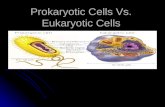
Identify structures and functions of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells; plant and animal cells.
-
Upload
louise-wilkerson -
Category
Documents
-
view
239 -
download
0
Transcript of Identify structures and functions of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells; plant and animal cells.

Identify structures and functions of prokaryotic
and eukaryotic cells; plant and animal cells

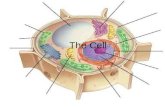
Identify this part• Cell (plasma)
membrane
• “thin, flexible barrier that surrounds all cells, regulates what enters and leaves the cell”
• “controls entry into and out of the cell”
• “controls what goes in and out of the cell”

Identify this part• nucleus• “in cells, the structure
that contains the cell’s genetic material in the form of DNA”
• “chromosomes are found here”
• “contains all the genetic information of the cell, controls all cell functions”

Identify this part• Flagella/cilia
• Used for motion

Organelle that makes proteins
•ribosomes
• “cell organelle consisting of RNA and protein found throughout the cytoplasm in a cell; the site of protein synthesis.”
• “where proteins are made”• “small particles of RNA; they make proteins”

Identify this part
• nucleolus
• “a small dense region….where the assembly of ribosomes begin”
• “spherical body within the nucleus”

Converts glucose into ATP for energy
•Mitochondria• “cell organelle that converts the chemical energy stored in
food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use”
• “powerhouse” of the cell• “makes energy for the cell, site of cell respiration”

Organelle that makes ribosomes
•nucleolus

Identify this part• Endoplasmic
reticulum
• Can be rough ER (with ribosomes) or smooth ER (without)
• “internal membrane system found in eukaryotic cells; place where lipid components of the cell membrane are assembled”
• “stores and releases chemicals”
• “packages proteins, sometimes has ribosomes on it”

Identify this part• ribosomes

What part of the cell controls what goes in
and out of the cell
•Cell (plasma) membrane

Identify this part• cytoplasm• “fluid portion of the cell
outside the nucleus”• “contains water and
dissolved minerals”• “provides structure for
the cell’s organelles, contains dissolved substances and water and some chemical processes take place her”

• Mitochondria
Identify this part

Transports things around inside the cell
•Endoplasmic reticulum

In animal cells only, sets of microtubules that help
during cell division
•centrioles
• “structure in an animal cell that helps to organize cell division”• “structures involved in mitosis in animal cells only”• “found only in animal cells and it aids in cell division”

Breaks down food for the cell
•Lysosomes• “cell organelle that breaks down lipids, carbohydrates, and
proteins into small molecules that can be used the rest of the cell”
• “digestion center”• “breaks down wastes in the cell, filled with digestive enzymes”

Modifies proteins for movement outside the
cell•Golgi Apparatus
(bodies)• “organelle in cells that modifies, sorts and packages proteins
and other materials from the ER for storage in the cell or release outside the cell.”
• “serves as storage centers for the secretory products of the cell”
• “Modifies proteins/materials from ER for use outside or inside cell”

Give shape to cell and help organelles move
around
•Microtubules and microfilaments

Identify this part
• Lysosomes

Identify this part• Golgi Apparatus
(bodies)

Material in the cell that contains water and dissolved nutrients
•cytoplasm

Help animal and prokaryotic cells move
around•Cilia/flagella
• “short hairlike projections that produces movement”
• “hairlike structures with the capacity for movement”
• “structure sued by Protists for movement, produces movement in a wavelike motion”
• “long, hairlike structure used for movement”
• “long, whip like structures; used for motion”

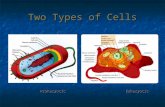
What is a eukaryote?• Cells that do have a nucleus and
organelles with membranes• Examples include plants, animals
and fungi
• “organism who cells contain a nucleus”• “…nucleus separates the material from the rest of the cell”• “are cells that have a nucleus and organelles with
membranes”

Identify this part
• centrioles

Give support and structure to plant cells
(only)
•Cell wall• “strong, supporting layer around the cell membrane in some
cells”• “shapes and supports a plant cell”• “rigid outer layer that supports the cell; found in plant but not
animal cells”

How can you tell the difference between a plant and animal cell?
• Plant cells have– Cell walls, chloroplasts and a large
central vacuole
• Animal cells have– a cell membrane as only outer layer,
centrioles and may have cilia or flagella

Storage area, very large in plants
•Vacuole (central vacuole in plants)
• “cell organelle that stores materials such as water, salts proteins and carbohydrates”
• “contains water and dissolved minerals”• “place where wastes are stored; in plants it is very large but
in animals there can be many small ones”

In plants, where photosynthesis takes
place
•chloroplasts
• “organelle found in cells of plants and some other organisms that captures the energy from sunlight and converts it into chemical energy”
• “site of photosynthesis”• “organelle where sunlight is converted into energy by the
process of photosynthesis”

Identify this part
• Cell wall

What is a prokaryote?• Has no membrane bound nucleus
(still has DNA) or organelles• Bacteria are prokaryotes
• “unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus”• “…do not enclose their DNA in nuclei”• “cells that have no nucleus or membrane-bound
organelles”

Identify this part
• Vacuole (central vacuole in plants)

Is this cell prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
• Prokaryote• Like
bacteria

Is this cell prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
• Eukaryote• Like animals, plants and
fungi

Controls the functions of the cell
•nucleus

Identify this part
• chloroplasts

Cell membrane• Also called plasma membrane• Allows only certain things to enter
and leave the cell (selectively permeable).
• Membrane around organelles has similar structure.
• Phospholipid bilayer:– 2 layers of phospholipids (phosphate
group (PO4) and two fats (lipids))

Cell membrane• Fluid Mosaic:
– Bilayer also contains proteins (mark the cell as one of
yours and help things move in and out of cell)
– Things in the cell membrane move around, they don’t stay
still

Cell membrane

Cells• First discovered and named by
Robert Hooke in 1665• Saw them in cork samples• Looked like rooms where monks
stayed• 1673 Anton van Leewenhoek
saw first live cells

Cells• 1838 Max Schleiden…all plants
made of cells• 1839 Theodor Schwann…all
animals made of cells• Rudolf Virchow…all cells come
from other cells

Cell Theory• All living things are made of cells• Cells come from other cells• Cells are the basic unit of life (i.e.
life functions happen at cell level; cells can do all life
functions)

Cells• Have different shapes, according to
their functions• Limited in size by the ratio of surface
area to volume• As a cell gets bigger, it’s volume
increases faster than surface area• Bigger cells need more substances
(water, oxygen, etc.) but don’t have enough surface area to let
everything in/out

Cell shapes

Describe what a phospholipid bilayer is
• phospholipids: a molecule that has a phosphate group as a head and two lipid tails
• In a double layer (bilayer)
• for cell membrane