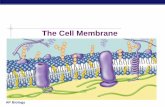
Cell Membranes Semi-permeable Lipid bilayer. Function of Plasma Membrane Physically separates cell...
-
Upload
lizbeth-payne -
Category
Documents
-
view
213 -
download
0
Transcript of Cell Membranes Semi-permeable Lipid bilayer. Function of Plasma Membrane Physically separates cell...

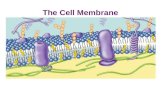
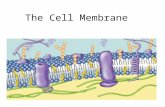
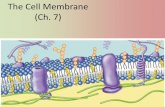
Cell Membranes
Semi-permeable
Lipid bilayer

Function of Plasma Membrane Physically separates cell from outside world
Maintains homeostasis
Regulates passage of materials into and out of cell

Endomembrane System Membranes of organelles such as:
Nuclear membrane Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Complex Vesicles/Vacuoles Lysosome
Divide cell into compartments
Serve as surfaces for chemical reactions

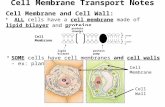
Basic Structure of the Membrane
Made of phospholipids:
Hydrophilic head Glycerol + PO4
Hydrophobic tail 2 fatty acid chains
Since cells are in an aqueous solution, bilayer is most stable form

Additional Molecules

Fluid Mosaic Model Currently accepted molecule of plasma
membrane structure
Lipids of membrane are fluid and move laterally
Proteins are embedded/scattered throughout
http://home.earthlink.net/~shalpine/anim/Life/memb.htm

Membrane Proteins Arranged asymmetrically
2 main types:
Integral proteins May be transmembrane
Peripheral proteins

Functions of Membrane Proteins: Passive transport - passageways
Active transport – pump materials
Enzymes – catalyze reactions
Signal Transduction
Identification


Membrane Potential Cell membrane is polarized
Inside of cell is more neg. than outside Electrical gradient
Voltage Can be used to do work
Membrane potential = voltage Resting potential = -70mV

Cell Junctions Form between cells in
close contact with one another
Allow for rapid communication, prevent passage of material, form strong connections

Cell Junctions: Tight junctions
Gap junctions
Anchoring Junctions Desmosomes Adhering Junctions
Plasmodesmata