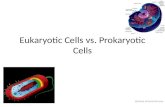
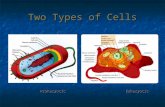
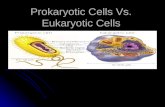
CELLS. 2 Types of Cells Prokaryotic (Bacteria) Eukaryotic (Plant & Animal) Both contain Organelles.
CELLS Two main types of cells are ______ and _______. A. Prokaryotic; eukaryotic B. Bacterial;...
-
Upload
bonnie-peters -
Category
Documents
-
view
228 -
download
4
Transcript of CELLS Two main types of cells are ______ and _______. A. Prokaryotic; eukaryotic B. Bacterial;...
CELLS
Two main types of cells are ______ and _______.
A. Prokaryotic; eukaryotic
B. Bacterial; animal
C. Nerves; muscles
D. Plant; animal
© 2009 W.W. Norton & Company, Inc. DISCOVER BIOLOGY 4/e 43
The boundary structure that physically defines a cell is the .
A.Cell wall
B.Selective permeability
C.Plasma membrane
D.Protein coat
© 2009 W.W. Norton & Company, Inc. DISCOVER BIOLOGY 4/e 42
Where is the secreted protein insulin synthesized?
A. In the Golgi apparatusB. On the rough ERC. On ribosomes in the cytoplasmD. In the nucleus
© 2009 W.W. Norton & Company, Inc. DISCOVER BIOLOGY 4/e 2
Cell Is the Basic Unit of Life Cell theory: An organism can be one celled or
multicellular
Multicellular organisms have billions of cells
Humans have over 200 types of cells
Hooke first described cells in 1665 Schleiden (1838) recognized plant cells Schwann (1839) reported animal cells
cells are too small to be viewed by the naked eye, one way to increase resolution is to increase magnification, such as by using a microscope
two major types: Prokaryotic: bacteria
and archae lacks a nucleus Without a system of
internal membranes
Eukaryotic: algae, fungi, plants, animals
has a nucleus has internal
membrane-bound compartments
Cell types
© 2009 W.W. Norton & Company, Inc. DISCOVER BIOLOGY 4/e 8
ProkaryotesLittle internal organizationMuch smaller than eukaryotes
© 2009 W.W. Norton & Company, Inc. DISCOVER BIOLOGY 4/e 9
Figure 5.2
■ EukaryotesDNA contained in nucleus Membrane‑enclosed
organellesInternal compartments
for special functions
Different eukaryotic cells
Protist, fungi, plants= cell wall beyond the plasma membrane
Protist, plants= chloroplasts Plants= central vacuoleAnimals= centrioles
© 2009 W.W. Norton & Company, Inc. DISCOVER BIOLOGY 4/e 7
The Plasma Membrane
• Defines the boundary of the cell
• Consists of a bilayer of lipids with proteins for communication with external environment– Selective permeability
– and act as markers= blood types
• Fluid mosaic model– Mobility of components of the membrane
© 2009 W.W. Norton & Company, Inc. DISCOVER BIOLOGY 4/e 11
Nucleus: The Administrative Office command and control
center of the cell stores hereditary
information: DNA Surrounded by a
double-membrane nuclear envelope
Nuclear pores are gateways for molecules
Nucleolus dark-staining region of the nucleus contains the genes that code for the rRNA
(ribosomal RNA) that makes up the ribosomes the subunits leave the nucleus via the nuclear
pores and the final ribosome is assembled in the cytoplasm
© 2009 W.W. Norton & Company, Inc. DISCOVER BIOLOGY 4/e 23
Mitochondrion: Power Plant Double‑membrane organelle Inner membrane folded
into cristae Harnesses energy from
chemical breakdown Cellular respiration
Produce ATP
© 2009 W.W. Norton & Company, Inc. DISCOVER BIOLOGY 4/e 25
Chloroplast: Photosynthesis Double‑membrane
organelle Contains grana,
made of thylakoids Converts CO2
and H2O into sugars using light
Chlorophyll enables photosynthesis
Figure 5.10
© 2009 W.W. Norton & Company, Inc. DISCOVER BIOLOGY 4/e 13
The Endoplasmic Reticulum: The Factory Floor
Figure 5.4
Interconnected tubes and flattened sacs
Rough ER Ribosomes Makes membrane
and secreted proteins Smooth ER
Makes membrane vesicles
© 2009 W.W. Norton & Company, Inc. DISCOVER BIOLOGY 4/e 17
Golgi: Shipping Department
Stacked, flattened
membrane sacs
Processes new
proteins and lipids Adds specific
chemical groups
Targets them
to their destinations
© 2009 W.W. Norton & Company, Inc. DISCOVER BIOLOGY 4/e 15
Vesicles: Movement in the Cell Vesicles
Membrane‑enclosed sacs Transport vesicles
Moving substances from one location to another
© 2009 W.W. Norton & Company, Inc. DISCOVER BIOLOGY 4/e 19
Lysosomes: Clean-up Crew Small spherical organelles Contain enzymes to break down macromolecules Release simple sugars, amino acids,
and fats to be recycled To clear cell of damaged organelles As a source of food To destroy invading bacteria
Derivate from membranes in the cell The functions are:
1. detoxify harmful byproducts of metabolism
2. convert fats to carbohydrates in plants seeds for growth
Peroxisomes: Detoxy centers
© 2009 W.W. Norton & Company, Inc. DISCOVER BIOLOGY 4/e 21
The Central Vacuole: Storage
Figure 5.8
A specialized structure in plants and fungi Breaks down substances Stores chemicals
for later use Fills with water to
provide rigidity
27
Cytoskeleton:
Gives the cell its shape
Provides internal support
Is responsible for movementmicrotubule
intermediatefilament
microfilament
© 2009 W.W. Norton & Company, Inc. DISCOVER BIOLOGY 4/e 31
Movement
Used as tracks for vesicle movement or the whole cell
© 2009 W.W. Norton & Company, Inc. DISCOVER BIOLOGY 4/e 33
Cilia and Flagella Cilia beat in unison like oars
Flagella beat like whips
Centrioles • complex structures • In animal cells and
protists• Functions:
• anchor locomotory structures
• assemble microtubules near the nuclear envelope for the cell division
– found in• Plants• Fungi• protists
– function in:• Protection• maintaining cell shape• preventing excessive water
loss/uptake
Cell Wall
• Outside the plasma membrane
• in animal cells
• mixture of proteins: Collagen and elastin for protective layer
• ECM coordinates cells functioning as tissues
Extracellular matrix (ECM)
© 2009 W.W. Norton & Company, Inc. DISCOVER BIOLOGY 4/e 39
Evolution of Organelles
• Eukaryotes most likely evolved from prokaryotes– Larger prokaryotes ingested smaller prokaryotes
• Free-living mitochondria and chloroplasts were captured – Formed an endosymbiotic relationship with the host cell
Extra credit…. Make flash cards with all the following terms
Cell
Chloroplast
Chromosome
Cilium
Ribosome
Rough ER
Smooth ER
Vacuole
Vesicle
Cytoplasm
Cytoskeleton
Eukaryote
Flagellum
Fluid mosaic model
Golgi apparatus
Extra cellular matrix
Lysosome
Mitochondrion
Nuclear envelope
Nucleolus
Nucleus
Organelle
Plasma membrane
Prokaryote
peroxysome
Review Question1: Cell theory includes the principle thatA) cells are the smallest living thingsB) all cells are surrounded by cell wallsC) all organisms are made up of many cells D) Nothing smaller than an organelle is considered alive.
2: The plasma membrane is:A) carbohydrate layer that to protect B) double lipid layer with proteins inserted in itC) thin sheet of structural proteins that lines the inside of some body cavitiesD) composed of blood plasma that has solidified into a protective barrier.
3: Organisms that have cells with cytoplasm and no organelles are called ______________, and organisms whose cells have organelles and a nucleus are called ______________
A) cellulose, nuclearB) flagellated, streptococcalC) eukaryotes, prokaryotesD) prokaryotes, eukaryotes
4: Within the nucleus of a cell you can find ________
5: The endomembrane system within a cell includesA) cytoskeleton and ribosomes.B) prokaryotes and eukaryotesC) endoplasmic reticulum and GolgiD) mitochondria and the chloroplasts.
6: Which of the following statements is true?A) All cells have a cell wall for protection and structure.B) Eukaryotic cells in plants and fungi, and all prokaryotes, have a
cell wall.C) There is a second membrane composed of structural
carbohydrates surrounding all cells.D) Prokaryotes and all cells of eukaryotic animals have a cell wall.