CHAPTER 2 STRUCTURES OF NUCLEIC ACIDS nucleic acids - CCGB | index
Chapter 3 – Nucleic Acids, Proteins and Enzymes
description
Transcript of Chapter 3 – Nucleic Acids, Proteins and Enzymes

CHAPTER 3 – NUCLEIC ACIDS, PROTEINS AND ENZYMES

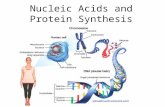
3.1 Nucleic Acids are Informational Macromolecule Diagram and describe the structure
of the DNA molecule including: The monomer and its parts (all
variations) Difference between purines and
pyrimidines Reaction that links the monomers into
the polymer and the bond formed What do we mean by 5’ and 3’ ends
of DNA? How is this terminology used to
describe how the chain is built?



3.1 Nucleic Acids are Informational Macromolecule Compare and contrast the structure
and function of DNA and RNA
Describe how complimentary base pairing works. Who pairs with who and why?


3.1 Nucleic Acids are Informational Macromolecule Describe the flow of information that
occurs in the following Replication Transcription Translation
Describe the relationship between a gene and a protein

3.2 Proteins are Polymers with important structural and
metabolic roles Know the roles of proteins in a cell
Diagram and label the structure of an amino acid What parts are key for condensation?
What bond forms? What part is unique for each amino acid?


3.2 Proteins are Polymers with important structural and
metabolic roles While you do not need to commit all
20 amino acids or their names to memory, you SHOULD be able to predict the characteristics of an amino acid if shown the structure


3.2 Proteins are Polymers with important structural and
metabolic roles Differentiate between primary,
secondary, tertiary and quaternary structures of proteins including relevant shapes, bonds and parts of the amino acids that are involved
Be aware of which of these bonds are strong/weak

3.2 Proteins are Polymers with important structural and
metabolic roles Why is the 3D shape of a protein
significant?
In what specific ways can the environment impact the 3D shape of a protein.

3.3 Some proteins act as enzymes to speed up biochemical reactions
Review energetics from chapter 2 Explain all parts of the diagrams
below

3.3 Some proteins act as enzymes to speed up biochemical reactions
Explain how an enzyme catalyzed reaction works How is the energy barrier lowered? How is the 3D structure of the protein
significant for the function of the enzyme?
Compare the characteristics of coenzymes, cofactors and prosthetic groups

3.3 Some proteins act as enzymes to speed up biochemical reactions
Describe the relationship between substrate concentration and the rate of a reaction

3.4 Regulation of metabolism occurs by regulation of
enzymes Why is it necessary for cells to
regulate enzymes?

3.4 Regulation of metabolism occurs by regulation of
enzymes Compare the following mechanisms
of regulation Irreversible inhibition Reversible inhibition
Competitive Non-competitive
Feedback inhibition Allosteric regulation


3.4 Regulation of metabolism occurs by regulation of
enzymes Explain the specific ways the
environment can affect an enzyme and how pH Temperature




![Enzymes and Nucleic acids recap-AS Biology [JM]](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/5550405ab4c905b2788b48f8/enzymes-and-nucleic-acids-recap-as-biology-jm.jpg)