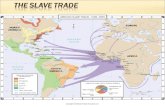
Atlantic Trade in Enslaved Africans
-
Upload
romanodaniel -
Category
Documents
-
view
226 -
download
0
Transcript of Atlantic Trade in Enslaved Africans
-
8/7/2019 Atlantic Trade in Enslaved Africans
1/27
Atlantic Trade in Enslaved
Africans
-
8/7/2019 Atlantic Trade in Enslaved Africans
2/27
When enslaved Africans were introduced on theplantations in the Caribbean there alreadyexisted systems of enslavement in Africa
Slavery probably existed from the time mansettled in large groups
Between 100 to 900BC slave societies existed inNorth Africa where the Arabs transferred theirsystem of enslavement to societies in North
Africa
-
8/7/2019 Atlantic Trade in Enslaved Africans
3/27
As Islam spread to West Africa so too did thetrade in enslaved persons
Thus organised trade in human cargo developedbetween West African societies and Arab states.
When the Portuguese, Spanish and later Dutchrequired enslaved labour, they were alreadyaware that there was the possibility of tappinginto that Trans Sahara trade.
-
8/7/2019 Atlantic Trade in Enslaved Africans
4/27
Trans Saharan Trade Routes
-
8/7/2019 Atlantic Trade in Enslaved Africans
5/27
The Portuguese, being in such close proximity toAfrica, logically became the first Europeans toconsistently import enslaved African labour.
This trade was spearheaded by the Henry TheNavigator.
By 1482 the Portuguese had built the fort atElmina (in Ghana) which facilitated the TransAtlantic trade in enslaved Africans
-
8/7/2019 Atlantic Trade in Enslaved Africans
6/27
Elmina Castle, 1668
-
8/7/2019 Atlantic Trade in Enslaved Africans
7/27
STRUCTURE OF THE TRADE IN
ENSLAVED AFRICANS & THE
EXPERIENCES OF THE ENSLAVED
-
8/7/2019 Atlantic Trade in Enslaved Africans
8/27
The Trans Atlantic Trade in enslaved Africans wasnot the first form of enslavement
It differed qualitatively from the other systems
The first distinction is that the other systems ofenslavement were not synonymous with a
certain race, ethnicity, religion.
When Africans came across the Atlantic, theywere the only group enslaved.
-
8/7/2019 Atlantic Trade in Enslaved Africans
9/27
Enslaved persons in the Cbean were enslaved for life andthis status was transferred to their children
Only in exceptional cases did enslaved persons in the
Cbean not spend their entire lives enslaved
Enslaved people in the Caribbean were considered chattel;they were the property of an individual who could passthem on in a will, or sell with other household items
The cultivation of sugar was partly responsible for thedifference in the structure of the slave system thatdeveloped in across the Atlantic.
-
8/7/2019 Atlantic Trade in Enslaved Africans
10/27
Structure of Trade in Enslaved
Africans The slave trade was very well organised
There were three main areas of the organisation:
Sourcing prospective slaves from the interior
Coastal arrangements
The Middle Passage
-
8/7/2019 Atlantic Trade in Enslaved Africans
11/27
Stage 1 The Interior
-
8/7/2019 Atlantic Trade in Enslaved Africans
12/27
Africans and Europeans acted as middlemen
They sourced prospective slaves from among prisoners of war
individuals who were already enslaved
those persons who were indebted
by raiding villages and kidnapping
creating criminals
-
8/7/2019 Atlantic Trade in Enslaved Africans
13/27
Stage 2 The Coast
Slave Market on West Coast of Africa
-
8/7/2019 Atlantic Trade in Enslaved Africans
14/27
Africans were taken to the coast
The trek to the coast required the support of kings andchiefs through whose territories the trek was made
At the coast there were forts established by Europeans,each headed by an agent/factor
Captured persons were battered for textiles, iron bars,utensils, tobacco, alcohol
The forts were used to house the enslaved until a shiparrived
-
8/7/2019 Atlantic Trade in Enslaved Africans
15/27
-
8/7/2019 Atlantic Trade in Enslaved Africans
16/27
When a ship was contracted the captives wereprepared; they were medically examined, brandedand shackled
The ships arrived with goods and it was necessary toconvert them for shipping the human cargo
Spaces of apprx 5 feet were created for eachindividual
Some ships carried as many as 700 captives
-
8/7/2019 Atlantic Trade in Enslaved Africans
17/27
THE CAPTION READS: PLAN SHEWING THE STOWAGE OF 130 ADDITIONAL
SLAVES ROUND THE WINGS OR SIDES OF THE LOWER DECK BY MEANS OF
PLATFORMS OR SHELVES (IN THE MANNER OF GALLERIES IN A CHURCH) THE
SLAVES STOWED ON THE SHELVESAND BELOW THEM HAVE ONLY A HEIGHT OFTWO FEET 7 INCHES BETWEEN THE BEAMS AND THE FAR LESS UNDER THE
BEAMS
-
8/7/2019 Atlantic Trade in Enslaved Africans
18/27
Stage 2 The Middle Passage
The Middle Passage was one leg of the TriangularTrade: From the coast of West Africa across the
Atlantic to the Caribbean
-
8/7/2019 Atlantic Trade in Enslaved Africans
19/27
The Middle Passage was a horrific journeyacross the Atlantic
The journey lasted between 5 weeks and 3months
The captives were fed rice, millet, cornmeal,yam, manioc/plantains and water
-
8/7/2019 Atlantic Trade in Enslaved Africans
20/27
The captives were fed rice, millet, cornmeal,yam, manioc/plantains and water
They were made to jump on deck as a meansof exercise with the whip as a threat
Captives were kept below deck and allowedout 3 times a day to be fed and exercise
-
8/7/2019 Atlantic Trade in Enslaved Africans
21/27
Below Deck
-
8/7/2019 Atlantic Trade in Enslaved Africans
22/27
Overcrowded Lower Deck
In order that the largest possible cargo might be carried, the African captives werewedged horizontally, chained to low-lying platforms stacked in tiers, with an average
individual space allotment of6 feet by 16 inches wide (183 by 41 cm). Unable to standerect or turn over, many slaves died in this position.
-
8/7/2019 Atlantic Trade in Enslaved Africans
23/27
From the time of their capture, the captivesresisted
During the Middle Passage some
Committed suicide
Revolted/mutinied
Engaged in hunger strikes
-
8/7/2019 Atlantic Trade in Enslaved Africans
24/27
Attempted Mutiny
-
8/7/2019 Atlantic Trade in Enslaved Africans
25/27
-
8/7/2019 Atlantic Trade in Enslaved Africans
26/27
Difficult to estimate the deaths
Death rate
20% during early period 17th to early 18th century
5% between the late 18th and early 19th century
Even the deaths among the crew was high: Ofthe slave-ship crews that embarked fromLiverpool in 1787, less than half returned alive.
-
8/7/2019 Atlantic Trade in Enslaved Africans
27/27
Even the death rate among the crew was high
There is much debate over the actualnumbers of captives that made the crossing
P. Curtin (1969): 8 million over apprx 360 yrs
J. Inikori (1976): 15 million Patrick Manning*(1998): 12 million
transported; 10.5 million arriving alive in theAmericas
* The historian and NOT the PM of Tdad & Tobago