Chapter 2 Section 3 Life Science. THE Cell Membrane Cells survive by allowing some items to pass...
-
Upload
madeline-allison -
Category
Documents
-
view
222 -
download
4
Transcript of Chapter 2 Section 3 Life Science. THE Cell Membrane Cells survive by allowing some items to pass...

Chapter 2Section 3
Life Science

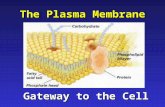
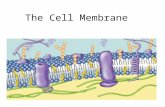
THE Cell Membrane
Cells survive by allowing some items to pass through the cell membrane.
***Cell Membrane is “Selectively Permeable”
Selectively Permeable- “selects” certain materials to go in and out of the cell membrane.

2 types of Movement through the Cell Membrane:
1. Passive Transport- does not require energy to pass through cell membrane
2. Active Transport- requires energy

Mrs. C’s Hill

FOCUS:Passive Transport
The movement of substances through the cell membrane without the input
of energy is called Passive Transport.
There are three types of Passive Transport that can occur.

1st Type of Passive Transport
Diffusion- movement of “materials” from an area of high concentration to low concentration.
Examples- Febreeze Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
molecules moving across membrane

EQUILIBRIUM Ending Result- Equilibrium
This is when it’s EQUAL on both sides– BALANCED!!!
Balance the smiley faces


2nd Type of Passive Transport
Osmosis- movement of water from an area of high concentration to low concentration
Examples- Wilting Plant (needs H2O)

EQUILIBRIUM Ending Result... Equilibrium
This is when it’s EQUAL on both sides– BALANCE!!!
Balance the H2O molecules


3rd Type of Passive Transport
Facilitated Diffusion- Diffusion that is helped by transport proteins with NO energy needed.
Like a “revolving door”
– When large items are too big to pass through the cell membrane they enter with “help” from transport proteins !!! (squeezing through)

Ending Result??? Ending Result... Equilibrium
This is when there is the same amount of items on both sides.– BALANCE!!!
Examples- Sugar molecules entering cells; Minerals entering plant roots.



• Think of student at bottom of hill…
• What type of Transport requires Energy?
• Active Transport!

Active Transport involves…
Transport Proteins and Energy are used to move materials through cell membrane

Examples- A Soccer/Football Game; Overtime requires a lot of extra energy.
Balance the glucose molecules

Active Transport What if items are too big to pass
through the Transport Proteins?
When items are too big, the cell membrane folds in on itself and encloses the item in a sphere called a vesicle (or vacuole).
Example of Plastic Bag…

How do items enter???
1. Endocytosis- when items are surrounded by the cell membrane and create a vesicle/vacuole (“a pod”)

2. Exocytosis- when large items are passed out of the cell by having the vesicle/vacuole attach to the cell membrane and open up to the outside.