Ch 10 part 1 Fundamentals of the Nervous System Chapter Learning Objectives 1.List the basic...
Transcript of Ch 10 part 1 Fundamentals of the Nervous System Chapter Learning Objectives 1.List the basic...

Ch 10 part 1 Fundamentals of the
Nervous System
Chapter Learning Objectives1. List the basic functions of the nervous system.2. Explain the structural and functional divisions of the nervous system.3. Describe neuroglia and cite their function(s).4. Define a neuron including its characteristic anatomy and functions.5. Discuss ganglia; also myelin sheaths.6. Classify neurons structurally and functionally.7. Explain how nerve impulses travel (use the terms synapse and
neurotransmitters).8. Identify common neurotransmitters and what they do.
Got nerve cells? There are more nerve cells in the human brain than there are stars in the Milky Way. (BTW, the human brain has about 100,000,000,000 (100 billion) neurons).
Read pgs 195-212

11 Interesting Facts About Einstein's Brain
After Death Dr. Ellen Weber September 29, 2006 Did you know these facts about the life of Einstein’s brain after his death?
1. On April 18, 1955 at Princeton Hospital in Trenton, New Jersey , the amazing life of Einstein’s brain ended.
2. His body arrived at the cremation oven incomplete the day he died… it was lacking a brain.
3. In a jar of formaldehyde in Dr. Thomas Harvey, the pathologist who performed Einstein's autopsy, stored the brain for his own study.
4. Some say that Einstein offered his brain for research, but the executor of his estate said that Einstein's son Hans made the decision to keep it.
5. When the press soon learned that Einstein's brain had been set aside for study, Dr. Harvey became very protective of the brain… and the attention infuriated the genius’ family.
6. Harvey divided the brain into 240 sections, kept in jars at his home.
7. In spite of studying the organ for many years, he published no findings, saying that there was nothing unusual about it.
8. Over time… Harvey offered parts of the brain to researchers, such as Dr. Marian Diamond from UC Berkeley, who reported its interesting features.
9. Dr. Diamond reported the percentage of glial cells … which nourish neurons … in Einstein's brain … contained about 73% more than the average male brain. There had been a greater metabolic need … his brain cells needed and used more energy.
10. In 1996 Dr. Harvey surrendered the remaining pieces of Einstein's brain to Dr. Elliot Krauss, at Princeton Hospital , who donated it to McMaster University where it was described as remarkable.
11. Researchers measured a 15% wider than average brain, with the inferior parietal regions on both hemispheres … much more developed than most.
Do you think the journey of one genius' brain after death ... can teach the rest of us anything new about intelligence in life...?

If We Lined Up All the Neurons (Nerve Cells) in
Our Body, How Long Would That Line Stretch?
Assume that one neuron is about 10 microns long (this is just an example, because neurons come in all different sizes). So, if we line up 100 billion neurons which are 10 microns long . . . (can you do the math?) Try it!
This may help with the math (or not):1000 microns= 1milimeter (mm)
10 mm= 1centimeter (cm)100 cm= 1 meter (m)
1000 m= 1 kilometer (km)

Functions of the Nervous System, pg 200
1.
2.
3.
Instructions: Quickly find and write down the 3 functions of the nervous system. Time: 1 minute

Discussion
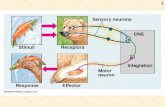
• Can anyone name the two main categories that the nervous system is split into for study purposes?

One Highly Integrated Nervous System
Divided into two principal parts for study purposes:
• Central nervous system (CNS) Pg. 197
– ________ and ______________– Integration and command center
• Peripheral nervous system (PNS) pg.198
• Paired _______ and _______ nerves– Carries messages __________ the spinal
cord and brain

PNS: Two Divisions pg 198-199
1. __________ (or afferent) divisiona) Sensory afferent fibers – carry impulses from
skin, skeletal muscles, and joints to the brain
b) Visceral afferent fibers – transmit impulses from visceral organs to the brain
2. _______ (or efferent) division – Transmits impulses from the CNS to certain
target organs called effector organs

Motor Division Further Divides Into
• ________nervous system which is voluntary– ____________ control of skeletal muscles
• ________ nervous system (ANS)– Regulates _____ muscle, _______ muscle, and
________ and is involuntary.– Divisions:
a) ____________ – mobilizes body systems during activity
b) _______________ – conserves energy; promotes housekeeping functions during rest

Self-Practice & Reinforcement pg. 198
Nervous SystemDivided into two what two principal parts?
Instructions: In order to help yourself better understand the way the nervous system is divided, take time to complete the following graphic organizer in your notes:
I. CNS or ________________
II. ________________
This one is further divided into:
1) Sensory 2) ____________
This one is further divided into:
(or voluntary) (or involuntary)
a. b.
i. ii
EXAMPLE

Two Main Cell Types of the Nervous System Pgs. 200-204
1. _________ – excitable cells that transmit electrical signals
2. ______________ – cells that surround and wrap neurons

Supporting Cells continued
• The supporting cells are collectively known as _______ or ___________ (pg 203)
• They:– Provide a supportive scaffolding for neurons– Segregate and insulate neurons– Guide young neurons to the proper
connections – Promote health and growth

6 Types of Neuroglia pg 204 Instructions: List the 6 types of neuroglia and what they do here now:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.

Astrocytes
• Most ________, versatile, and highly ____ glial cells
• They cling to neurons and their synaptic endings, and cover capillaries
• Functionally, they:– Support and brace neurons– Anchor neurons to their nutrient supplies– Guide migration of young neurons– Control the chemical environment

Microglia and Ependymal Cells
Microglia – small, ovoid cells with spiny processes
- Phagocytes that monitor the health of _________
Ependymal cells – range in shape from squamous to columnar
- They line the central cavities of the __________________

Oligodendrocytes, Schwann Cells, and
Satellite Cells
Oligodendrocytes – branched cells that wrap CNS ____________ Schwann cells (neurolemmocytes) – surround fibers of the PNSSatellite cells surround neuron cell bodies with ganglia

Neurons pg. 200
• ______________ of the nervous system– Composed of a body, axon, and dendrites– Long-lived, amitotic, and have a high
metabolic rate
• Their plasma membrane functions in:– Electrical signaling – Cell-to-cell signaling during development

Basic Neuron Structure pg. 201
Draw & label your practice diagram on page 203, question #5 in your workbook now.
Don’t label this one

Disorder: Multiple Sclerosis
In multiple sclerosis (MS), the ______________ are gradually destroyed and causes short-circuiting and eventually impulse conduction ceases. This autoimmune disease affects mostly young adults.
Symptoms: visual disturbances, problems controlling muscles, clumsiness, speech disturbances, urinary incontinence, and ultimately paralysis.
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=voMQ26IW3Wg&feature=related

Structure Meets Function, pg 201
1. axon
2. dendrites
3. Nissl bodies
4. Schwann cell
5. Node of Ranvier
6. Myelin sheath
7. neurilemma
INSTRUCTIONS: What do these structures do? Match the structure with its function. Write the letter of the answer only next to this slide. Estimated Time: 5-6 minutes
a. neurofibril nodes or gaps in the myelin sheath that occur along a myelinated axon
b. rough endoplasmic reticulum
c. short, branching structures responsible primarily for reception or input
d. single structure on each neuron also known as a nerve fiber; generates and transmits nerve impulses
e. neurolemmocytes that surround and form myelin sheaths around the larger nerve fibers in the PNS
f. a portion of a Schwann cell
g. whitish-fatty protein material that protects and insulates fibers and increases the speed of nerve transmission

How Do Neurons Work? Pg. 201
• Neurons talk to one another with ___________ and __________ signals
• Neurons do not touch one another (there is a gap or __________) between them
• Chemicals called ______________ help conduction of nerve impulses.
Check it out: http://video.google.com/videoplay?docid=7134684121021483823&q=neuron+impulse&total=22&start=0&num=10&so=0&type=search&plindex=0

Neurotransmitters, pg 202 Neurotransmitters are essential to the nervous system and brain chemistry. There are
more than 50 identified neurotransmitters. We’re going to focus on 4 key ones.
Acetylcholine - triggers muscle contraction and stimulates the excretion of certain hormones. In the CNS, it is involved in wakefulness, attentiveness, anger, aggression, sexuality, and thirst, among other things.
Alzheimer’s disease is associated with a lack of acetylcholine in certain regions of the brain.
Dopamine is an inhibitory neurotransmitter involved in controlling movement and posture. It also modulates mood and plays a central role in positive reinforcement and dependency.
The loss of dopamine in certain parts of the brain causes the muscle rigidity typical of Parkinson’s disease.

Neurotransmitters continued
Norepinephrine is a neurotransmitter that is important for attentiveness, emotions, sleeping, dreaming, and learning. It is also released as a hormone into the blood, where it causes blood vessels to contract and heart rate to increase.
Norepinephrine plays a role in mood disorders such as manic depression.
Serotonin contributes to various functions, such as regulating body temperature, sleep, mood, appetite, and pain.
Depression, suicide, impulsive behavior, and aggressiveness all appear to involve certain imbalances in serotonin.

Neurotransmitter Review Questions
1. If a patient is known to have Alzheimer's, what neurotransmitter is lacking?
2. If a patient has manic depression, what neurotransmitter is not properly balanced?
3. How about a patient displaying suicidal behavior, aggression, and clinical depression?
4. Parkinson’s with muscle rigidity?