The neuropathy solution solves your peripheral neuropathy pain
alcoholic neuropathy
-
Upload
histhunder122 -
Category
Documents
-
view
24 -
download
2
description
Transcript of alcoholic neuropathy

By: Millicent Gayle M. Villariza
ALCOHOLIC NEUROPATHY Definition
Neuropathy partly due to associated malnutrition esp. Vitamin B
Peripheral neuropathy in alcohol abusers
Axons die back
Mixed motor & sensory Etiology
Still debated
Theories o Nutritional deficiencies and direct toxicity from prolonged alcohol
consumption are the most likely causes o Direct toxic effect of ethanol
Epidemiology
Disease is uncommon in the US
Chronic alcohol users are commonly affected Pathogenesis
Nutritional deficiencies and direct toxicity from prolonged alcohol consumption are the most likely causes of the axonal neuropathies.
Persons with alcoholism tend to have nutritional deficiencies due to deceased consumption and/or impaired gastrointestinal absorption.
Thiamine is an essential vitamin in the breakdown of pyruvate and plays a role in the health of the peripheral nervous system.
Some studies have also linked direct toxic effects of alcohol on peripheral nerves. The combination of nutritional deficiency and direct toxicity leads to wallerian degeneration of axons and reduced myelination in peripheral nerves, which results in neuropathy.
Clinical Manifestations
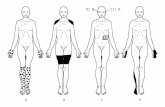
Sx first occur in LE
(+) paresthesia
Decreased sensation especially proprioception
Distal muscle weakness & wasting
Depressed distal reflexes
As disorder worsens o Changes appear proximally in LE & begin in UE
Common impairments
o Numbness
o Paresthesia
o Pain
o burning feet
o muscle weakness (changes in sensation and muscle strength tend to be bilateral and affect the legs more than the arms)
o heat intolerance
o impotence (men)
o incontinence
o constipation
o diarrhea
o nausea/vomiting
Common functional limitations
o Difficulty ambulating
o performing self care activities,
o Driving

By: Millicent Gayle M. Villariza
o etc.
Potential disabilities o Unable to
maintain employment personal relationships
o could become socially isolated o trouble reintegrating into community
Differential Diagnosis
Laboratory or imaging studies used to confirm or rule out diagnosis o Nutritional studies may show deficiencies
thiamine (vit B 1) pyridoxine (vit B6) vit B12 folic acid niacin (vit B3) vit A other deficiencies
o Nerve conduction tests and EMG may be used to determine the extent of neurological damage
Decreased sensory action potential amplitudes Minimal slowing of motor conduction velocity Distal latencies are minimally prolonged Positive sharp waves & fibrillation potentials in distal muscles
with polyphasic units of increase amplitude o Nerve biopsy may be used to rule out other causes o EGD, upper GI, and small bowel series may be used to r/o physical
obstruction as cause of vomiting and other GI symptoms o Voiding cystourethrogram (VCUG) may show decreased bladder
emptying caused by damaged nerves controlling the bladder o Chronic alcohol consumption may cause increased liver enzyme levels
as measured by AST and ALT tests o Elevated blood creatinine levels may implicate renal insuffiency as a
cause for peripheral neuropathy o An elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) may implicate an
inflammatory condition. o A screen for heavy metal toxicity since it can be a cause for neuropathy
Additional information to confirm diagnosis o thorough patient history to document any abuse of alcohol
Distinguishing characteristics of similar conditions o diabetic neuropathy
similar in its presentation of symptoms However, patients with this condition typically have a long-
standing history of diabetes Blood glucose tests are used to diagnose diabetes
Prognosis/Complications
GOOD prognosis if treated promptly
Medical factors impacting prognosis and outcome o current level of nerve damage is usually permanent and will progress if
Px continues to abuse alcohol o continued nutritional deficiencies could cause the condition to progress
Medical Management
Ensure good diet
Diet supplements including thiamine and folic acid, depending on individual's deficiencies

By: Millicent Gayle M. Villariza
Medication to treat pain, including OTC analgesics such as aspirin, ibuprofen, or acetaminophen.
Efforts to reduce orthostatic hypotension: eating extra salt, sleeping with the head elevated, medications.
Manual expression ofurine, catheterization, or medications to treat bladder dysfunction.
Referral to AA, medication, and Px education for treatment of alcoholism
PT INTERVENTION
PT Tests/Measures o Aerobic capacity and endurance
Patients with this disorder tend to have decreasing BP during sit to stand or supine to stand.
So BP should be assessed prior to activity. These patients may also have decrease endurance so baseline
endurance should also be recorded. o Arousal, attention, and cognition
Due to decreased neurological function these patients should be screened in this area
o Assistive and adaptive devices These patients can have balance and gait disorders and may
need to be assessed for the need to use assistive devices for safety purposes.
o Community and work integration or reintegration These patients may have still have emotional issues related to
alcoholism and may need help to reintegrate into the community or work place.
o Cranial nerve integrity This should be assessed to rule out other potential
neuromuscular disorders. o Environment, home and work
these patients may need assistance to reintegrate into their normal daily lives
o Gait, locomotion, and balance This can be a major impairment for this type of patient and
should be a major focus in the examination. This type of patient tends to present with ataxia and wide base of
support and can also present with bilateral foot drop. o Integumentary integrity
due to the decreased sensation to the lower extremities these patients should be screened for skin break down
o Motor function observe the patient's quality of movement (speed, smoothness)
and coordination o Orthotic, protective, and supportive devices
The decrease sensation in this disorder can lead to the need for protective shoes and socks.
These patients can also have decrease dorsiflexion and plantarflexion so these patients should be assessed for the need for AFOs.
o Pain These patients may or may not have pain a pain rating should be recorded as a baseline
o Range of motion Contractures may be present in this patient population due to
weakness in dorsiflexion and plantarflexion, length of gastroc should be assessed as the ROM in other joints
o Reflex integrity

By: Millicent Gayle M. Villariza
Tendon reflexes can be reduced in this population especially those in the lower extremity and should be assessed thoroughly
o Self-care and home management These patients may have trouble doing ADLs and IADLs so this
area should be assessed in order to determine appropriate intervention.
o Sensory integrity Sensation loss is very common in these patients
the loss usually starts in the lower extremities and in severe cases can include the upper extremities
Sensation loss is also usually found to be symmetrical these patients should also be assessed for vibration and
proprioception integrity
Additional Resources o These patients may benefit from
Psychiatric Nutritional and substance abuse support group resources These resources will depend on where the patient is at in their
rehabilitation program PT MANAGEMENT
Primary treatment is STOP DRINKING ALCOHOL BEVERAGES
Most likely outcome of PT o Comprehensive physical therapy for patients with alcoholic neuropathy
may include the following to address individual's impairments Gait and balance training, possibly with an assistive device
For safety ROM exercises and stretching, particularly for the gastroc-soleus
muscle
to prevent contracture and maintain normal gait mechanics
Strength training of weakened muscles Recommended activities
HEP to maintain LE strength and flexibility Education of Proper Foot Care
Feet should be washed each night with mild soap and warm water.
Wear clean socks daily.
Shoes should be loose fitting and custom fitted.
Cut the nails straight.
Do not cut corns or calluses.
Do not wear tight or constricting clothing.
Do not use tobacco in any form.