Biological School It is all about the body!!!!. The Nervous System It starts with an individual...
-
Upload
lexi-knipe -
Category
Documents
-
view
215 -
download
0
Transcript of Biological School It is all about the body!!!!. The Nervous System It starts with an individual...
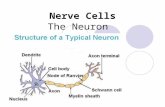
NeuroanatomySynapseSynapse
Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that travel through synaptic gap)
How does a Neuron fire?
• Resting Potential: slightly negative charge.
• Reach the threshold when enough neurotransmitters reach dendrites.
• Go into Action Potential.• All-or-none response.• Transfer of ions across
axon’s membrane causes electrical charge.
Acetylcholine (ACH)• Deals with learning, memory,
& muscle movement • At every junction b/w motor
neurons & muscles– When released to our
muscles the muscle contracts
– When it is blocked muscles are paralyzed & cannot contract• Black widow spider?
• Is involved in autonomic nervous system
• Lack of has been linked to Alzheimer’s disease & ADD
Dopamine• Involved in movement &
posture, alertness, & leveling out mood
• Cocaine (and other drugs) blocks dopamine reuptake=high
• Lack of dopamine has been linked to Parkinson’s disease
• Too much has been linked to schizophrenia (overstimulated brain)
Serotonin
• Involved in mood, appetite, arousal
• Low levels have been linked to clinical depression, suicide, loss of appetite (anorexia)
GABA (gamma amino-butyric acid)
• In Central Nervous System
• Induces relaxation & sleep
• Balances the brain• Too little = insomnia,
anxiety, epilepsy
Glutamate• Involved in memory
& learning• Low levels =
interferes with memory & learning, sluggish, difficulty concentrating
• High levels = must be “reuptook?” or it can destroy neurons
Endorphins
• Natural pain killers• Feeling of euphoria,
pleasurable emotions• Opiates (morphine,
codeine…) bind to receptors– Many of our most addictive
drugs deal with endorphins
• Produced during exercise – “gym rats”
Drugs can be…..
• Agonists- make neuron fire• Antagonists- stop neural
firing• Reuptake Inhibitors- block
reuptake
Peripheral Nervous System
• All nerves that are not encased in bone.
• Everything but the brain and spinal cord.
• Is divided into two categories….somatic and autonomic.
Autonomic Nervous System
• Controls the automatic functions of the body.
• Divided into two categories…the sympathetic and the parasympathetic
Sympathetic Nervous System
• Fight or Flight Response.
• Automatically accelerates heart rate, breathing, dilates pupils, slows down digestion.
Parasympathetic Nervous System
• Automatically slows the body down after a stressful event.
• Heart rate and breathing slow down, pupils constrict and digestion speeds up.
Reflexes
• Normally, sensory (afferent) neurons take info up through spine to the brain.
• Some reactions occur when sensory neurons reach just the spinal cord.
• Survival adaptation.
The Brain
• Made up of neurons and glial cells.
• Glial cells support neural cells.
My fiance is my glial cell. He takes care of me!!!
Less Invasive ways to study the Brain
• Electroencephalogram (EEG)
• Computerized Axial Tomography (CAT)
• Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
• Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
• Functional MRI
Brain Structures
• Some scientists divide the brain up into three parts.
• Hindbrain• Midbrain• Forebrain
• Let’s talk first about the brainstem
Medulla Oblongata
• “Central Office”=keeps your whole body working
• Located where spinal cord enters the skull
• Controls heart rate, breathing & blood pressure
SPINAL CORD
• (the nerves) interneurons that carry signals
• protected by vertebrae & spinal fluid (cushions the nerves)
Cerebellum• means “little
brain”• located in the
back of our head• Coordinates
muscle movements & emotions
Thalamus• Located in Forebrain• “Brain’s Sensory
Switchboard”– 2 egg shaped structures
• receives information from all the senses (except smell) & routes it to the brain regions that deal with vision, hearing, taste & touch
• it’s the main traffic hub en route to other destinations
Reticular Formation(reticular activating system)
• Located between your ears
• Finger-shaped network of neurons that relays info to other areas of the brain
• controls arousal & ability to focus attention
Limbic System• EMOTIONAL CONTROL CENTER
of the brain• Linked to emotions (fear,
anger…) & basic motives (food, sex…)
• The 4 “F”s– Feeding– Fighting– Fear– F (sex)
• Made up of Hypothalamus, Amygdala, Hippocampus & Cingulate Gyrus
Hypothalamus• “the brain’s thermostat” • perform specific bodily
maintenance duties (eating, drinking, body temperature, sex drive…), takes orders from the other parts of the brain
• Orchestrates the sympathetic nervous & endocrine systems– interplay b/w endocrine & nervous
systems, both influence each other
– EX: thinking about sex can trigger your body to secrete hormones
•
Hippocampus and Amygdala
• Hippocampus is involved in memory processing (creating new memories)– Think lost on campus as a
freshmen on first day– Shaped like a seahorse– Damage to this area will
prevent you from forming new memories
• Amygdala is vital for our basic emotions– Expressions of Fear &
Aggression/Frustration
Cingulate Gyrus
• Latin for “belt”• Helps regulate
emotion & pain• Monitors and guides
behavior• Helps predict
negative consequences
Cerebral Cortex• The wrinkled outer layer of
our brain• Laid out it would be about
the size of a large pizza (yum!)
• YOUR BODY’S ULTIMATE CONTROL & INFO PROCESSING CENTER
• Thinking, perceiving, speaking
• This part of our brain separates us from all other animals
Areas of the Cerebral Cortex• Divided into eight
lobes, four in each hemisphere (frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal)
• Any area not dealing with our senses or muscle movements are called association areas– Deal with higher
mental functions like learning, remembering, thinking & speaking
Frontal Lobe• Deals with higher level
thought & reasoning– Making plans, forming
judgments, performing movements
• Motor Cortex: controls voluntary movements
• Prefrontal Cortex: problem solving & emotion
• Broca’s Area: left hemisphere in frontal lobe, controls ability to speak (muscles)– Broca’s Aphasia: damage to
Broca’s area will impair speaking
Parietal Lobes
• Located at the top of our head
• Receives sensory info about temperature, pressure, texture, & pain
• Somato-sensory cortex: registers and processes touch and movement sensations
Temporal Lobes
• Located above the ears• Process sound sensed by
ears• Wernicke’s area:
processes the words we hear spoken– Wernicke’s Aphasia: impairs
your ability to understand words
• Angular Gyrus: responsible for understanding written language
Occipital Lobes
• Located in the back of our head
• Handles visual input from eyes
• Right half of each retina goes to left occipital lobe and vice versa (seriously!!!)
Corpus Callosum & Basil Ganglia
• Corpus Callosum: a large band of neural fibers that connect the 2 hemispheres of the brain (we’ll talk about what happens when you cut this this soon)
• Basil Ganglia: group of neurons that learns, remembers, & coordinates voluntary movement (Williams in Zumba!!!!)
Hemispheres
• Divided into a left and right hemisphere.
• Contralateral controlled- left controls right side of body and vice versa.
• Brain Lateralization.• Lefties are better at
spatial and creative tasks.
• Righties are better at logic.
Split-Brain Patients
• Corpus Collosum attaches the two hemispheres of cerebral cortex.
• When removed you have a split-brain patient.
Brain Plasticity
• The ability for our brains to form new connections after the neurons are damaged.
• The younger you are, the more plastic your brain is.