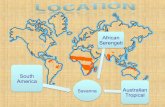
African Savanna .
-
Upload
rosamond-sanders -
Category
Documents
-
view
226 -
download
0
Transcript of African Savanna .

African Savanna http://bioexpedition.com/savanna-biome/
http://www.planetpatrol.info/savannah.htmlhttp://hydrodictyon.eeb.uconn.edu/eebedia/images/8/81/ZA_Biomes.pdf

BANG
The Big Bang happened about 13.75 billion years ago, soon following Universe became extremely hot and dense thus forcing it to expand rapidly. After the initial expansion, the Universe cooled enough to allow energy to
turn into various subatomic particles, such as protons, neutrons, and electrons. Soon following simple atomic nuclei rapidly developed and
multiplied eventually causing life ad the rest is history.

Galactic Ecosystem
The timescale for the Galactic ecology is determined by the rate of star formation and the lifetime of the
most massive stars, gradually changing form, over the life of the Galaxy. This is based on the energy flows
from the massive stars, and the material cycle through these same stars. This process also creates carbon
and heavier elements and released through winds and supernova explosions. They cycle between the
various phases of the interstellar phase, before again being incorporated into stars and, in some cases,
planetary systems and life. Despite this delicate balance and interplay between many aspects of the star
formation cycle, it remains to be asked whether it is evolving with time, for evolution in the Galaxy is limited
compared to the tremendous biodiversity it has produced on Earth. Star formation produces a range of
stellar masses; with the initial mass function (IMF) determining how many stars of a particular mass are
found. The different masses are similar to the different species within an ecosystem. While astronomers
often refer to this as stellar evolution, this is an inappropriate use of the word, as it is used to describe the
life processes of individual stars, not their changes from one to another.
http://arxiv.org/ftp/astro-ph/papers/0110/0110694.pdf

Galaxies -A system of millions or billions of stars, together with gas and dust, held together by gravitational attraction.
Dark matter- a type of matter said to account for a large part of the total mass in the universe. Dark matter cannot be seen directly with telescopes; because it doesn’t emits or absorbs light or other electromagnetic radiation at any significant level.
Gas-Nitrogen , Oxygen , Argon , Carbon dioxide , Neon, Helium , Methane , Krypton , Hydrogen , Nitrous Oxide
Dust- It is for the most part a type of small dust particles which are a few. A smaller fraction of all dust in space consists of larger refractory minerals that condensed as matter left the stars. It is called "stardust" and is included in a separate section below.
Gravity-the natural occurrence where physical objects appear to attract each other with a with a force directed by the proportion of their mass
Electromagnetism-A branch of science concerned what happens between electrically charged particles.
Stellar nebulae-where a star is born
Protostar-a large mass that forms by contraction out of the gas of a giant molecular cloud in the process of star formation
Yellow star- A stellar classification for one of the least hottest stars
Blue star-A stellar classification for the hottest stars
Red giant- is a luminous giant star of low or mass in a late phase of stellar evolution.
Super red giant-They are the largest stars in the universe in terms of volume, although they are not the most massive.
Nova- an explosion in a white dwarf star caused by the accretion of hydrogen on to the surface of the star, which ignites and starts nuclear fusion in a runaway manner
Super nova-a stellar explosion that is more energetic than a nova
Planetary nebula-an emission nebula consisting of an expanding glowing shell of ionized gas ejected during the asymptotic giant branch phase of certain types of stars late in their life
white dwarf-a white dwarf's mass is comparable to that of the Sun and its volume is comparable to that of the Earth brown dwarf
Black hole.- a region of space time from which gravity prevents anything, including light , from escaping.