Africans & The Atlantic Slave Trade
-
Upload
lois-whitaker -
Category
Documents
-
view
20 -
download
2
description
Transcript of Africans & The Atlantic Slave Trade

Africans & The Africans & The Atlantic Slave TradeAtlantic Slave Trade

Portuguese - Portuguese - interior trade - interior trade - especially goldespecially gold-Generally with -Generally with local consentlocal consent-El Mina-El MinaMissionaries Missionaries followed –gain followed –gain Christian Christian converts converts
Mozambique - Mozambique - gold trade gold trade Some Portuguese Some Portuguese settle in Africasettle in Africa
P – set the P – set the common common European pattern European pattern of trading of trading stations w/ the stations w/ the slave trade as slave trade as central central componentcomponent

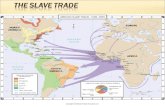
1450-1850 - 12 million Africans sent across 1450-1850 - 12 million Africans sent across AtlanticAtlantic– 10-11 survive 10-11 survive – Primarily young men for hard agric/mine labor Primarily young men for hard agric/mine labor
18th century – 80% of total trade18th century – 80% of total trade
Muslim world slave tradeMuslim world slave trade– Trans-Saharan, Red Sea, East AfricaTrans-Saharan, Red Sea, East Africa– Mostly womenMostly women– 3 million slaves traded3 million slaves traded

African SocietyAfrican Society
Slave LivesSlave Lives– Millions killedMillions killed– Families destroyedFamilies destroyed
Africans in the AmericasAfricans in the Americas– Plantation systemPlantation system
American Slave SocietiesAmerican Slave Societies– MiscegenationMiscegenation

The Dutch boot the The Dutch boot the PortuguesePortuguese
Seize El Mina - 1630Seize El Mina - 1630
English get involved - 1660sEnglish get involved - 1660s
French join in on the action - 18th French join in on the action - 18th centurycentury
Dahomey - Royal monopoly on flow of Dahomey - Royal monopoly on flow of slavesslaves
Economic significance?Economic significance?– Same profits as other tradeSame profits as other trade– Value tied up with plantation and mining Value tied up with plantation and mining
economyeconomy– Definitely ties Africa to global economyDefinitely ties Africa to global economy

African societies leading up to African societies leading up to the slave tradethe slave trade West & Central Africa was West & Central Africa was
made up of small, volatile made up of small, volatile statesstates– Warfare endemic – societal Warfare endemic – societal
emphasis on military emphasis on military Europeans use hostilities to Europeans use hostilities to
their advantage – slaves for their advantage – slaves for guns influenceguns influence
African states closest to the African states closest to the coast dominate b/c of coast dominate b/c of European weaponsEuropean weapons

East Africa and the SudanEast Africa and the Sudan Swahili trading towns - ivory, Swahili trading towns - ivory,
gold slaves to Middle Eastgold slaves to Middle East Northern Savanna - new Northern Savanna - new
IslamizationIslamization Songhay breaks up in 1500sSonghay breaks up in 1500s
– Successor statesSuccessor states
Muslim Hausa states in Muslim Hausa states in northern Nigerianorthern Nigeria
Muslim reform movements Muslim reform movements began 1770sbegan 1770s
Usuman Dan Fodio - 1804 - Usuman Dan Fodio - 1804 - Hausa statesHausa states

Capetown – South AfricaCapetown – South Africa Dutch colony – Boers - 1652Dutch colony – Boers - 1652
– Plantation estates worked by Plantation estates worked by slavesslaves
– Wars with San, KhoikhoiWars with San, Khoikhoi– 1760s warring w/ Bantu1760s warring w/ Bantu
1795 - Britain occupies 1795 - Britain occupies colonycolony
1815 – GB takes possession1815 – GB takes possession After 1834 - Afrikaners push After 1834 - Afrikaners push
beyond boundariesbeyond boundaries