Basics of amplifier
-
Upload
sajjad-hussain-raja -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
189 -
download
0
Transcript of Basics of amplifier
Amplifier:
• An electronic amplifier, amplifier, or (informally) amp is an electronic device that increases the power of a signal.
• It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude. In this sense, an amplifier modulates the output of the power supply to make the output signal stronger than the input signal.
Cont…• The basic theory of an amplifier is also based on voltage
divider across a series of resister. A small amount of current flowing into this device that change resistance depending on a small ‘input’ current, i.e the resister is proportional to input current. A small amount of current flowing into this device can vary the resistance from zero to infinity. The device is called “TRANSISITER” (TRANsfer reSISTER). When it is used in voltage divider circuit we have a one trnsister amplifier.
• With a few modifications, several of transistor amplifiers can be connected in series: the output of 1st transistor goes on to control of 2nd, the output of the second transistor goes on to control the third, and so on.
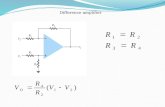
Differential amplifier:
• A differential amplifier is a type of electronic amplifier that amplifies the difference between two voltages but does not amplify the particular voltages.
1.Sensors:• The 1st component in the recording of biological signals is
the sensors, which in the case of EEG would be the scalp electrodes. The electrodes is an extremely important element in determining quality of the recorded signals.
• 2. Amplifier:• The analog amplifier is the second component in the
recording pathway. The continuous analog signals fed into the amplifier that typically boosts the signal so that it can be further processed in the recording system. For a pen writing system, the signal voltage would be converted to pen displacement that would produce a paper recording.
Cont…
• 3. Storage vs processing:The third component in a digital EEG system has the
amplifier sending the amplified signal to a special circuit known as ADC (analog-to-digital converter) circuit. This is to be contrasted to the analog EEG system, where the third component would be the pen-writing system. The ADC circuit is also called a digitizer b/c its function is to transform an analog measurement into a number.
Cont…
It measures the amplified signal voltage and converts it into a number that is than sent to a computer to process it is this step that changes analog signals to a digital signal and allows the signal to be represented as a number that machine can easily process and store on a variety of mediums (CD, DVD, Tape, etc).Digitized signals are only a sampling of the original analog signal since a finite number of values can be stored and processed.
Factors and limitations:
• The technologist will need to be aware of the frequency and amplitude of the signal of interest in comparison to the resolution of the digital records in term of amplitude and time. Amplitudes and time factor will determine the types of EEG signals that could be recorded. Some of pitfalls in recording and interpreting digitized data would include the introduction of virtual signals that actually not present in the original analog signal. These virtual signals are called alias signals (or aliasing) which are commonly seen as cyclical recorded signals.
Cont…
• Two main factors that determine the resolution of the digitized data are the amplitude range and the sampling rate of ADC circuit.
• Digitizing is performed by sampling the continuous signal at regular and small intervals
• How small should the intervals be to ensure a faithful representation of the signal?
• The sampling theorem states that no information is lost in the sampling process if the sampling rate is at least twice the highest frequency in the signal
• In theory, if a signal includes frequencies up to 100Hz, then sampling at 200Hz will ensure a perfect representation of the signal
• Half the sampling frequency is called the Nyquist frequency.
Amplitude resolution (y-axis)
• The amplitude of the signal is the magnitude of vertical height of the signal and is displayed analog the vertical axis (y-axis) of the display. The ADC circuit translate the measured voltage into a binary numerical value of amplitude. The range of the numerical value depend on the largest binary number that the ADC circuit can hold in its memory banks for one sample in measurement in time.
Time resolution (x-axis)
• In EEG recordings, the ADC uses time along the horizontal axis (x-axis) of the recordings. As a result, the time setting will depend on how it records and displays increments of time along the horizontal axis. The smallest unit of time recorded by the ADC circuit is called the dwell time. Dwell time is the amount of time b/w 2 sampling points. It is within this dwell time that the voltage amplitude of the signals is captured and recorded.
Cont..
• The mathematical inverse of the dwell time is the sampling frequency, which is the number of samples per second that the ADC circuit is able to record.
• When dwell times are long, the number of samples/sec (sampling rate) is low, making the resolution low along the time axis.
• When the sampling rate is increased, the time axis resolution increased.
For e.g. when the dwell time is 5ms, the sampling rate is 200 samples/sec.If the dwell time is increased to 50ms the sampling rate is 20 samples/sec.
NYQUIST FREQUENCY:
• Sampling rate determine the highest frequency recordable by the system. The nyquist theorem states that for digitized data, the fastest signal that can be recorded will have a frequency that is half the sampling rate of the digitizer. Half the sampling rate of the digitizer is called the nyquist frequency and is the highest frequency the system can record at specific sampling rate.
• SR=50samples/s than the highest frequency that system cam record is 25Hz.
• In most EEG machine sampling rate=200samples/s, so they can record HF=100Hz























![[ AMPLIFIER PACKAGES ] Amplifier Packages · [ AMPLIFIER PACKAGES ] CLAIR BROTHERS PRODUCT INFO | Updated 2/2019 Features of PLM Smart Amplifier Packages AC Distro Inlet Lake® Processing](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/60e6bcd6c8041341c72d9d93/-amplifier-packages-amplifier-amplifier-packages-clair-brothers-product-info.jpg)