Appendicular skeleton
-
Upload
allensoriano08 -
Category
Documents
-
view
42 -
download
7
description
Transcript of Appendicular skeleton

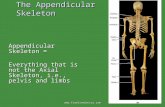
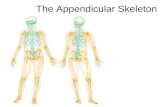
APPENDICULAR APPENDICULAR SKELETONSKELETON
ENDOSKELETON OF ENDOSKELETON OF VERTEBRATESVERTEBRATES

The Appendicular SkeletonThe Appendicular Skeleton The The appendicular appendicular
skeletonskeleton includes: includes: Pectoral girdlePectoral girdle Pelvic girdlePelvic girdle Upper extremitiesUpper extremities Lower extremitiesLower extremities
The The appendicular appendicular skeletonskeleton functions functions primarily to facilitate primarily to facilitate movementmovement

Fig. 9.4

Tetrapod LimbTetrapod Limb
Typical 4 limbsTypical 4 limbs
Primarily a modification of the Rhipidistian Primarily a modification of the Rhipidistian finfin
wingspaddles
Lost 2
Lost 4Modified elements

Recall: VRecall: Vpp = V = Vgg + V + Vee + V + Vgxegxe
V = variationV = variation p = phenotypicp = phenotypic g = genotypicg = genotypic e = environmentale = environmental
Morphology(anatomy)
Behavior& Performance
Resource use(ecology)
Fitness

Three main componentsThree main components
With respect to the pectoral and pelvic With respect to the pectoral and pelvic girdles:girdles:
• Serially homologous – Serially homologous –
1.1. Propodium (= stylopodium) – upper arm, Propodium (= stylopodium) – upper arm, upper legupper leg
2.2. Epipodium (= zeugopodium) – forearm, Epipodium (= zeugopodium) – forearm, shinshin
3.3. Autopodium – manus or pes (digits, and Autopodium – manus or pes (digits, and wrist and palm, or ankle and solewrist and palm, or ankle and sole

MesopodiumMesopodium MetapodiumMetapodium PhalangesPhalanges


Fig. 9.12



Focus 9.2

Pectoral (Shoulder) GirdlePectoral (Shoulder) Girdle• The The pectoralpectoral or or shoulder shoulder
girdlegirdle attaches the bones attaches the bones of the upper limbs to the of the upper limbs to the axial skeleton axial skeleton
Consists of Consists of scapulascapula & & clavicleclavicle
ClavicleClavicle articulates with articulates with sternumsternum ( (sternoclavicular sternoclavicular jointjoint) )
ClavicleClavicle articulates with articulates with scapulascapula ((acromioclavicular jointacromioclavicular joint))
ScapulaScapula held in place by held in place by muscle onlymuscle only
Upper limb attached to Upper limb attached to pectoral girdlepectoral girdle at at shoulder (shoulder (glenohumeral glenohumeral jointjoint))

Clavicle (Collarbone)Clavicle (Collarbone)
S-shaped bone with two curvesS-shaped bone with two curves Extends from Extends from sternumsternum to to scapulascapula above 1st rib above 1st rib Sternal & acromial extremitiesSternal & acromial extremities One of the most commonly fractured bones in the human bodyOne of the most commonly fractured bones in the human body Fracture site is junction of curves Fracture site is junction of curves Ligaments attached to Ligaments attached to clavicleclavicle stabilize its position. stabilize its position. Shoulder separationShoulder separation is sprain of the is sprain of the acromioclavicular ligamentacromioclavicular ligament

Anterior Surface of ScapulaAnterior Surface of Scapula
Articulates with the Articulates with the clavicleclavicle and the and the humerushumerus Subscapular fossaSubscapular fossa filled with muscle filled with muscle Coracoid processCoracoid process for muscle attachment for muscle attachment

Posterior Surface of ScapulaPosterior Surface of Scapula
Triangular flat bone found in upper back regionTriangular flat bone found in upper back region Scapular spineScapular spine ends as ends as acromion processacromion process Glenoid cavityGlenoid cavity forms shoulder joint with head of forms shoulder joint with head of humerushumerus SupraspinousSupraspinous & & infraspinousinfraspinous fossafossa for muscular attachments for muscular attachments

Upper Upper ExtremityExtremity Upper extremity consists of 30 Upper extremity consists of 30
bonesbones HumerusHumerus within the arm within the arm UlnaUlna & & radiusradius within the forearm within the forearm CarpalCarpal bones within the wrist bones within the wrist MetacarpalMetacarpal bones within the palm bones within the palm PhalangesPhalanges in the fingers in the fingers
Joints Joints ShoulderShoulder ( (glenohumeralglenohumeral), ), elbowelbow, , wristwrist, ,
metacarpophalangealmetacarpophalangeal, , interphalangealinterphalangeal Shoulder dislocationShoulder dislocation is separation of the is separation of the
humerushumerus from the from the glenoid cavityglenoid cavity of the of the scapulascapula

Shoulder DislocationShoulder Dislocation
Head of humerus slips out of glenoid cavityHead of humerus slips out of glenoid cavity Closed reductionClosed reduction is term for slipping humerus back into place without is term for slipping humerus back into place without
surgerysurgery Severe or frequent dislocations may require surgical ligament repairSevere or frequent dislocations may require surgical ligament repair

Humerus: Proximal Humerus: Proximal EndEnd Largest and longest bone of upper Largest and longest bone of upper
extremity, part of shoulder joint, extremity, part of shoulder joint, articulates with articulates with scapulascapula
HeadHead
GreaterGreater & & lesserlesser tuberclestubercles for muscle attachmentsfor muscle attachments
IntertubercularIntertubercular sulcussulcus or or bicipitalbicipitalgroovegroove
ShaftShaft or or bodybody

Humerus: Distal EndHumerus: Distal End Forms elbow joint with Forms elbow joint with ulnaulna
and and radiusradius
CapitulumCapitulum articulates with head of articulates with head of radiusradius
TrochleaTrochlea articulation with articulation with ulnaulna
Olecranon fossaOlecranon fossa posterior depression for posterior depression for
olecranon processolecranon process of of ulnaulna
MedialMedial & & laterallateral epicondylesepicondyles attachment of forearm muscles attachment of forearm muscles

Ulna & Radius: Proximal Ulna & Radius: Proximal EndEnd
UlnaUlna (on little finger side) (on little finger side) Trochlear notchTrochlear notch articulates with articulates with
humerushumerus & & radial notchradial notch with with radiusradius Olecranon processOlecranon process forms point of elbow forms point of elbow
RadiusRadius (on thumb side) (on thumb side) Head articulates with Head articulates with capitulumcapitulum of of
humerushumerus & & radial notchradial notch of of ulnaulna TuberosityTuberosity for muscle attachment for muscle attachment

Ulna & Radius: Proximal Ulna & Radius: Proximal EndEnd
RadiusRadius (on thumb side) (on thumb side) HeadHead articulates with articulates with
capitulumcapitulum of of humerushumerus & & radial notchradial notch of of ulnaulna
TuberosityTuberosity for muscle for muscle attachmentattachment
Ulnar notchUlnar notch articulates with articulates with ulnaulna

Elbow JointElbow Joint
Articulation of Articulation of humerushumerus with with ulnaulna and and radiusradius UlnaUlna articulates with articulates with trochleatrochlea of of humerushumerus RadiusRadius articulates with articulates with capitulumcapitulum of of humerushumerus InterosseousInterosseous membrane between membrane between ulnaulna & & radiusradius
provides site for muscle attachmentprovides site for muscle attachment

Ulna and Radius: Distal EndUlna and Radius: Distal End UlnaUlna
Styloid processStyloid process provides provides attachment for attachment for ulnar collateral ulnar collateral ligamentligament
Head separated Head separated from wrist joint from wrist joint by by fibrocartilage fibrocartilage discdisc
RadiusRadius Forms wrist joint Forms wrist joint
with with scaphoidscaphoid, , lunatelunate & & triquetrumtriquetrum
Forms Forms distal distal radioulnar jointradioulnar joint with head of with head of ulnaulna

8 Carpal Bones (Wrist)8 Carpal Bones (Wrist) Proximal row - Proximal row -
lateral to mediallateral to medial ScaphoidScaphoid: boat : boat
shapedshaped LunateLunate: moon shaped: moon shaped TriquetrumTriquetrum: 3 corners: 3 corners PisiformPisiform: pea shaped: pea shaped
Distal row - lateral Distal row - lateral to medialto medial TrapeziumTrapezium: four sided: four sided TrapezoidTrapezoid: four sided: four sided CapitateCapitate: large head: large head HamateHamate: hooked : hooked
processprocessScared Lovers Try Positions
That They Can’t Handle

Metacarpals and PhalangesMetacarpals and Phalanges MetacarpalsMetacarpals
5 total: #1 5 total: #1 proximal to thumbproximal to thumb
basebase, , shaftshaft, , headhead knuckles knuckles
((metacarpophalangmetacarpophalangealeal joints) joints)
Phalanges Phalanges (Digits)(Digits) 14 total: each is 14 total: each is
called called phalanxphalanx proximalproximal, , middlemiddle, ,
distaldistal on each on each finger, except finger, except thumbthumb
basebase, , shaftshaft, , headhead

Pelvic Girdle and Hip Pelvic Girdle and Hip BonesBones
Pelvic girdlePelvic girdle = two hip bones united at = two hip bones united at pubic symphysispubic symphysis articulate posteriorly with articulate posteriorly with sacrumsacrum at at sacroiliac jointssacroiliac joints
Each hip bone (Each hip bone (os coxaos coxa) = ) = iliumilium, , pubispubis, and , and ischiumischium fuse after birth at fuse after birth at acetabulumacetabulum
Bony pelvis = 2 hip bones, Bony pelvis = 2 hip bones, sacrumsacrum and and coccyxcoccyx

IliumIlium
Iliac crestIliac crest and and iliac spinesiliac spines for muscle attachment for muscle attachment Iliac fossaIliac fossa for muscle attachment for muscle attachment Gluteal linesGluteal lines indicating muscle attachment indicating muscle attachment Sacroiliac jointSacroiliac joint at at auricular surfaceauricular surface & & iliac tuberosityiliac tuberosity Greater Greater sciatic notchsciatic notch for for sciatic nervesciatic nerve

Ischium Ischium and Pubisand Pubis
IschiumIschium Ischial spineIschial spine & &
tuberositytuberosity Lesser sciatic notchLesser sciatic notch RamusRamus
PubisPubis BodyBody SuperiorSuperior & & inferiorinferior
ramusramus Pubic symphysisPubic symphysis is is
pad of pad of fibrocartilagefibrocartilage between 2 between 2 pubic pubic bonesbones

Female Pelvis Female Pelvis Male PelvisMale Pelvis
Many Many differences differences between the between the twotwo
In particular, In particular, pubic archpubic arch in in males is usually males is usually less than 90˚, less than 90˚, whereas in whereas in females it is females it is usually greater usually greater than 90˚than 90˚

Lower ExtremityLower Extremity Each lower limb = 30 Each lower limb = 30
bonesbones femurfemur and and patellapatella within the within the
thighthigh tibiatibia & & fibulafibula within the leg within the leg tarsaltarsal bones in the foot bones in the foot metatarsalsmetatarsals within the forefoot within the forefoot phalangesphalanges in the toes in the toes
Joints Joints hip, knee, ankle hip, knee, ankle proximalproximal & & distaldistal tibiofibulartibiofibular metatarsophalangealmetatarsophalangeal

FemurFemur The The femurfemur or thighbone is or thighbone is
the largest, heaviest, and the largest, heaviest, and strongest bone of the bodystrongest bone of the body
It articulates with the It articulates with the hip hip bonebone and the and the tibiatibia HeadHead articulates with articulates with acetabulumacetabulum MedialMedial & & laterallateral condylescondyles
articulate with articulate with tibiatibia
Neck is common fracture Neck is common fracture sitesite
Muscle attachments atMuscle attachments at greatergreater & & lesser trochanterslesser trochanters, , linea asperalinea aspera, & , & gluteal gluteal tuberositytuberosity
PatellarPatellar surface is visible surface is visible anteriorly between anteriorly between condylescondyles

FemurFemur
Fovea capitisFovea capitis in the in the center of the headcenter of the head
Medial epicondylesMedial epicondyles above the condylesabove the condyles
Intercondylar fossaIntercondylar fossa between the condylesbetween the condyles

PatellaPatella Triangular Triangular
sesamoidsesamoid bonebone
Apex & baseApex & base
Articular Articular facetsfacets for for the the femurfemur
Increases Increases leverage of leverage of quadriceps quadriceps femoris femoris tendontendon

Tibia and Tibia and FibulaFibula Tibia (Shinbone)Tibia (Shinbone)
Medial & larger bone of Medial & larger bone of legleg
Weight-bearing boneWeight-bearing bone
HeadHead
LateralLateral & & medialmedial condylescondyles
Intercondylar eminenceIntercondylar eminence
Tibial tuberosityTibial tuberosity for for patellar ligamentpatellar ligament
Proximal tibiofibular jointProximal tibiofibular joint
Fibular notchFibular notch
Medial malleolusMedial malleolus at at ankleankle

Tibia and Tibia and FibulaFibula
FibulaFibula Parallel and lateral Parallel and lateral
to the to the tibiatibia
Smaller than the Smaller than the tibiatibia
Not weight bearingNot weight bearing
Not part of the knee Not part of the knee jointjoint
Muscle attachments Muscle attachments onlyonly
Head Head on proximal on proximal end,end, lateral lateral maleolusmaleolus at ankle at ankle
Fits intoFits into fibular fibular notch notch at distal end at distal end of tibiaof tibia

Tarsals, Metatarsals, and Tarsals, Metatarsals, and PhalangesPhalanges Seven Seven tarsaltarsal bones constitute bones constitute
the the ankle (tarsus)ankle (tarsus) and share and share the weight associated with the weight associated with walkingwalking
Five Five metatarsalmetatarsal bones are bones are contained in the contained in the footfoot
Fractures of the Fractures of the metatarsalsmetatarsals are common among dancers, are common among dancers, especially ballet dancers, and especially ballet dancers, and also among martial artistsalso among martial artists
The arrangement of The arrangement of phalangesphalanges in the in the toestoes is the same as that is the same as that described for the fingers and described for the fingers and thumb above: fourteen bones thumb above: fourteen bones in each footin each foot

Tarsus Tarsus (Ankle)(Ankle)
Proximal Proximal region region of foot (contains 7 of foot (contains 7 tarsal bones)tarsal bones)
TalusTalus = ankle bone = ankle bone (articulates with (articulates with tibiatibia & & fibulafibula))
CalcaneusCalcaneus = heel = heel bonebone
CuboidCuboid, , navicularnavicular & & 3 3 cuneiformscuneiforms
Metatarsal Metatarsal fractures fractures occur when you occur when you drop something drop something heavy on your footheavy on your foot

Metatarsus and PhalangesMetatarsus and Phalanges
MetatarsalsMetatarsals Midregion of the footMidregion of the foot 5 metatarsals (#1 is most medial)5 metatarsals (#1 is most medial) Each with Each with basebase, , shaftshaft and and headhead
PhalangesPhalanges Distal portion of the footDistal portion of the foot Similar in number and Similar in number and
arrangement to the handarrangement to the hand Big toe is Big toe is halluxhallux

Arches of the FootArches of the Foot FunctionFunction distribute body weight over footdistribute body weight over foot yield & spring back when weight is liftedyield & spring back when weight is lifted
Longitudinal arches along each side of footLongitudinal arches along each side of foot Transverse arch across midfoot regionTransverse arch across midfoot region
navicular, cuneiforms & bases of metatarsalsnavicular, cuneiforms & bases of metatarsals

HOMOLOGY OF HOMOLOGY OF APPENDICULAR BONESAPPENDICULAR BONES
FORELIMBFORELIMB
1.1. HumerusHumerus
2.2. RadiusRadius
3.3. UlnaUlna
4.4. CarpalsCarpals
5.5. MetacarpalsMetacarpals
6.6. PhallangesPhallanges
HINDLIMBHINDLIMB
1.1. FemurFemur
2.2. TibiaTibia
3.3. FibulaFibula
4.4. TarsalsTarsals
5.5. MetatarsalsMetatarsals
6.6. PhallangesPhallanges

HOMOLOGY OF GIRDLESHOMOLOGY OF GIRDLES
PECTORAL GIRDLEPECTORAL GIRDLE
1.1. ScapulaScapula
* coracoid * coracoid processprocess
2. Clavicle2. Clavicle
PELVIC GIRDLEPELVIC GIRDLE
1.1. IliaIlia
2. Ischia2. Ischia
3. Pubis 3. Pubis

I. GIRDLESI. GIRDLES
A.A. PECTORAL GIRDLEPECTORAL GIRDLE- COMPOSITION:- COMPOSITION:1. Replacement Bones1. Replacement Bones
a. coracoida. coracoidb. Scapulab. Scapulac. Suprascapulac. Suprascapula
2. Dermal Bones – 4 bones of more2. Dermal Bones – 4 bones of morea. claviclea. clavicleb. large cleithriumb. large cleithriumc. small supracleitriumc. small supracleitriumd. post temporald. post temporale. post cleithria (ganoid fishes)e. post cleithria (ganoid fishes)

VARIATION OF PECTORAL VARIATION OF PECTORAL GIRDLEGIRDLE
1.1. CHONDRICHTHYESCHONDRICHTHYES
- ventral coracoid- ventral coracoid
- scapula- scapula
- suprascapula- suprascapula
2. OSTEICHTHYES2. OSTEICHTHYES
- suprascapula is absent- suprascapula is absent
- coracoid +scapula=coracoscapula- coracoid +scapula=coracoscapula

3. TETRAPODS3. TETRAPODS
A.A. AMPHIBIANSAMPHIBIANS- girdle retained in dermal bones- girdle retained in dermal bones-components:-components:a. 2 coracoida. 2 coracoid c. 2 suprascapula c. 2 suprascapulab. 2 scapulab. 2 scapula d. 1 epicoracoid d. 1 epicoracoid
B. REPTILESB. REPTILES- coracoids are fused to form one - coracoids are fused to form one
bone bone PROCORACOIDPROCORACOID

c. AVESc. AVES- components:- components:
a. furcula a. furcula -2 clavicles-2 clavicles-1 interclavicle-1 interclavicle
b.2 scapulab.2 scapulac. 2 precoracoidc. 2 precoracoid
D. MAMMALSD. MAMMALS - components:- components:
a. 2 claviclesa. 2 claviclesb. 2 scapula (shoulder blade)b. 2 scapula (shoulder blade)
- coracoid process- coracoid process- acromial process- acromial process- glenoid fossa- glenoid fossa

II. PELVIC GIRDLESII. PELVIC GIRDLES
VARIATION OF PELVIC GIRDLESVARIATION OF PELVIC GIRDLES1.1. FISHESFISHES
- fusion of ishium and pubis forming - fusion of ishium and pubis forming ISHIIO-PUBIC PLATE ISHIIO-PUBIC PLATE
- (median pubic symphysis)- (median pubic symphysis)
2. AMPHIBIANS2. AMPHIBIANS- 2 Ilia- 2 Ilia- 1 sichium (ischiac sysmphysis)- 1 sichium (ischiac sysmphysis)- 1 pubis (pubic symphysis)- 1 pubis (pubic symphysis)

3. REPTILES3. REPTILES- 2 Ilia - 2 Ilia - sacral rib – fused with the carapace- sacral rib – fused with the carapace
- 2 ishia- 2 ishia - 2 pubis- 2 pubis
4. AVES4. AVES- 2 Ilia (concave and convex area)- 2 Ilia (concave and convex area)
- 2 pubis- 2 pubis- 2 ischia- 2 ischia
- 2 foramens- 2 foramensa. obturator foramena. obturator foramenb. ilio-ischiac foramen b. ilio-ischiac foramen
– –fused to synsacrumfused to synsacrum

5. MAMMALS5. MAMMALS- 2 Ilia- 2 Ilia- 2 ischia- 2 ischia
- 2 pubis- 2 pubis
(os coxae, innominate bone, pelvic (os coxae, innominate bone, pelvic bone)bone)

III. LIMBSIII. LIMBS
VARIATION OF FORELIMBSVARIATION OF FORELIMBS1.1. AMPHIBIANSAMPHIBIANS
- 2 humerus- 2 humerus- 2 radio-ulna (fused)- 2 radio-ulna (fused)
- 2 rows of carpals- 2 rows of carpalsa. proximal row a. proximal row
* radiale, ulnare,centrale* radiale, ulnare,centraleb. distal rowb. distal row
* 3 ordinary fused carpals* 3 ordinary fused carpals - phalanges : 2: 3: 3:2- phalanges : 2: 3: 3:2

2. REPTILES2. REPTILES - different size and shape, diameter- different size and shape, diameter - addition – increase in number- addition – increase in number - fusion - reduction in size- fusion - reduction in size
3. AVES - modified for flight3. AVES - modified for flight - 2 Humerus- 2 Humerus - 2 radius- 2 radius - 2 ulna- 2 ulna - 2 carpometacarpus- 2 carpometacarpus - phalanges: 1:3:2- phalanges: 1:3:2

4. MAMMALS4. MAMMALS 2 humerus2 humerus 2 radius2 radius 2 ulna2 ulna 8 carpals8 carpals a. proximal rowa. proximal row * scaphoid* scaphoid * triquetral* triquetral
* lunate* lunate * pisiform * pisiformb. distal rowb. distal row
*trapezium*trapezium *capitate*capitate* trapezoid* trapezoid * hamate* hamate
* Phalanges : 2:3:3:3:3* Phalanges : 2:3:3:3:3

II. HINDLIMBII. HINDLIMB
FEMUR – THIGHFEMUR – THIGH TIBIA AND FIBULA – SHANKTIBIA AND FIBULA – SHANK TARSALS - ANKLETARSALS - ANKLE METATARSALS – SOLEMETATARSALS – SOLE PHALANGES – DIGITS /TOESPHALANGES – DIGITS /TOES

VARIATION OF HINDLIMBVARIATION OF HINDLIMB
1.1. AMPHIBIANSAMPHIBIANS- 2 Femur- 2 Femur
- 2 tibio-fibula- 2 tibio-fibula
- 2 proximal tarsals - 2 proximal tarsals
* astragalus *calcaneum* astragalus *calcaneum
- 2 ordinary tarsals – fused- 2 ordinary tarsals – fused
- 5 metatarsals - 5 metatarsals
- phalanges : 1 :3:4:4:3- phalanges : 1 :3:4:4:3



2. REPTILES2. REPTILES
- in sphenodons and lizards- tarsal - in sphenodons and lizards- tarsal
bones are fused forming bones are fused forming
ASTRAGALOCALCANEUMASTRAGALOCALCANEUM
3.AVES3.AVES
- TIBIOTARSUS - TIBIOTARSUS
- TARSOMETATARSUS- TARSOMETATARSUS
- METATARSALS- METATARSALS
- 4 DIGITS WITH CLAWS, KNEE CAP- 4 DIGITS WITH CLAWS, KNEE CAP



3. MAMMALS3. MAMMALS- 2 FEMUR- 2 FEMUR- 2 TIBIA- 2 TIBIA- 2 FIBULA- 2 FIBULA- 7 TARSALS- 7 TARSALS
A. PROXIMALA. PROXIMAL- calcaneum,talus,navicular- calcaneum,talus,navicular
B. DISTALB. DISTAL- 3 cunieforms, 1 cuboid- 3 cunieforms, 1 cuboid
- 5 metatarsals- 5 metatarsals- phalanges: 2:3:3:3:3- phalanges: 2:3:3:3:3



ADAPTATION OF MANUSADAPTATION OF MANUS
1.1. WRISTWRIST2.2. PALMPALM3.3. DIGITSDIGITS
• FUNCTIONS:FUNCTIONS:• For graspingFor grasping• For swift-footednessFor swift-footedness
• DigitigradeDigitigrade * unguligrade* unguligrade• Plantigrade Plantigrade


For flight – wingsFor flight – wings For swimming – flippers for life in the For swimming – flippers for life in the
oceanocean
FINSFINS
- stabilizers- stabilizers
- steering device for undulation- steering device for undulation

TYPES OF FINSTYPES OF FINS
1.1. PAIRED FINSPAIRED FINS1.A BONY FISH1.A BONY FISH A. PECTORAL FINS –coracoscapulaA. PECTORAL FINS –coracoscapula B. PELVIC FINS - ischio-pubic plateB. PELVIC FINS - ischio-pubic plate
1.B. CARTILAGINOUS FIS1.B. CARTILAGINOUS FIS A. PECTORAL FINS A. PECTORAL FINS
– – coracoid,scapula, suprascapulacoracoid,scapula, suprascapula B. PELVIC FINS - ischio-pubic plateB. PELVIC FINS - ischio-pubic plate

2. UNPAIRED FINS2. UNPAIRED FINS
A. ANAL FINSA. ANAL FINS
B.CAUDAL FINSB.CAUDAL FINS
C. MEDIAN DORSAL FINSC. MEDIAN DORSAL FINS
A. ANTERIOR DORSAL FINA. ANTERIOR DORSAL FIN
B. POSTERIOR DORSAL FINB. POSTERIOR DORSAL FIN

DIVERSITIES IN SKELETAL DIVERSITIES IN SKELETAL STRUCTURES OF PAIRED FINSSTRUCTURES OF PAIRED FINS
1.1. SPINY FINSSPINY FINS2.2. LOBED FINSLOBED FINS3.3. FINFOLD FINSFINFOLD FINS4.4. FIN SPINEFIN SPINE
VARIATION OF MEDIAN FINSVARIATION OF MEDIAN FINS1.1. HETEROCERCAL -unidenticalHETEROCERCAL -unidentical2.2. HOMOCERCAL HOMOCERCAL - identical- identical3.3. DIPHYCERCALDIPHYCERCAL - symmetrical- symmetrical4.4. HYPOCERCAL HYPOCERCAL - directed downward- directed downward



THEORIES OF THE THEORIES OF THE ORIGIN OF FINSORIGIN OF FINS
1.1. FIN FOLD HYPOTHESIS FIN FOLD HYPOTHESIS ––paired fins are derived from a pair of continuous paired fins are derived from a pair of continuous
fleshy folds of the lateral body wall analogous to the fleshy folds of the lateral body wall analogous to the metapleural folds of amphioxusmetapleural folds of amphioxus
2. GILL ARCH HYPOTHESIS (Gegenbaur)2. GILL ARCH HYPOTHESIS (Gegenbaur)- pectoral and pelvic fins are modified gill arches - pectoral and pelvic fins are modified gill arches
and the skeleton within the fin is an expansion of gill raysand the skeleton within the fin is an expansion of gill rays
3. FIN SPINE HYPOTHESIS (Gregory and Raven)3. FIN SPINE HYPOTHESIS (Gregory and Raven)-in early acanthodians, pectoral and pelvic -in early acanthodians, pectoral and pelvic
appendages were the largest of the series of lateral appendages were the largest of the series of lateral hollow spiny appendageshollow spiny appendages
-lateral extension of the trunk-lateral extension of the trunk

LOCOMOTION OF LIMBLESS LOCOMOTION OF LIMBLESS VERTEBRATESVERTEBRATES
1.1. SERPENTINE OR LATERAL UNDULATIONSERPENTINE OR LATERAL UNDULATION – – movement forming irregular loopsmovement forming irregular loops
2.2. CONCERTIVE OR RECTILINEARCONCERTIVE OR RECTILINEAR- move from place to place by - move from place to place by
gliding using the cervical ribsgliding using the cervical ribs3. SIDESWINDING3. SIDESWINDING
- occupy territory or sandy - occupy territory or sandy dessertdessert
- rattlesnakes- rattlesnakes