mjslab/image

http://users.umassmed.edu/michael.sanderson/mjslab/image
Video clip of cilia in respiratory tract beating

The End