Antibiotics in Our Streams How Much is There and Where Are They Coming From? Colorado State...
-
date post
20-Dec-2015 -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
4
Transcript of Antibiotics in Our Streams How Much is There and Where Are They Coming From? Colorado State...

Antibiotics in Our StreamsAntibiotics in Our StreamsHow Much is There and Where Are They How Much is There and Where Are They
Coming From?Coming From?
Colorado State UniversityColorado State University
Kenneth CarlsonKenneth Carlson
([email protected])([email protected])
Sung-Chul KimSung-Chul Kim
Shinwoo YangShinwoo Yang
October, 2005October, 2005

Annual Antimicrobials UsageAnnual Antimicrobials Usage 2002 Animal Health Industry Sales
Total Pounds Total Pounds
(Thousands)(Thousands)Percent of Total (%)Percent of Total (%)
Human UsesHuman Uses
Disease TreatmentDisease Treatment
Other Human UseOther Human Use
3,0003,000
1,5001,50099
55
Livestock UsesLivestock Uses
Therapeutic – All SpeciesTherapeutic – All Species
Nontherapeutic – Cattle, Swine, Nontherapeutic – Cattle, Swine, Poultry Poultry
2,0002,000
24,50024,50066
7777
OthersOthers
Companion AnimalsCompanion Animals 1,0001,000 33
Total Antimicrobials UseTotal Antimicrobials Use 32,00032,000 100100

Sources, Distribution and Sinks Sources, Distribution and Sinks of of
Pharmaceuticals in the Pharmaceuticals in the EnvironmentEnvironment
Sources from: K Kummerer, Pharmaceuticals in the Sources from: K Kummerer, Pharmaceuticals in the Environment, SpringerEnvironment, Springer
Human Used Pharmaceuticals:Human Used Pharmaceuticals: STP as point sourceSTP as point source
Veterinary Pharmaceuticals:Veterinary Pharmaceuticals: Manure as fertilizer Manure as fertilizer Soil Soil Surface Runoff or Surface Runoff or Leaching through sub-surfaceLeaching through sub-surface
Risk to Drinking Water andRisk to Drinking Water and Watershed EcologyWatershed Ecology

Main ObjectivesMain Objectives Monitoring Occurrence of Human and Animal Monitoring Occurrence of Human and Animal
Antibiotics in Water and SedimentAntibiotics in Water and Sediment
Monitoring Occurrence in Animal Waste Lagoons Monitoring Occurrence in Animal Waste Lagoons and Manureand Manure
Evaluating Transport Pathways and MechanismsEvaluating Transport Pathways and Mechanisms
Evaluating Fate of Antibiotics and Waste Evaluating Fate of Antibiotics and Waste Management Management
Practice (BMPs)Practice (BMPs)

NH2
OHO
O OHOH
O
OH
NCH3 CH3R1R2
R3R4
12
3
4
5
6
7
89
1011
1214
15
16
17ABCD
13
pKaa Compounds R1 R2 R3 R4
pK1 pK2 pK3 Oxytetracycline(OTC) OH OH CH3 H 3.3 7.3 9.1
Chlortetracycline(CTC) H OH
Cl
3.3 7.4
9.3
Minocycline(MNC) H H H 2.8 5.0 7.8 Demeclocycline(DMC) H OH H Cl
Melocycline(MCC) OH CH2 - Cl Tetracycline(TC) H OH CH3 H 3.3 7.7 9.7
Doxycycline(DXC) OH H CH3 H 3.5 7.7 9.5
TetracyclinesTetracyclines

Name
R Name R pKa
Sulfathiazole (STZ)
S
N
Sulfametho-xazole (SMX)
ON
CH3
Sulfamerazine (SMR)
N
N
CH3
Sulfachloro-
pyridazine
(SCP)
NN Cl
Sulfamethazine (SMT)
N
N
CH3
CH3
Sulfadimeth-
oxine
(SDM) N
N
CH3O
CH3O
NH2
S
O
O
NH
R
SulfonamidesSulfonamides

MacrolidesMacrolides
H
CH3 H
OH
O
CH3
O
CH3
CH3
O
CH3
O
OH
CH3
O
OHCH3
OH OCH3
OCH3
OHCH3
NCH3CH3
C
OCH3
H
CH3 H
OH
O
CH3
H3CO-H2C-H2C-O-H2C-O-N
CH3
CH3
O
CH3
O
OH
CH3
O
OHCH3
OH OCH3
OCH3
OHCH3
NCH3CH3
C
OCH3
O
C2H3 O
CH3
O
CH3OH
O
CH3
O
O CH3
CHOOH
O
NCH3 CH3
OOH
CH3
OH
CH3
OHO
CH3
OCH3
OCH3
Erythromycin
Tylosin
Roxithromycin

IonophoresIonophores
HCH3
O
O
OH
O O
O
H5C2
HCH3
CH3
H
O
OH
OH
CH3CH3O
CH3
H
CH3
CH3
OHCH3
H3C
1
23
4
5
6
78
91 0
1 1
1 2 1 3
1 4
1 5
1 6
1 71 8
1 9
2 0
2 12 2
2 3
2 4
2 5
2 6
2 7
2 82 9
HCH3
O
O
OH
O O
O
H5C2
HCH3
CH3
H
O
OH
OH
CH3CH3O
H
CH3
CH3
OHCH3
H3C
1
23
4
5
6
78
910
11
12 13
14
15
16
1718
19
20
2122
23
24
25
26
27
2829
CH3OH3C
CH3
H
O
O
O
OH CH3
CH3
H
O
OH
O
CH3
H
OHOH
CH3
CH3
CH3 CH2OH
12
3
4
5
6
78
9
10 11
12 13
14 15
16 17
18 19
20
2122
23
24
25
Monensin
Salinomycin Naracin

Main ObjectivesMain Objectives Monitoring Occurrence of Human and Animal Monitoring Occurrence of Human and Animal
Antibiotics in Water and SedimentAntibiotics in Water and Sediment
Monitoring Occurrence in Animal Waste Lagoons Monitoring Occurrence in Animal Waste Lagoons and Manureand Manure
Evaluating Transport Pathways and MechanismsEvaluating Transport Pathways and Mechanisms
Evaluating Fate of Antibiotics and Waste Evaluating Fate of Antibiotics and Waste Management Management
PracticePractice

Solid Phase Extraction (SPE) Solid Phase Extraction (SPE) ProcedureProcedure
HLBHLB
3mL MeOH3mL HCL(5%,v/v)
3mL DI
3mL MeOH3mL HCL(5%,v/v)
3mL DI
Flow Rate2mL/min
Flow Rate2mL/min
33mLDI Water
33mLDI Water
22.5mLMeOH
22.5mLMeOH

Schematic Diagram of the Sediment Sample Schematic Diagram of the Sediment Sample PreparationPreparation
SampleSample(Air dried)(Air dried)
Pre-ExtractionPre-Extraction
Clean-upClean-up(SPE)(SPE)
Evaporation and ReconstitutionEvaporation and Reconstitution
HPLC/MS/MS AnalysisHPLC/MS/MS Analysis
TCs and SAs:TCs and SAs:Mcllvaine Buffer Solution (pH 4.0)Mcllvaine Buffer Solution (pH 4.0)
MLs and IPs:MLs and IPs:Ammonium Hydroxide Buffer (pH 10.0)Ammonium Hydroxide Buffer (pH 10.0)
Nitrogen Gas Water Bath (50Nitrogen Gas Water Bath (50C)C)5050l Sample + 70l Sample + 70l mobile phase Al mobile phase A

High Performance Liquid Chromatography High Performance Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry (HPLC/MS/MS)Tandem Mass Spectrometry (HPLC/MS/MS)
EquipmentEquipment HP 1100 HPLC equipped with Thermostatted Auto Sampler and HP 1100 HPLC equipped with Thermostatted Auto Sampler and
variable UV detectorvariable UV detector
ThermoFinnigan LCQ Duo ion trap mass spectrometerThermoFinnigan LCQ Duo ion trap mass spectrometer
Xterra MS CXterra MS C1818 (2.1 (2.150mm, 2.550mm, 2.5m pore size, end-capped)m pore size, end-capped)
Optimized HPLCOptimized HPLC
ConditionConditionColumnColumn
TemperatuTemperaturere
((C)C)
Flow Flow RateRate
(ml/min)(ml/min)
Mobile Phase Conditions:Mobile Phase Conditions:
Mobile Phase A (99.9% DI+ 0.1% Formic Acid)Mobile Phase A (99.9% DI+ 0.1% Formic Acid)
Mobile Phase B (99.9% ACN + 0.1% Formic Acid)Mobile Phase B (99.9% ACN + 0.1% Formic Acid)
Mobile Phase C (100% MeOH)Mobile Phase C (100% MeOH)
Tetracyclines Tetracyclines (TCs)(TCs)
Sulfonamides Sulfonamides (SAs)(SAs)
1515 0.320.32 A: 96% + B: 4%: 0 (min) A: 96% + B: 4%: 0 (min) A: 70% + B: 30%: 29 A: 70% + B: 30%: 29 (min) (min) A: 96% + B: 4%: 30 (min) A: 96% + B: 4%: 30 (min)
Macrolides (MLs)Macrolides (MLs) 4545 0.320.32 A: 80% + B: 20%: 0 (min) A: 80% + B: 20%: 0 (min) A: 65% + B: 35%: 13 A: 65% + B: 35%: 13 (min) (min) A: 80% + B: 20%: 14 (min) A: 80% + B: 20%: 14 (min)
Ionophore Ionophore PolyethersPolyethers
(IPs)(IPs)
1515 0.250.25 A: 50% + C: 50%: 0 (min) A: 50% + C: 50%: 0 (min) A: 10% + C: 90%: 1 A: 10% + C: 90%: 1 (min) (min) A: 50% + C: 50%: 20 (min) A: 50% + C: 50%: 20 (min)
Optimized MSOptimized MS
ConditionConditionNitrogen Gas used for drying and nebulizingNitrogen Gas used for drying and nebulizing
Spray Voltage – 4.5VSpray Voltage – 4.5V
Capillary Voltage – 21VCapillary Voltage – 21V
Capillary Temperature - 165Capillary Temperature - 165°C°C

Quality Assurance: Quality Assurance: Recovery,Limit of Quantification (LOQ)Recovery,Limit of Quantification (LOQ)
RecoveryRecovery
Range (%)Range (%)TCsTCs SAsSAs MLsMLs IPsIPs
AqueousAqueous
(0.1,1,5 (0.1,1,5 g/L)g/L)102 - 124102 - 124 77 – 12477 – 124 89 – 11489 – 114 82 – 11782 – 117
SedimentSediment
(1,30,90 (1,30,90 g/kg)g/kg)
33 -11533 -115 62 - 10862 - 108 53 - 12853 - 128 51 - 10551 - 105
Lowest calibration curve point based on signal/noise 3 (0.01 Lowest calibration curve point based on signal/noise 3 (0.01 g/L and 1 g/L and 1 g/kg )g/kg )Standard Deviation Standard Deviation Student’s t-variate for one sided Student’s t-variate for one sided tt-test at the 95% confidence -test at the 95% confidence intervalinterval
LOQLOQ TCsTCs SAsSAs MLsMLs IPsIPs
AqueousAqueous
((g/L)g/L)0.01 – 0.040.01 – 0.04 0.01 – 0.020.01 – 0.02 0.01 – 0.030.01 – 0.03 0.012 – 0.012 –
0.0270.027
SedimentSediment
((g/kg)g/kg)0.3 – 2.50.3 – 2.5 0.3 – 1.70.3 – 1.7 0.5 – 1.70.5 – 1.7 0.4 – 3.60.4 – 3.6
Recovery Ratio Recovery Ratio ==
Detect Response of Spiked Sample prior to SPEDetect Response of Spiked Sample prior to SPE
100100Detect Response of Spiked Sample after SPEDetect Response of Spiked Sample after SPE

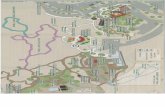
Sampling Sites DescriptionSampling Sites DescriptionSampling Site 1:Sampling Site 1:
Pristine watershedPristine watershed
Sampling Site 2:Sampling Site 2:
Rural landscapeRural landscape
Sampling Site 3:Sampling Site 3:
Urban influencedUrban influenced
Wastewater Reclamation Wastewater Reclamation FacilityFacility
Sampling Site 4:Sampling Site 4:
Heavily agricultural Heavily agricultural influenced areainfluenced area
Sampling Site 5:Sampling Site 5:
Both urban and agricultural Both urban and agricultural
influenced area influenced area Sampling Sites Dairy ■ Feedlots ▲ Ranches USGS Gages ★

Site 2 - Site 2 - AqueousAqueous
Site 2
Tetracyclines
TC CTC OTC DMC MCC DXC
Con
cent
ratio
n (
g/L
)
0.00
0.01
0.02
0.03
0.04
0.05
0.06
May-03April-04August-04February-05
Site 2
Sulfonamides
STZ SMR SMT SCP SMX SDM
Con
cent
ratio
n (
g/L
)0.00
0.01
0.02
0.03
0.04
0.05
May-03April-04August-04February-05
Site 2
Macrolides
ETM-H2O RTM TLS
Con
cent
ratio
n (
g/L
)
0.00
0.01
0.02
0.03
0.04
May-03April-04August-04February-05
Site 2
Ionophore Polyethers
MNS SLM NRS
Con
cent
ratio
n (
g/L
)
0.000
0.005
0.010
0.015
0.020
0.025
0.030
May-03April-04August-04February-05
No observedNo observedconcentrationconcentrationin May and Aprilin May and Aprilexcept Narasinexcept Narasin
Local small farmLocal small farmmight contributemight contributethe detection of the detection of NarasinNarasin
Higher Higher concentrationconcentrationin February within February withhigh detect high detect frequencyfrequencyFor TCs and SAsFor TCs and SAs

Site 3 - AqueousSite 3 - Aqueous
Site 3
Tetracyclines
TC CTC OTC DMC MCC DXC
Con
cent
ratio
n (
g/L
)
0.00
0.02
0.04
0.06
0.08
0.10
0.12
May-03April-04August-04February-05
Site 3
Sulfonamides
STZ SMR SMT SCP SMX SDM
Con
cent
ratio
n (
g/L
)
0.00
0.05
0.10
0.15
0.20
0.25
0.30
0.35
Site 3
Macrolides
ETM-H2O RTM TLS
Con
cent
ratio
n (
g/L
)
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
May-03April-04August-04February-05
Site 3
Ionophore Polyethers
MNS SLM NRS
Con
cent
ratio
n (
g/L
)
0.00
0.01
0.02
0.03
0.04
May-03April-04August-04February-05
Higher concentrationHigher concentrationof human usedof human usedantibiotics orantibiotics orantimicrobialsantimicrobials
High concentration ofHigh concentration ofETM-H2O in low flowETM-H2O in low flowand cold temperatureand cold temperature

Site 4 - Site 4 - AqueousAqueous
Site 4
Tetracyclines
TC CTC OTC DMC MCC DXC
Con
cent
ratio
n (
g/L
)
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
1.2
1.4
May-03April-04August-04February-05
Site 4
Sulfonamides
STZ SMR SMT SCP SMX SDM
Con
cent
ratio
n (
g/L
)0.00
0.02
0.04
0.06
0.08
Site 4
Macrolides
ETM-H2O RTM TLS
Con
cent
ratio
n (
g/L
)
0.00
0.02
0.04
0.06
0.08
0.10
May-03April-04August-04February-05
Site 4
Ionophore Polyethers
MNS SLM NRS
Con
cent
ratio
n (
g/L
)
0.000
0.005
0.010
0.015
0.020
0.025
0.030
0.035
May-03April-04August-04February-05
3 IPs were detected3 IPs were detected

Site 5 - Site 5 - AqueousAqueous
Site 5
Tetracyclines
TC CTC OTC DMC MCC DXC
Con
cent
ratio
n (
g/L
)
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
Site 5
Sulfonamides
STZ SMR SMT SCP SMX SDMC
once
ntra
tion
( g
/L)
0.00
0.02
0.04
0.06
0.08
0.10
0.12
0.14
0.16
Site 5
Macrolides
ETM-H2O RTM TLS
Con
cent
ratio
n (
g/L
)
0.00
0.05
0.10
0.15
0.20
0.25
May-03April-04August-04February-05
Site 5
Ionophore Polyethers
MNS SLM NRS
Con
cent
ratio
n (
g/L
)
0.00
0.01
0.02
0.03
0.04
May-03April-04August-04February-05
Higher concentrationHigher concentrationof MNS in Mayof MNS in May

Site 2 - Site 2 - SedimentSediment
Site 2
Tetracyclines
TC CTC OTC DMC MCC DXC
Con
cent
ratio
n (
g/k
g)
0
10
20
30
40
50
May-03April-04August-04February-05
Site 2
Sulfonamides
STZ SMR SMT SCP SMX SDMC
once
ntra
tion
( g
/kg)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
May-03April-04August-04February-05
Site 2
Macrolides
ETM-H2O RTM TLS
Con
cent
ratio
n (
g/k
g)
0.00
2.00
4.00
6.00
8.00
10.00
12.00
14.00
May-03April-04August-04February-05
Site 2
Ionophore Polyethers
MNS SLM NRS
Con
cent
ratio
n (
g/k
g)
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
May-03April-04August-04February-05
No measurement forNo measurement forMLs and IPs MLs and IPs in Februaryin February
More frequent detectionMore frequent detectioncompared to aqueouscompared to aqueous

Site 3 - Site 3 - SedimentSediment
Site 3
Tetracyclines
TC CTC OTC DMC MCC DXC
Con
cent
ratio
n (
g/k
g)
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
May-03April-04August-04February-05
Site 3
Sulfonamides
STZ SMR SMT SCP SMX SDMC
once
ntra
tion
( g
/kg)
0
2
4
6
8
Site 3
Macrolides
ETM-H2O RTM TLS
Con
cent
ratio
n (
g/k
g)
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
May-03April-04August-04February-05
Site 3
Ionophore Polyethers
MNS SLM NRS
Con
cent
ratio
n (
g/k
g)
0
1
2
3
4
May-03April-04August-04February-05
Higher concentrationHigher concentrationIn February for TCs andIn February for TCs andSAsSAs
No IPs except NarasinNo IPs except Narasin

Site 4 - Site 4 - SedimentSediment
Site 4
Tetracyclines
TC CTC OTC DMC MCC DXC
Con
cent
ratio
n (
g/k
g)
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
May-03April-04August-04February-05
Site 4
Sulfonamides
STZ SMR SMT SCP SMX SDMC
once
ntra
tion
( g
/kg)
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
Site 4
Macrolides
ETM-H2O RTM TLS
Con
cent
ratio
n (
g/k
g)
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
May-03April-04August-04February-05
Site 4
Ionophore Polyethers
MNS SLM NRS
Con
cent
ratio
n (
g/k
g)
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
May-03April-04August-04February-05
Higher Higher concentrationconcentrationin August for in August for SMT,SMT,ETM-HETM-H22O, and IPsO, and IPs
High High concentrationconcentrationOf CTC, STZ, and Of CTC, STZ, and TLSTLS

Site 5 - Site 5 - SedimentSediment
Site 5
Tetracyclines
TC CTC OTC DMC MCC DXC
Con
cent
ratio
n (
g/k
g)
0
20
40
60
80
Site 5
Sulfonamides
STZ SMR SMT SCP SMX SDMC
once
ntra
tion
( g
/kg)
0
2
4
6
8
Site 5
Macrolides
ETM-H2O RTM TLS
Con
cent
ratio
n (
g/k
g)
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
May-03April-04August-04February-05
Site 5
Ionophore Polyethers
MNS SLM NRS
Con
cent
ratio
n (
g/k
g)
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
May-03April-04August-04February-05
Combination of human usedCombination of human usedAnd veterinary medicinesAnd veterinary medicines

Summary of Measured Concentration at Summary of Measured Concentration at watershedwatershed
WaterWater SedimentSediment
CompounCompoundsds
Frequency Frequency of of
Detection Detection (%)(%)
Detected Concentration (Detected Concentration (g/L)g/L) Frequency Frequency of of
Detection Detection (%)(%)
Detected Concentration (Detected Concentration (g/kg)g/kg)
MeanMean StandarStandard d
DeviatioDeviationn
MaximuMaximumm
MinimuMinimumm
MeanMean StandarStandard d
DeviatioDeviationn
MaximuMaximumm
MinimuMinimumm
TCTC 4242 0.020.02 0.010.01 0.030.03 0.010.01 8080 17.917.9 24.324.3 102.7102.7 1.11.1
CTCCTC 4545 0.080.08 0.070.07 0.210.21 0.010.01 8080 10.810.8 9.29.2 30.830.8 1.11.1
OTCOTC 3737 0.180.18 0.400.40 1.211.21 0.010.01 8080 14.814.8 13.913.9 56.156.1 2.42.4
DMCDMC 3030 0.030.03 0.010.01 0.050.05 0.020.02 8080 6.96.9 5.55.5 23.623.6 2.12.1
MCCMCC 4747 0.030.03 0.030.03 0.100.10 0.010.01 8080 24.324.3 21.521.5 72.072.0 4.34.3
DXCDXC 3333 0.020.02 0.010.01 0.050.05 0.010.01 6565 15.715.7 10.110.1 38.938.9 2.22.2
STZSTZ 3333 0.010.01 0.010.01 0.030.03 0.010.01 7070 3.33.3 2.32.3 5.45.4 1.31.3
SMRSMR 3030 0.020.02 0.020.02 0.060.06 0.010.01 1515 4.84.8 2.32.3 6.86.8 2.32.3
SMTSMT 1010 0.020.02 0.000.00 0.020.02 0.020.02 2525 4.74.7 5.25.2 13.713.7 1.01.0
SCPSCP 55 0.030.03 0.000.00 0.030.03 0.030.03 2525 2.72.7 0.50.5 3.23.2 1.91.9
SMXSMX 6060 0.110.11 0.090.09 0.320.32 0.040.04 2525 1.61.6 0.30.3 1.91.9 1.21.2
SDMSDM 3333 0.020.02 0.020.02 0.040.04 0.010.01 3030 3.83.8 2.12.1 6.86.8 1.71.7
ETM-H2OETM-H2O 6565 0.120.12 0.130.13 0.450.45 0.020.02 7575 10.010.0 7.67.6 25.625.6 1.31.3
RTMRTM 00 0.000.00 0.000.00 0.000.00 0.000.00 3030 2.12.1 1.91.9 5.95.9 1.11.1
TYLTYL 55 0.050.05 0.000.00 0.050.05 0.050.05 5353 3.03.0 2.82.8 9.39.3 1.11.1
MNSMNS 5050 0.0090.009 0.0010.001 0.0360.036 0.0020.002 4040 13.813.8 11.211.2 31.531.5 2.42.4
SLMSLM 4343 0.0020.002 0.0020.002 0.0070.007 0.0010.001 4040 9.19.1 11.011.0 30.130.1 1.81.8
NRSNRS 3737 0.0180.018 0.0160.016 0.0380.038 0.0010.001 4040 6.46.4 4.24.2 16.316.3 2.82.8

Pseudo Partitioning Pseudo Partitioning CoefficientCoefficient
Pseudo Partitioning Coefficient Pseudo Partitioning Coefficient (L/kg) =(L/kg) =
Sediment Concentration Sediment Concentration ((g/kg)g/kg)
Aqueous Concentration (Aqueous Concentration (g/L)g/L)CompoundsCompounds RangeRange AverageAverage ReferenceReference
CTCCTC 623 - 1160623 - 1160 891891 670 – 1620670 – 1620
SMXSMX 20 - 2820 - 28 2424 0.6 – 4.90.6 – 4.9
ETM-H2OETM-H2O 72 - 39772 - 397 243243 8.3 – 1288.3 – 128
MNSMNS 1000 - 20501000 - 2050 15251525 --
PPC: MNS > CTC > ETM-H2O > SMXPPC: MNS > CTC > ETM-H2O > SMX
Sources from: J Tolls, Environmental Science and Technology (2001), 35, 3397 - 3406Sources from: J Tolls, Environmental Science and Technology (2001), 35, 3397 - 3406

Animal Waste Animal Waste OperationsOperations
Operation Lagoon Water Manure
Dairy 7 7
Beef 6 5
Hog 10 5
Sheep 2 4
Turkey 0 2

Animal Waste Animal Waste OperationsOperationsConcentration in lagoon water
Samples OTC CTC TC MNSug/L ug/L ug/L ug/L
MDL 1.79 1.33 2.09 0.86
Dairy A 5.04 1.71 9.89Dairy B 17.46 4.78 11.48Dairy C 10.62 1.56Dairy D 2.25Dairy EDairy F 2.95 12.45Dairy G 2.41Beef A 3.27 51.80 7.44 101.34Beef B 7.85 54.56Beef C 2.08 6.94 502.34Beef D 3.53 3.02 8.61 75.32Beef E 2.31 43.27Beef F 2.52 395.76Hog A 7.53 12.93Hog B 2.36 6.23Hog C 11.30 1193.00 6.47Hog D 12.77 2.54Hog E 135.43 16.95Hog F 99.52 14.40Hog G 1524.82 9498.69 26.47Hog H 1310.23 9450.37 24.83Hog I 6.65 2.58Hog J 8.05 2.40
Sheep 1 1.60 6.29Sheep 2

Animal Waste Animal Waste OperationsOperationsConcentration in lagoon water
Samples STZ SCP SDM SMR SMT SMXug/L ug/L ug/L ug/L ug/L ug/L
MDL 0.81 0.87 1.03 1.02 0.94 0.58
Dairy A 3.83 4.41 0.95 0.61Dairy B 1.01 16.80 1.02 2.91 0.59Dairy C 1.76 2.34Dairy DDairy EDairy F 28.04Dairy G 1.82Beef A 1.44 2.43 0.64Beef B 1.17Beef CBeef D 3.83Beef E 2.14 0.96 0.70Hog A 2.07Hog B 4.43Hog C 1941.53 66.07Hog D 1.77Hog E 3.80 2.96 1.12Hog F 3.88 4.53 2.70 1.26Hog G 2079.27 270.73 1.59 9.44Hog H 2430.30 280.58 2.31 8.05Hog IHog J 1.51 1.19
Sheep 1 64.23 2.47 0.60Sheep 2 132.68

Animal Waste Animal Waste OperationsOperationsConcentration in lagoon water
Samples TLS ETM-H2O RTMug/L ug/L ug/L
MDL 0.46 0.65 0.59
Dairy A 1.16Dairy B 4.05 3.05 19.20Dairy C 0.51Dairy D 9.60 0.74Dairy E 19.53 7.95 4.58Dairy F 5.88Dairy G 4.84Beef A 102.52 7.39 43.66Beef B 0.90 0.68Beef C 11.69Beef D 27.88Beef E 37.59Beef F 36.78 0.67Hog A 0.69 0.63Hog BHog C 12.58 3.76 1.09Hog D 60.01 4.25Hog E 5.04Hog F 2.27Hog G 0.46Hog HHog IHog J
Sheep 1Sheep 2 1.80 1.40 1.06

Animal Waste Animal Waste OperationsOperationsConcentration in liquid manure
Samples OTC CTC TC MNSug/kg ug/kg ug/kg ug/kg
MDL 2.43 1.93 2.27 1.96
Dairy/Fresh 16.32 8.87 45.00Dairy/Fresh 42.43 33.38Dairy/Fresh 38.62 34.56Dairy/Fresh 15.73 356.62Dairy/Fresh 5130.42 2.47 1045.52Dairy/Fresh 5.58 39.01 78.53Dairy/Fresh 620.92 31.34 83.00Beef/Fresh 4.58 345.67Beef/Fresh 20.59 380.77 585.34 542.57Beef/Fresh 6.05 10.28 983.56Beef/Fresh 22.93 234.49 184.97 456.30Beef/Fresh 8.29 30.71 36.78Hog Fresh 11.94 23.88 128.44Hog Fresh 91.73 23138.27 1115.56Hog Fresh 1076.27 634.89 394.06Hog Fresh 372.78 148.60 284.15Hog Fresh 176779.21 22837.04 808.12
Sheep Fresh 172.33 3622.96 343.53Sheep Fresh 5.90 5.07 26.45Sheep Fresh 34.04 9990.72 3071.49Sheep Fresh 175832.67 9.64 10896.72Turkey/Old 160.53 26.91Turkey/Old 18.69 308.70 37.78

Animal Waste Animal Waste OperationsOperations
Actual concentration in liquid manureSamples STZ SCP SDM SMR SMT SMX
ug/kg ug/kg ug/kg ug/kg ug/kg ug/kg
MDL 1.35 1.43 1.54 1.17 1.62 1.08
Dairy/Fresh 16.51 7.85 1.75Dairy/Fresh 7.04 1.67Dairy/Fresh 11.49 1.89Dairy/Fresh 8.57Dairy/Fresh 24.32 3.04 647.85 2.64 3.57Dairy/Fresh 46.39 9.53 3.01 1.47Dairy/Fresh 2.74 11.67Beef/Fresh 12.77 3.25Beef/Fresh 127.47 2.18 12.11 5.30 7.28Beef/Fresh 19.70 6.31 2.82Beef/Fresh 257.78 8.43 2.49Beef/Fresh 7.88 5.97Hog Fresh 14.75 1.72 3.07 3.59Hog Fresh 17.40 3.19 2.71Hog Fresh 4.76 5.73Hog Fresh 36.69 38.38 1.81 1.50Hog Fresh 1.74
Sheep Fresh 1.37Sheep Fresh 12.96 419.21 1.96Sheep Fresh 4.19 1.82 2.01Sheep Fresh 10.19 248.42 2.73 1.80Turkey/Old 31.35 69.86 3.18 6.47Turkey/Old 5.51 6.17 1.68

Column Leaching ExperimentsColumn Leaching Experiments
PurposesPurposes Evaluating potential mobility of antibioticsEvaluating potential mobility of antibiotics Estimating partition coefficient (Kd)Estimating partition coefficient (Kd) Comparing surface runoff field experimentComparing surface runoff field experiment
Expected ResultsExpected Results Mobility: Sulfonamides > Macrolides > Mobility: Sulfonamides > Macrolides >
Ionophores > Ionophores > Tetracyclines Tetracyclines Kd values: Tetracyclines > Ionophores > Kd values: Tetracyclines > Ionophores >
Macrolides > Macrolides > Sulfonamides Sulfonamides

Mass Loading From Local Irrigation Mass Loading From Local Irrigation Ditches to WatershedDitches to Watershed ID Site name or
description
Averaged MeanStream Flow (cfs) a
A Eaton Canal 195
B Local Ditch -
C Eaton Canal 195
DGraham Seep Ditch
3
E Greeley #2 Canal 119
FGraham Seep Ditch
3
G Eaton Canal 195
H Greeley #2 Canal 119
I Greeley #2 Canal 119
M Agricultural Area 45
NUrban and agricultural combined area
a Averaged mean stream flow of canal or ditch was provided by Cache la Poudre River water commitioner and river mean stream flow was adapted from U.S. Geological Survey (USGS). Unknown data is not shown.
Inflow Inflow TC: 153.4TC: 153.4
CTC: 266.4CTC: 266.4OutflowOutflowTC: 2.5TC: 2.5
CTC: 2.9CTC: 2.9Mass Flux Mass Flux
TC: 1.6TC: 1.6CTC: 1.1CTC: 1.1
Inflow Inflow STZ: 6.2STZ: 6.2
SMT: 151.3SMT: 151.3OutflowOutflowSTZ: 0.3STZ: 0.3SMT: 3.0SMT: 3.0
Mass Flux Mass Flux STZ: 4.6STZ: 4.6
SMT: 2.0SMT: 2.0
Inflow Inflow ETM-HETM-H
22O: 48.2O: 48.2
TLS: 118.3TLS: 118.3OutflowOutflow
ETM-HETM-H22O: 2.1O: 2.1
TLS: 4.2TLS: 4.2Mass FluxMass Flux
ETM-HETM-H22O: 4.4O: 4.4
TLS: 3.5TLS: 3.5
InflowInflow MNS: 13.0MNS: 13.0SLM: 6.0SLM: 6.0NRS: 12.6NRS: 12.6OutflowOutflowMNS: 0.3MNS: 0.3SLM: 0.3SLM: 0.3NRS: 0.6NRS: 0.6
Mass FluxMass Flux MNS: 1.9MNS: 1.9SLM: 5.0SLM: 5.0NRS: 4.5NRS: 4.5
Unit of Inflow and Outflow: ton/yr, Mass Flux: %Unit of Inflow and Outflow: ton/yr, Mass Flux: %

ConclusionConclusionss
Occurrence frequency high in semi-arid watershedOccurrence frequency high in semi-arid watershed
Sediment-partitioned concentrations much higherSediment-partitioned concentrations much higher
With different site characteristics and land use, With different site characteristics and land use, concentration of human and animal antibiotics concentration of human and animal antibiotics varies significantly – BMPs can be developedvaries significantly – BMPs can be developed
Surface runoff may contribute to the release of Surface runoff may contribute to the release of antibiotics or antimicrobials to the antibiotics or antimicrobials to the environmentenvironment
Local irrigation ditches might act as intermediate Local irrigation ditches might act as intermediate transport pathways transport pathways

AcknowledgemAcknowledgementent
Colorado State UniversityColorado State University
Dr Amy PrudenDr Amy Pruden
Dr Jessica DavisDr Jessica Davis
Kathy DoeskenKathy Doesken
Support:Support:
United States Department of Agriculture United States Department of Agriculture (USDA)(USDA)
National Integrated Water Quality ProgramNational Integrated Water Quality ProgramIntegrated Research, Education, and Extension Competitive Grants Integrated Research, Education, and Extension Competitive Grants
ProgramProgram