Chapter #20 Plant Support and Transport. Chapter 20.1 2 stem types 1.Woody- a non green stem grows...
-
Upload
april-adams -
Category
Documents
-
view
223 -
download
0
Transcript of Chapter #20 Plant Support and Transport. Chapter 20.1 2 stem types 1.Woody- a non green stem grows...

Chapter #20
Plant Support
and Transport

Chapter 20.1
• 2 stem types
1. Woody- a non green stem grows thick and hard bark. (Trees)
2. Herbaceous- are soft, green stems. Grow no taller than meters. Have few xylem cells. (Flowers and grass)

Woody Stems• 5 Cell layers
1. Cork- outer layer made of dead cells and protects the stem from insects, disease and water loss.
2. Cortex- stores food.
3. Phloem cells- move food
4. Cambium- thin layer of cells that makes new phloem and xylem cells.
5. Layers 1-4 make up the Bark
6. Xylem- takes up water.
Cork
Cortex

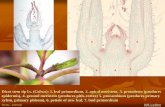
• Terminal bud- is the bud at the tip of a stem, responsible for the plants growth in length.
• Lateral bud- gives rise to new branches, leaves or flowers.

• Annual ring- cambium forms a ring of new xylem cells each year. Each ring is made up of a dark and light band.
• Light rings form in Spring when there is plenty of rain and growth is rapid.
• Dark rings form in Summer when there is less rain and growth is slower. They look dark because the xylem tubes are close together.
Oldest wood found in center

Chapter 20.2
• Roots take up water
• Water roots stem leaves stomata
• Leaves make food
• Food leaves stem roots
• Water storage in herbaceous stems is used to prevent wilting. Water acts like a skeleton.

• Plants store sugar as starch. • Plants use most of their stored food for new
growth in the spring (leaves and flowers).• Stem are used for:
1. Wood
2. Dollar bills
3. Paper
4. Food packets
5. Food (Cauliflower and Broccoli)• Sap liquid that flows up the xylem.

Chapter 20.3 • Two types of Roots
1. Taproot- large, single root with smaller side roots. Stores food. Example: beets, carrots, turnips, dandelions.
2. Fibrous roots- are many branched roots that grow in clusters. No main, large root.

Root layers1. Root hairs- are threadlike
cells of the epidermis that absorb water and minerals.
2. Epidermis- protects3. Cortex- stores food4. Endodermis- waxy cells
that help reduce water loss.
5. Xylem- carry water6. Phloem- carry food7. Cambium- makes new xylem and phloem
Epidermis
Cortex
Endodermis
Xylem
Phloem
Root hairs
Cambium

• The first root of a new plant is its primary root other roots are called secondary roots.
• Most roots keep growing as long as the plant lives.
• New cells are added to the END of a root, that is why they grow DOWN.

Chapter 20.4
• Plants get needed materials (water and minerals) for growth through their roots.
• Plants would die without roots.• Root hairs increase surface area.• Roots are used for:1. Food2. Tea3. Perfumes4. Medicines5. Reduce erosion

Roots can cause damage to underground pipes.
Jobs of roots
Absorption Storage
Water minerals FoodUsed for new
growing season

• “Tree”. December 19, 2006. http://www.cs.cmu.edu/afs/cs/misc/rayshade/all_mach/omega/doc/Examples/jpg/tree.jpg
• “Stem Layers”. December 19, 2006. http://www.ju.edu.jo/ecourse/Basics%20of%20Fruit%20Trees/Material/Lect-3-Internal%20Structure%20of%20the%20Fruit%20Tree_files/image004.jpg
• “Tree Rings”. December 19, 2006. http://volcanoes.usgs.gov/Imgs/Gif/Assess/TreeRing.gif
• “Buds”. December 19, 2006. http://www.infovisual.info/01/004_en.html• “Roots”. December 20, 2006.
http://www.kidsgardening.com/onlinecourse/Diagrams/c5/c5-1root.gif• “Root layers”. December 20, 2006.
http://www.campbell.edu/faculty/metz/Biology202/images/botany%20diagrams/root-dc-labeled.jpg