anatomi panggul.ppt
description
Transcript of anatomi panggul.ppt

ANATOMY OF FEMALE PELVICBy: Tiyas K
Airlangga University
Department of Child-Maternity NursingNursing Faculty 2010

PELVIC
A. Solid part : Pelvic bone
B. Soft part : Pelvic ligament & muscle

A. PELVIC BONE
2 Innominate bone : - Os illium- Os ischium- Os pubic
Sacrum Coccyx

PELVIC BONE

PELVIC BONE

PELVIC BONE

Sacrum PELVIC BONE

Tulang CoccygisPELVIC BONE

Ischium Function
Support body weight (tuber ischiadica)

Fungsi os Coccygis
In labor this bone extent to posterior in order to wider the pelvic outlet

Pelvic Inlet/Pelvic brim
Area bordered by: Promontorium Sacrum Linea inominata Ramus Superior
ossis Pubis Uper border of
Symphisis pubis

Pelvic outlet
Area bordered by: Ujung bawah
Sacrum Tulang Tuber
Ischiadica Sacro-coccygeal Lower border of
symphisis pubis

Normal pelvic measurement
Distansia Spinarum
Distansia Cristarum
Distansia Cristarum: 28—29 cm
Distansia Spinarum: 25—26 cm

Inside Pelvic measurement
• Conjugata Diagonalis = 12,5—13cm
• Conjugata Vera = CD – (1,5—2cm)
• Conjugata Obstetrika = terpendek

Hodge line
Hodge I: imagination line drawn from promontorium to the upper border of symphisis pubis
Hodge II: parallel with hodge I measured from lower border of symphisis
Hodge III: parallel with hodge II, measured from spina ischiadica
Hodge IV: parallel with hodge III, measured from coccyx tip

H IH II
H IIIH IV

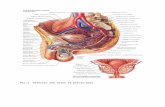
B. PELVIC LIGAMENT & MUSCLE LIGAMENT connect the pelvic joint
Ligament interpubic pada symphysis pubis Ligament sacro iliaca Ligament sacro-coccygeal Ligament sacro-tuberous Ligament sacro spinosus

PELVIC MUSCLE
The inner aspect of the bony pelvis is covered with muscles:
Above the brim --- iliacus & psoas
Sidewalls ---- obturator internus & its fascia
Post wall ---- pyriformis
Pelvic floor ---- lavator ani & coccygeus

PELVIC MUSCLE

Conjugata Vera

Sacral promontory
Left sacro-iliac joint
Iliopectineal line
Sacrospinous ligament
Sacrotuberous ligament
Symphysis pubis
Ischial tuberosity
Ischial spine

PELVIC EXAMINATION
• X-Ray• Jangka Panggul• Distansia Cristarum• Distansia Spinarum• Conjugata eksterna/Bouldeloque:
distance between upper border symphysis pubis with prosessus spinosus lumbal 5. the normal measurement 18—20 cm
• Vaginal Touché

Vaginal Touché Examintion
Promontorium touched/not Conjugata Vera normal/not Spina Ischiadica prominent/not Arkus pubis wide/narrow Sakrum curve/not
Note: •Touched Promontory usually indicated narrow pelvic•Height ≤145 cm also indicated narrow pelvic

Differentiation between female and male pelvic

Pelvic Shape

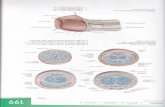
PELVIC SHAPE
1-GYNECOID Typical female pelvis found in 50% of
women Rounded—slightly oval inlet Straight pelvic sidewalls with roomy pelvic
cavity Good sacral curve Ischial spines are not prominent Pubic arch is wide

PELVIC SHAPE
2-ANDROID Typical male pelvis found in 1/3 white
women 1/6 non-white Pelvic brim is heart shaped Pelvis funnels from above downwards
(convergent sidewalls) Narrow pubic arch Prominent spines

PELVIC SHAPE
3-ANTHROPOID 25% white women & 50% nonwhite Pelvic brim APD > TD Long & narrow pelvic canal with long sacrum Straight pelvic sidewalls
4-PLATYPELLOID 3% of women Pelvic brim TD >>>APD kidney shape Sacral promontory pushed forwards

Pelvic Shape Deviation
A. Panggul Naegele
B. Panggul Rakhitis
C. Panggul Skoliosis
D. Panggul Kifosis
E. -”- dari Samping
F. Panggul Osteomalasia
G. Panggul Spondilolistesis
H. Panggul Robert

Causes of pelvic deviation Congenital:- Narrow palvic- Simple flat- Funnel (narrow outlet)- Assimilation Disease :- Rachitic- Osteomalasia- TBC- Lordosis- Skoliosis- Kifosis- Spondilosis

Deviation impact
Prolonged labor CPD (Chepalo Pelvic Disproportion) Breech presentation Infertility

POST TEST
Pelvic anatomy contains of what kind of part? What can you mention about Pelvic bone? What can you mention about Pelvic
ligament? What can you mention about pelvic muscle? What do you know about pelvic shape? What would happen if the pelvic is not
normal in measurement?

Daftar pustaka
Wyknyosastro , S., (2002) Ilmu Kebidanan. Jakarta: Yayasan Bina Pustaka Sarwono Prawiroharjo
Cunningham, H. et. al., (2005) Williams Obstetrics. 22nd. New York: McGRAW-HILL
Bobak, LM. & Jensen, MD., (2005) Maternity & Gynecology Care: The Nurse and The Family. 5th Ed. St. Louis: Mosby company

THANK YOU
“PLEASE WORK HARD IN THIS NEW SEMESTER”