Anatomical Planes
-
Upload
sagar-gawankar -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
0
Transcript of Anatomical Planes

8/6/2019 Anatomical Planes
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/anatomical-planes 1/3
Directional terms
Directional terms describe the positions of structures relative to other structures or locations in the body.
Superior or cranial
toward the head end of the body; upper (example, the hand is part of the superior extremity).
Inferior or caudal away from the head; lower (example, the foot is part of the inferior extremity).
Anterior or ventralfront (example, the kneecap is located on the anterior side of the leg).
Posterior or dorsal back (example, the shoulder blades are located on the posterior side of the body).
Medial toward the midline of the body (example, the middle toe is located at the medial side of
the foot).
Lateral away from the midline of the body (example, the little toe is located at the lateral side of
the foot).
Proximal toward or nearest the trunk or the point of origin of a part (example, the proximal end of
the femur joins with the pelvic bone).
Distal away from or farthest from the trunk or the point or origin of a part (example, the hand is
located at the distal end of the forearm).
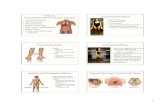
Medical professionals often refer to sections of the body in terms of anatomical planes(flat surfaces). These planes are imaginary lines - vertical or horizontal - drawn throughan upright body. The terms are used to describe a specific body part.
Coronal Plane (Frontal Plane)A vertical plane running from side to side; divides the body or any of its parts into
anterior and posterior portions.
Sagittal Plane (Lateral Plane)A vertical plane running from front to back; divides the body or any of its parts into rightand left sides.
Axial Plane (Transverse Plane)A horizontal plane; divides the body or any of its parts into upper and lower parts.
Median planeSagittal plane through the midline of the body; divides the body or any of its parts into
right and left halves.

8/6/2019 Anatomical Planes
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/anatomical-planes 2/3
Cardinal Plane - The plane where the center of mass passes through. The three
cardinal planes in human body when he/she stands in the anatomical position frontal
plane, sagittal plane and the transverse plane
*Frontal Plane (Coronal Plane) - The plane that cuts you down your side. It
would cut you from your ear though your hip to your feet
Horizontal Plane - Any plane dividing the body into upper and lower portions,
perpendicular to the vertical plane
*Median Plane (Midsagittal plane) - Passing directly along the midline of
the body so that perfect right and left halves of the body is created
Oblique plane - Slanting plane that is not in any of the other planes
*Sagittal Plane (Lateral plane) - The plane that cuts right down the middle of
your body
Spinous Plane - Horizontal plane transecting the body at the level of anterior superior
iliac spine

8/6/2019 Anatomical Planes
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/anatomical-planes 3/3
Sternoxiphoid Plane - Horizontal plane transecting the body at the level of
xiphisternal joint
Subcostal Plane - Horizontal plane transecting the body at the level of lower margin
of the tenth rib
Suprasternal Plane - Horizontal plane transecting the body at the level of jugular
notch
Thoracic Plane - Horizontal plane transecting the body at the level of the fourth
intercostal space
Transpyloric Plane - Horizontal plane transecting the body at the level of the
eighth intercostal space
*Transverse Plane (Axial Plane) - Plane that cuts across your stomach. It would
cut you from one hip to the other
Umbilical Plane - Horizontal plane transecting the body at the level of the umbilicus
Vertical Plane - Any plane dividing the body into left and right portions, or front and
back portions, perpendicular to the horizontal plane