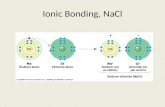
Mixing Aqueous ionic compounds… Na + Cl - Na + Cl - NaCl (aq) NaCl (s)
By showing the flash cards. NaCl
Transcript of By showing the flash cards. NaCl

60
By showing the flash cards.
NaCl
Common salt ki Dandi march ---- From the angle of chemistryTHE SOLID STATE :
1. NaCl is a -------------------(amorphous , crystalline) substance .2. NaCl belongs to ----------- crystal system? ( cubic , hexagonal , triclinic ,
orthorhombic )3. NaCl shows a property of ---------------- ( isotropic , anisotropic)4. Which one conducts both in molten and aqueous state but not conduct in solid
state ( Na , NaCl)5. NaCl is is which type of crystal? ( covalent , metallic , ionic , molecular)6. NaCl belongs to --------------- type crystal? ( primitive , bcc , fcc)7. What is the Co-ordination number of NaCl?8. NaCl belongs to --------------------- type of packing? (ABABAB… ,
ABCABCABC…..)9. In NaCl crystal, which one present in octahedral voids? (Na+ , Cl-)10.NaCl crystal act as ------ (insulator, semiconductor, conductor) at room temperature.11.How many number of chloride ions present in a cubic unit cell of Na Cl?12.When NaCl is heated conductivity ---------------------- ( increases , decreases)13.F-Centre is ---------------------- type of defect ( stoichiometric , non-
stoichiometric)
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com

61
14.NaCl shows ---------------------- defect ( Frenkel , Shottky )15.NaCl is ----------------- (diamagnetic, paramagnetic) substance.16.What happens when NaCl crystals are heated in an atmosphere of sodium
vapours?17.When NaCl added in SrCl2 , what type of defect is observed ?( Shottky defect ,
frenkel defect , impurity)18.F-centre shown by NaCl crystal is ----------------- in colour? ( pink , yellow ,
violet)19.If NaCl is doped with 10-3 mol% of SrCl2 ,The concentrations of cation vacancies
are ----20.Refractive index of which solid is /are observed to have the same value along all
directions? ( NaCl ,Quartz , Glass , PVC)21. What percent of octahedral voids are occupied in NaCl crystal? (25%, 50%, 100%)22. When NaCl crystal is heated what happens to its Co-ordination number?
(Increases, decreases)
CHAP-2 : SOLUTIONS23. What inter-particle interaction is present when NaCl is dissolved in water?24. Vapour pressure is ---------------(increased , decreased) when NaCl is added in
water .25. Which has more Freezing point and why? ( Distilled water or Sea water )26. What is the van’t Hoff factor of NaCl in very dilute solution in Water?27. Whose boiling point is more and why? ( 1mol of NaCl in 100 mL water , 1 mol of
Glucose in 100mL water)28. Which has more osmotic pressure and why? (1M NaCl solution , 1M Glucose
solution)29. Name the process used to get fresh water from salt water.30. Why NaCl act as de-icing agent?31. How NaCl helps to preserve meat?32. 1% NaCl solution is called ------- (hypertonic, hypotonic, isotonic) solution to the
plasma concentration of human blood cell?33. When you measure molar mass through colligative properties,why NaCl shows
abnormal molecular mass but nor glucose ?34. When a person takes lot of salt or salty food, he/she experience water retention in
tissue cells and intercellular spaces because of ----------------- . The resulting puffinessor swelling is called -------------------------.
35. When 5.85g of NaCl is added in 100 mL water , then the Formality(or Molarity)ofthe aq. Solution is -------- M
36. When heated solubility of NaCl in water -------------------------- ( decreases ,increases)
37. Aqueous NaCl solution is ------------------- solution ( ideal , non-ideal)38. Aqueous NaCl solution is shows ---------------- (positive, negative, no ) deviations from Raoult’s Law
.
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com

62
39. Kya apke tooth paste me NAMAK HAI”? Why NaCl is added in tooth paste?40. Whose “i” (van’t Hoff factor) is more and why? (0.1m , 0.01m)41. Why doctors asked the patient to take low sodium salt for high B.P patient?42. Why do you gargle luke warm salt water?
CHAP-3 : ELECTROCHEMISTRY43. NaCl is -------------------- (strong , weak) electrolyte44. Which one is used in salt bridge more frequently? (NaCl, KCl)45. Corrosion becomes --------------- (faster. slower) in saline condition.46. When dilution occurs in Aq. NaCl solution , conductivity ------(decreases , increases)47. Write the Kohlrausch limiting molar conductivity equation for NaCl?48. Molar conductivity of aq. NaCl -----(increases , decreases) with dilution linearly with √C49. What happens when aqueous NaCl is electrolysed at platinum electrode?50. What happens when molten NaCl is electrolysed at platinum electrode?51. Say True or False. Limiting molar conductivity cannot be obtained for aq. NaCl
graphically.52. Which one show more limiting conductivity in water at 298 K? ( Na+ , K+ )53. How much Chlorine gas in terms of gram would be produced when 96500 C is passed
in aq NaCl solution?
CHAP-5 : SURFACE CHEMISTRY54. NaCl in water is a ------------------------- ( crystalloid , colloid)55. Say TRUE or FALSE. – Aq solution of NaCl will show Tyndal Effect.56. What happens when NaCl is added in positively charged sol ferric hydroxide?57. Which has better coagulation capacity for potitively charged ferric hydrohyde sol?
(NaCl, Potassium Ferrocyanide)58. Name the enzyme that shows high catalytic activity in presence of NaCl which provides Na+.59. What is the charge of sol developed when NaCl is added in excess of AgNO3 solution?
Chap-7 : p-BLOCK ELEMENTS60. Name the gas obtained when NaCl is treated with Conc . H2SO4.61. Name the gas produced when NaCl is reacted with MnO2 and Conc. H2SO4?62. What do you observe when Aq.NaCl is treated with acidified KMnO4 solution?63. Which is more covalent in nature? (LiCl, NaCl )
Miscellaneous
64. Why NaCl is added in soap preparation?65. Why a small amount of NaCl is added during the preparation of egg albumin sol
.
So on ------- and so on ---------------------It’s not an End ------------------
please continue ……
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com

63
UNIT-1: TOPIC: SOLID STATE: worksheet for class-xii
MATCH THE FOLLOWING-MATCH THE FOLLOWING-1 MATCH THE FOLLOWING -2
COLUMN -I COLUMN -II COLUMN -I COLUMN-II1.H- bonded molecularsolid
A.NaCl 1.Schottky Defect A.Fe3+
2.Ionic crystal B.Diamond 2.F-Centre B.Fe ,Co , Ni ,CrO2
3.Covalent crystal C.Steel 3. Frenkel Defect C.NaCl/Na4.Metallic crystal D.Dry ice 4. Paramagnetic
SubstanceD.AgCl
5.Molecular crystal E. Ice 5.FerromagneticSubstance
E.NaCl
MATCH THE FOLLOWINGMATCH THE FOLLOWING-3 MATCH THE FOLLOWING-4
COLUMN -I COLUMN -II COLUMN -I COLUMN-II
1.p-typesemiconductor
A.Ga—As 1.Face diagonal A.74%
2.13—15 compounds B.Ge doped with As 2.Packing efficiency infcc
B. 2
3. 12—16 compunds C.Si doped with Ga 3.No. of atoms per unitcell in bcc
C.4r =√ 2a
4.n-typesemiconductor
D.ZnO 4.Body Diagonal D.4
5. metal excessdefects
E.CdS 5. No of octahedral voidspresent in fcc unit cell
E. 4r =√3a
MATCH THE FOLLOWINGMATCH THE FOLLOWING-5 MATCH THE FOLLOWING-6COLUMN -I COLUMN -II COLUMN -I COLUMN-II
1.Paramagnetism A.Intrinsicsemiconductor
1.The process of adding anappropriate amount ofsuitable impurity toincrease the conductivity ofsemiconductor .
A.Ferrimagnetism
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com

64
2.Anti-ferromagnetism
B.Spin and orbitalmotion of unpairedelectron
2. Since the arrangement ofparticles is different alongdifferent directions, the valueof same physical property isfound to be different alongeach direction.
B.Doping
3. F-centre C.Photovoltaic cell 3. Some of the glass fromancient civilizations which arewith us are milky inappearance
C.Schotky Defect
4.Pure Si-crystal D.Magnetic domainsare oppositelyoriented in equalquantity
4.When in a substance themagnetic moments of thedomains are
allingned in parallel andantiparallel directions inunequal numbers ,
D.Crystalisation
5.AmorphousSilicon
E.Electron trappedin anion vacantcentre
5. When equal number ofcations and anions are missingfrom their lattice sites.
E.Anisotropy
Prepared by A K PANDA , PGT(CHEMISTRY) ,KV NO-3 , BBSR
UNIT-1: TOPIC: SOLID STATE : worksheet for class-xiiFILL IN THE BLANKS/ CHOOSE THE CORRECT ANSWER
CONCEPT-CLOSE PACKING :CH-SOLID STATE CARD -1
[1×5=5M]
CONCEPT-CLOSE PACKING :CH-SOLID STATE CARD -2
[1×5=5M]1# Packing efficiency in fcc is ----
( 52.4% , 68% , 74% )2# The number of atom per unit cell(Z) in bcc is -------------- ( 1,2,4,6)3# In case of fcc , face diagonal =4r =---------------------- ( 2a , √2 a , √3 a ,π/6)4# The number of octahedral voidspresent per unit cell in fcc type crystalare ------- ( 13,4,8,6)5# What type of co-ordination ispossible in a crystal if the involvedradius ratio is in the range of (i)0.225—0.414 : CN = ---------------
(ii) 0.414—0.732 : CN = ---------------
(iii) 0.732—1.0 : CN = ---------------
6# The co-ordination number of anatom in
hcp (3D) is ---------- ( 4,6,8,12)7# Packing fraction in bcc is -- ( π / 3√2,π /6, √3 π /8)8# The number of nearest neighbours ofa particle is called its --------------------------- .9# In a binary compound, having cubicunit cells, the anion B are located at thecorners of the cube and the face centreswhereas cations A occupy all thetetrahedral voids . The formula of thecompound is ------10 # ABABAB….. pattern is found in ----
( ccp ,hcp , bcc , primitive)
CONCEPT-CLOSE PACKING : CONCEPT-CLOSE PACKING :
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com

65
CH-SOLID STATE CARD -3[1×5=5M]
CH-SOLID STATE CARD -4[1×2=2M]
11# -------------------number of unitcells are there in a 1.0 g cube shapedideal crystal of NaCl ?12# Cu forms ccp lattice . 12 .7 g ofCu produces ------------ mole of voids( 0.1 , 0.2 ,0.3 .0.6)13# 23 g Na-atom can cause ------------------- number of unit cell , if it ispacked in bcc type .14# Al forms ccp lattice .If themetallic radius of Al is 125 pm , thenthe length of the side of the unit cellis -------cm15# Silver forms ccp lattice and the edge lengthof its unit cell is 408.6 pm .The density of Ag is----------g/cm3 . ( Atomic mass of Ag is 107.9 u )
16# In a crystalline solid ,havingformula AB2O4 , oxide ions are arrangedin ccp lattice while cations are presentin td-voids and cations B are present inoh-voids . The percentage of the td-voids is occupied by Ais ------ Andthe percentage of the oh-voids isoccupied by B is ------17# A compound formed by elements Xand Y crystallizes in the cubic structurewhere X atoms are at the corners of thecube and Y atoms are at the centres ofalternate faces of the unit cell. Theformula of the compound is --------------------
CONCEPT- Defects chap-solid stateCH-SOLID STATE CARD -5
[1×5=5M]
CONCEPT- Defects chap-solidstateCH-SOLID STATE CARD -6
[1×5=5M]18# Si doped with B is a ---------------- type semiconductor ( p-type , n-type)19# 13-15 compound is --------------------(CdS ,GaAs , Si doped with Sb,Sidoped with Ga)20# ---------------- shows schottkydefects
( ZnS , NaCl , Steel, ZnO ,AgCl )21# Paramagnetism is shown in -------------------
( Cu++ , H2O , NaCl ,C6H6 , Cu+)22# -------------- is a ferromagneticmaterial .
( MnO , Fe3O4 , CrO2 , Cr3+ , C6H6 )
23# If temperature increasesconductivity in which case decreases (Al , NaCl , Ge )24# Which one will not show F-centrewhen the following is heated withexcess of its metal
( FeO , ZnO ,NaCl ,LiCl ,KCl)25# In which point defects densitydecreases ? ( Shottky , Frenkel ,interstitial)26#------------- substances arte weaklyrepelled by a magnetic field . (Paramagnetic , diamagnetic)27# ------is yellow when hot and whitewhen cold .( CaCl2 , ZnO , NaCl , Fe0..93O )
Prepared by A K PANDA , PGT(CHEMISTRY) ,KV NO-3 , BBSR
UNIT-1: TOPIC: SOLID STATE : worksheet for class-xii
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com

66
FILL IN THE BLANKS/ CHOOSE THE CORRECT ANSWERCONCEPT- Defects chap-solidstateCH-SOLID STATE CARD -7
[1×5=5M]
CONCEPT- Defects chap-solidstateCH-SOLID STATE CARD -8
[1×5=5M]28# The excess of lithium in LiCl makes itpink is due to -----------------------------29 # The compound that shows bothSchottky and Frenkel defect is -----------------------30# Doping ---------(minimizes ,maximizes) the forbidden energy gap .31# The forbidden energy is maximum in--------
( Ge , Mg , NaCl ,Ge doped with In )32# Which one show metal excess defects
( FeO , ZnO)
33# When an electron is trapped in ananion vacant centre , it is called ------------------------.34# Si , Ge can be doped with a group -------------- elements to produce p-typesemiconductor.
( Gp- 12,13,14,15)35# Solar cell is an efficient --------------------------
( photo-diode , photo-triode)36# Diode acts as a ------- ( rectifier ,amplifier)37# ---------------- oxide is like metallic cu inits conductivity and appearance .
CONCEPT- Defects chap-solid stateCH-SOLID STATE CARD -9 [1×3=3M]
CONCEPT- Defects chap-solid stateCH-SOLID STATE CARD -10 [1×3=3M]
38# The process of adding an appropriateamount of suitable impurity to increasethe conductivity of a intrinsic semi-conductor like S , Ge is called39# When in a substance the magneticmoments of the domains are allingned inparallel and antiparallel directions inunequal numbers , the phenomenonobserved is called ----------- .
(ferromagnetism, anti-ferromagnetism,
ferrimagnetism)40# In which type of semi-conductor ,electron holes are moving towardsnegatively charged plate under theinfluence of electric field ? ( p-type , n-type)
41# If an atom is missing from its latticesite and it occupies the interstitial site , theelectrical neutrality as well as thestoichiometry of the compound aremaintained . This type of defect is called -------------------- defect .42# The set of molecular orbitals generateddue to overalp of atomic orbitals havingvery close in energy is called ---------43# Frenkel defect is shown by the crystalshaving --------------- (high , low) co-ordination number
and ---- ( large , small) difference in thesize of the cations and the anions .
CONCEPT- Amorphous and crystallinesolidsCH-SOLID STATE CARD -11 [1×6=6M]
CH-SOLID STATE---MISCELLANEOUSCARD -12 [1×5=5M]
44# ---------------- is a covalent crystal( Iodine , NaCl , ice , Carborundum)
WRITE TRUE OR FALSE .51# In end –centred unit cell of an atomic
substance there are four atoms per
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com

67
45# Which one will show anisotropy ? (quartz , paraffin wax , rubber , quartzglass )46# ---- solids conducts electricity inmolten state but not in solid state.
( molecular , ionic , metallic , covalent)47# ---------------- solids have very highmelting point
( molecular , ionic , metallic ,covalent)48# Solar cell is an efficient -------------------
( photo-diode , photo-triode)49# Photovoltaic material is --------------------
( Amorphous silicon , Pure siliconcrystal)50# Some of the glass from ancientcivilizations which are with us are milky inappearance due to ----
unit cell. [ ]52# In rock-salt structure, the number offormula units per unit cell is four. [ ]53# Schottky defects disturb the ratio ofcations and anions in the compound .54# NaCl is a paramagnetic substance. []55# A compound having radius ratio (r+/r-)in the range 0.732—1 generally
has CsCl structure. [ ]
Prepared by A K PANDA ,PGT(CHEMISTRY) ,KV NO-3 , BBSR
CH-SOLID STATE---MISCELLANEOUSCARD -13 [1×5=5M]
CH-SOLID STATE---MISCELLANEOUSCARD -14 [1×5=5M]
WRITE TRUE OR FALSE.56# Fe3O4 is ferrimagnetic .Among thethree type of arrangement , hcp,ccp,andbcc, the most efficient packing is bcc. [ ]57# If the radius ratio is in the range
0.225—0.414 the cation prefers to bepresent in an octahedral void. [ ]58# Diamond is an example of atomicsolid. [ ]59# Orthorhombic unit cell has leastsymmetry[ ]60# F-centre is a type of stoichiometricdefect.[ ]
WRITE TRUE OR FALSE.61# 14 kinds of space lattices are possiblein the crystal. [ ]62# Pure alkali halides show FrenkelDefects. [ ]63# When temperature increasesconductivity of semi-conductor decreases. []64# Frenkel defect is shown by ionicsubstance in which there is a largedifference in the size of ions[ ]65# The existence of different chemicalcompounds in the same crystalline form iscalled allotropy. [ ]
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com

68
WORKSHEETCHAPTER –POLYMERCLASS-XII
Find the ODD-ONE OUT with convincing reason
1. Terylene, Nylon-66, Bakelite, PTFE2. Silk, Wool, Nylon, Rayon3. PMMA, PTFE, PVC, PHBV4. Polyisoprene, Neoprene, Buna-S, Buna-N5. PVC, Bakelite, Starch, Dacron6. Nylon-6, Nylon-66, Orlon, Dacron7. Cotton, Silk, Rubber, Terylene8. Amylose, Glycogen, cellulose, Amylopectin9. Starch, Cellulose, Glycogen, Protein.10. PHBV, Nylon-2-nylon-6, Nylon-6,Cellulose
ANALOGICAL TESTS:1) If Thermoplastic: PVC:: Thermosetting :----------------2) If Copolymer: Polyester:: Homopolymer :--------------3) Isoprene: Natural Rubber: : -------------------------- : Synthetic Rubber4) Teflon: Addition Polymer:: ------------------------- :: Condensation Polymer5) Fibres : H-Bonding ::---------------------------- : Van der waal’s bond
II# ANALOGICAL TESTS :
6) Step growth polymerization: Bakelite:: Chain growth polymerization : -------------7) Linear chain non-cross linking polymer: polystyrene :: Cross linking polymer : -----
------------------------
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com

69
8. PHBV : used in orthopaedic devices and controlled released of drugs :: Buna-N:------------------------------
9. Caprolactum : Nylon-6 :: ---------------- + --------------- : Nylon-2-nylon-6
10. Terylene : Polyster :: Nylon-66 :: ------------------------
II # ANALOGICAL TESTS:
11) Buna-S: Elastomer:: ------- : Fibre12) Wool: Polyamide:: Cotton : ---------------13) Alpha Glucose: Starch:: Beta Glucose : ---
14. Amylose: Linear polymer of alpha-Glucose ::---------- : Branch polymer ofalpha-Glucose
15. Melamine: Thermosetting plastic:: Teflon :-------------------------
III# STATE TRUE OR FALSE - correct the statement if it is false.
1. PHBV is a biodegradable polymer2. Buna-s is a homo polymer3. Cotton is a an example of natural polyamide fibre4. Nylon-6 is used for the manufacture of tyre cords, fabrics and ropes, carpets.5. Vulcanisation of rubber involves introduction of poly sulphide cross – links.
III # STATE TRUE OR FALSE :- correct the statement if it is false.
6. Terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol condense to give a polyester calledDacron.
7. Phenol – Formaldehyde polymer is a Thermoplastic Polymer.8. SBR and Buna-N are elastomer.9. In thermosetting plastics, there is extensive cross-linking between chains.10.In elastomers, the polymer chains are held together by hydrogen bonds.
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com

70
III # STATE TRUE OR FALSE :- correct the statement if it is false.11. Thermoset materials are infusible and don’t melt or soften on heating.
12. Nylon-6 is made by the poly condensation of hexa methylene diamine andadipic acid.
13. Vulcanisation of rubber involves introduction of excellent elasticity low waterabsorption tendency, resistance to oxidation and organic solvents.
14. Melamine polymer is a synthetic fiber.
15. High density polythene has linear structure.III# STATE TRUE OR FALSE :- correct the statement if it is false.
16. Neoprene is used for making hoses for transporting gasoline and otherorganic solvents
17. Cis-poly isoprene molecule is not a straight chain but has a coiled structure.
18. Bakelite finds major uses in making electrical goods due to excellent electricalinsulating character.
19. Polymerizations in which molecules of the same monomer polymerized toform a co-polymers.
20. Natural Rubber is a cis-1, 4-poly isoprene.III# STATE TRUE OR FALSE :- correct the statement if it is false.
21. Neoprene has superior resistance to vegetable and mineral oils.
22. PMMA is a substitute of glass and making decorative materials.
23. In presence of CCl4, Styrene polymerizes to form polystyrene of lower averagemolecular mass.
24. Amines, phenols and quinines act as inhibitors.
25.Dextron was the first biodegradable stuture .
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com

71
IV# Match the following
Column -A Column-B1.Zinc acetateantimony trioxidecatalyst at 420 to 460 K Bakelite2. Ziegler-Natta catalyst During the preparation ofTerylene3. Benzoyl peroxide ,acetyl peroxide,tert-butyl peroxide During the preparationof low Density Polythene4. Under high pressure of 1000 to2000 atm and 350K to 570K inpresence of O2 or a Peroxide initiator(catalyst)
During the preparation ofHigh Density Polythene5. Novolac on heating withformaldehyde Free radical generatingInitiator6. Poly β-hydroxybutyrate-co- β-hydroxyvalerate Used as substitute forwool7. Polyacrylonitrile Used for non-sticksurface coating8. Polytetrafluroethylene Used in controlledrelease of drugs9. Nylon-6 Used in manufacture oftyre cord
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com

72
IV# Match the following
Column-A Column-B
1.Natural Rubber A. Caprolactum ( aminocaproic acid)
2.Teflon B.Phenol and formaldehyde
3. Bakelite C.Acrylonitrile
4. PAN D.Tetrafluoroethylene
5. Nylon-6 E. Isoprene(2-methyl but-1,3 diene)
CHEMISTRY DEMONSTRATIONSACTIVITY 1
The “Magic Blue Bottle” ExperimentTarget Audience:This experiment can be used with younger children (e.g. grades 3-5 or so) to simply show thedissolution of gases into liquids. Generally they are more familiar with say, sugar or saltdissolving in water – this demonstrates that gases can be dissolved in liquids, just like solids can.Alternatively, the reaction’s thermodynamics can be discussed – i.e., the reversibility of thereaction can be used to introduce concepts of reaction pathways and energy of reaction to older,more advanced students.
Safety Considerations:Methylene blue is a dye used to stain DNA and bacteria in laboratories. First of all, it is light-sensitive, so should be stored in the dark (you can wrap your solutions, or your stock powder intin foil). Second, it is not something you want to get on your skin – when making up a solution,or handling methylene blue, you should be wearing gloves – it is a known mutagen.0.1 M NaOH is a strong base which is very corrosive – again, use caution when handling thissolution!
The Experiment:Putting together a reaction system in which a reversible chemical reaction takes placeBackground Information and Discussion:• What is a reversible chemical reaction? A reaction in which the energy required totransform starting reagents into products is approximately equal to the energy required totransform the products back into their starting reagents. You can demonstrate the energydiagram. (i.e., ΔG ≈ 0)
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com

73
• Describe the reagents. You may have to make up a solution of 0.1 M NaOH if it is notavailable. You can discuss the calculation of molarity using the formula C1V1=C2V2. Fructose isa simple sugar (i.e., carbohydrate) that is naturally occurring. Methylene blue is an indicator,specifically a molecule which has different absorbances (colours) in different states. In the caseof methylene blue, one form is blue and the other is pale yellow.• Why study reversible chemical reactions and indicators? There are huge numbers ofreversible chemical reactions that are important to understanding the basic principles of reactionkinetics. Indicators are often used in many areas of science, including medicine andenvironmental pollution. In this case, methylene blue is a redox indicator (this can lead toanother discussion! In the blue form, it is oxidized – has fewer electrons…..but in the colourlessform, it is reduced – it has more electrons – this difference is what leads to the different colours.• Safety Issues: Emphasize wearing the gloves and glasses.
How to Do the Blue Bottle Chemistry Demonstration - Introductionand Materials
In this chemistry demonstration, a blue solution gradually becomes clear. When the flask ofliquid is swirled around, the solution becomes blue again. Instructions are given for performingthe reaction, the chemistry is explained, and options for making red -> clear -> red and green ->red/yellow -> green color change reactions are explained. The blue bottle reaction is easy toperform and uses readily-available materials.
Materials
tap water two 1-liter Erlenmeyer flasks, with stoppers 7.5 g glucose (2.5 g for one flask; 5 g for the other flask) 7.5 g sodium hydroxide NaOH (2.5 g for one flask; 5 g for the other flask) 0.1% solution of methylene blue (1 ml for each flask)
Procedure
1. Half-fill two one-liter Erlenmeyer flasks with tap water.2. Dissolve 2.5 g of glucose in one of the flask (flask A) and 5 g of glucose in the other flask
(flask B).3. Dissolve 2.5 g of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) in flask A and 5 g of NaOH in flask B.4. Add ~1 ml of 0.1% methylene blue to each flask.5. Stopper the flasks and shake them to dissolve the dye. The resulting solution will be blue.6. Set the flasks aside (this is a good time to explain the chemistry of the demonstration).
The liquid will gradually become colorless as glucose is oxidized by the dissolveddioxygen. The effect of concentration on reaction rate should be obvious. The flask withtwice the concentration uses the dissolved oxygen in about half the time as the othersolution. A thin blue boundary can be expected to remain at the solution-air interface,since oxygen remains available via diffusion.
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com

74
7. The blue color of the solutions can be restored by swirling or shaking the contents of theflask.
8. The reaction can be repeated several times.
Safety & Clean-Up
Avoid skin contact with the solutions, which contain caustic chemicals.
The reaction neutralizes the solution, which can be disposed of by pouring it down the drain.How the Blue Bottle Reaction Works
In this reaction, glucose (an aldehyde) in an alkaline solution is slowly oxidized bydioxygen to form gluconic acid:
CH2OH–CHOH–CHOH–CHOH–CHOH–CHO + 1/2 O2
CH2OH–CHOH–CHOH–CHOH–CHOH–COOH
Gluconic acid is converted to sodium gluconate in the presence of sodium hydroxide.Methylene blue speeds up this reaction by acting as an oxygen transfer agent. Byoxidizing glucose, methylene blue is itself reduced (forming leucomethylene blue), andbecomes colorless.
If there is a sufficient available oxygen (from air), leucomethylene blue is re-oxidized andthe blue color of solution can be restored. Upon standing, glucose reduces the methyleneblue.
In dilute solutions the reaction takes place at 40-60°C, or at room temperature (describedhere) for more concentrated solutions. e dye and the color of the solution disappears.
INNOVATIVE EXPERIMENTS IN CHEMISTRYACTIVITY 21) Dancing ballsTake a measuring jar fill it with an acetic acid solution then add sodium carbonate solution .putone naphthalene ball, it will be found dancing.ACTIVITY 32) Chemical volcanoTake a little amount of potassium permanganate in a china dish add glycerol in to it, after sometime the mixture will burn with fire just as volcano.
ORTake ammonium dichromate in a watch glass and it should be arranged in shape of volcano.Then introduce a burning match stick in to its top, we can see it is burning like a volcano.ACTIVITY 43) Chemical garden
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com

75
Take a solution of augur-augur in a beaker (big size beaker will be good) to it add salts likemagnesium sulphate, copper sulphate, ferrous sulphate,etc and keep it for nearly one week time.Garden will be obtained.ACTIVITY 54) Chemical sun rise and sun setTake sodium thiosulphate solution in a beaker cover the beaker in such a way that through oneside light will come and the other side white screen .Then add a little amount of dilute hydrochloric acid. Just wait we can see the sun rise and sun set.ACTIVITY65) Chemical crackersDissolve iodine solid in ammonia solution and spread it in to the floor, when you will walk itwill break with sound.ACTIVITY 76) Chemical rocketTake KNO3 + sugar make a paste of the same, add also some amount of rust in to it. Make a
paste of the same heat the same using a coil heater. Fill the same in a small plastic box withsmall out let. Put fire, we can see the same will jump and will move like a rocket.Projects
1) Conversion of oscillatory motion to rotational motion for creating electricity2) By applying pressure we can cool air that air can substitute air conditioners
DEMOSTRATION BY GROUP- 2ACTIVITY 8
ACTIVITY NO. 1AIM- To show the application of Le Chatelier’s Principle by Fe+3 with SCN- solution.Material’s required – 1. FeCl3 solution 2. NH4SCN solution 3. Oxalic Acid solution 4. Testtube.THEORY-
Fe+3 + SCN- ↔ [Fe(SCN)]+2
Yellow blood redAfter equilibrium is achieved, when we add oxalic acid soln. then it combines with Fe+3 toremove reactant. So, the reaction will move to the reverse direction and the colorchanges to yellow. When we add again Fe+3 to the soln. it would become blood red again.Procedure – 1. FeCl3 solution is added to the NH4SCN solution at first. Keep it for sometime. Blood red color is observed.2. In the same test tube small amount of oxalic acid solution is added. The color of thesolution changes to colorless.3. Again few drops of Fe+3 Solution is added. Once again color changes to blood red.ACTIVITY 9
ACTIVITY NO. 2Aim- To explain the Equilibrium and Le Chatelier’s Principle.Material’s required –K2CrO4, HCl, NaOH soln.
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com

76
Theory- When an acid is added to a yellow soln. containing chromate ion, an orange coloris obtained due to the formation of dichromate ions.
2CrO4-2 + 2H+ → Cr2O7
-2 + H2OYellow orange red
By adding alkali the orange soln. containing dichromate ions changes to yellow color.Cr2O7
-2 + 2OH- → 2CrO4-2 +H2O
Orange red yellowProcedure – 1. 5mL of potassium chromate soln. is taken in a test tube.2. A few drops of HCl is added to the same test tube. Orange red color is obtained.3. To the same soln. a few drops of NaOH is added, again yellow color is formed due to theformation of chromate ions.Conclusion- In the given soln. chromate and dichromate ions exist in equilibrium and areinter convertible by changing the pH of the soln.ACTIVITY 10
ACTIVITY NO. 3AIM- To show the change of pH by adding acid and alkali to an indicator.Material’s required – Phenolphthalein, acid and alkali.THEORY-
Phenolphthalein (in acid) ↔ Phenolphthalein (in base)Colorless pink
Procedure- Phenolphthalein soln. is taken in a beaker. A base is added. The color changesto pink. When acid is added to the same soln. pink color decolorises.
GROUP VACTIVITY 11CONSTRUCTION OF GALVANIC CELLREQUIREMENTS
1. 250 ML BEAKERS: 2No.2. 1M Copper Sulphate solution3. 1M Zinc Sulphate solution4. U shaped tube5. Agar Agar + KNO3 solution6. Voltmeter7. Connecting wires.8. Copper plate and zinc plate
PROCEDURE;1. Fill the U shaped tube with agar agar with KNO3
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com

77
2. Take 1 M Copper sulphate solution in 250 ml beaker, place copper plate in thissolution, it acts as cathode half-cell.
3. Take 1 M Zinc sulphate solution in 250 ml beaker, place zinc plate in thissolution, it acts as anode half-cell.
4. Through connecting wires connect anode half-cell to negative terminal andcathode half-cell to positive terminal of volt meter.
5. Connect these two half cells by U shaped tube (salt bridge)
REACTION TAKES PLACE IN THE GALVANIC CELLZn(s) + Cu2+(aq) ---- Zn2+(aq) + Cu (s)
OBSERVATION:A voltage of nearly 1.1 volts is observed in the volt meter.
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com




![CHAPTER 8 - WordPress.comwrite the step of preparation of the salts on the diagram] NaCl solution Evaporating dish NaCl crystal salt NaCl salt crystal mohd faisol mansor/chemistry](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/5ab110007f8b9a1d168c1b2b/chapter-8-write-the-step-of-preparation-of-the-salts-on-the-diagram-nacl-solution.jpg)