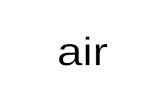Biomes. Learning Objectives Describe what biotic and abiotic factors characterize biomes. Identify...
-
Upload
leslie-cox -
Category
Documents
-
view
249 -
download
0
Transcript of Biomes. Learning Objectives Describe what biotic and abiotic factors characterize biomes. Identify...

Biomes

Learning Objectives Describe what biotic and abiotic factors characterize
biomes. Identify the areas that are not classified into a major
biome.

Regional Climates
Upwind side Downwind side
Air rises and cools, releasing moisture.
Air descends, warms, and becomes drier, decreasing moisture.

Earth’s Biomes

Reading a Climate Diagram

Tropical Rain Forest
Abiotic: warm and wet year-round; soils are thin and nutrient-poor
Abiotic: warm and wet year-round; soils are thin and nutrient-poor
Biotic: plants with large leaves and buttress tree roots; animals active year-round
Biotic: plants with large leaves and buttress tree roots; animals active year-round

Tropical Dry Forest
Rainy season
Abiotic: warm year-round; alternating wet-dry seasons; rich soils
Abiotic: warm year-round; alternating wet-dry seasons; rich soils
Biotic: deciduous plants, waxy plant leaves; many animals estivate or migrate
Biotic: deciduous plants, waxy plant leaves; many animals estivate or migrate

Tropical Grassland/Savanna/Scrubland
Biotic: plants with waxy leaves, seasonal leaf loss; many animals migrate or are dormant during dry season
Biotic: plants with waxy leaves, seasonal leaf loss; many animals migrate or are dormant during dry season
Abiotic: warm; seasonal rainfall; compact soils; frequent fires set by lightning
Abiotic: warm; seasonal rainfall; compact soils; frequent fires set by lightning

Desert
Precipitation, not temperature, defines deserts.
Biotic: small plant leaves; many animals nocturnal, many get water from their food
Biotic: small plant leaves; many animals nocturnal, many get water from their food
Abiotic: low precipitation; variable temperatures; soils poor in organic material
Abiotic: low precipitation; variable temperatures; soils poor in organic material

Temperate Grassland
Biotic: plants resistant to grazing and fire; small animals use camouflage and burrowing as protection
Biotic: plants resistant to grazing and fire; small animals use camouflage and burrowing as protection
Abiotic: warm summers, cold winters; moderate precipitation; fertile soils; occasional fires
Abiotic: warm summers, cold winters; moderate precipitation; fertile soils; occasional fires

Temperate Woodland and Shrubland
High threat of wildfire
Biotic: plants adapted to drought and fire; animals commonly browsers
Biotic: plants adapted to drought and fire; animals commonly browsers
Abiotic: warm, dry summers; cool, moist winters; nutrient-poor soils; periodic fires
Abiotic: warm, dry summers; cool, moist winters; nutrient-poor soils; periodic fires

Temperate Forest
Biotic: deciduous trees; some animals hibernate, some migrate in winter
Biotic: deciduous trees; some animals hibernate, some migrate in winter
Abiotic: cold winters, warm summers; year-round precipitation; fertile soils
Abiotic: cold winters, warm summers; year-round precipitation; fertile soils

Northwestern Coniferous Forest
Biotic: dense plant growth, tall trees; many animals have varied diets
Biotic: dense plant growth, tall trees; many animals have varied diets
Abiotic: mild temperatures; abundant precipitation in fall, winter, and spring; cool, dry summers; rocky, acidic soils
Abiotic: mild temperatures; abundant precipitation in fall, winter, and spring; cool, dry summers; rocky, acidic soils

Boreal Forest
Biotic: dark-green conifers; many animals have extra insulation, some migrate in winter
Biotic: dark-green conifers; many animals have extra insulation, some migrate in winter
Abiotic: long, cold winters; mild summers; moderate precipitation; acidic, nutrient-poor soils
Abiotic: long, cold winters; mild summers; moderate precipitation; acidic, nutrient-poor soils

Tundra
Low precipitation
Biotic: small plants growing low to the ground; many animals migrate in winter or have heat-saving adaptations
Biotic: small plants growing low to the ground; many animals migrate in winter or have heat-saving adaptations
Abiotic: strong winds; low precipitation; short, soggy summers; long, cold, dark winters; permafrost
Abiotic: strong winds; low precipitation; short, soggy summers; long, cold, dark winters; permafrost

Other Land Areas
Mountain ranges and polar ice caps are not easily defined by typical plant and animal communities.

Overview: Biomes