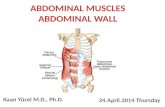
Abdominal wall defects
-
Upload
drmanish-kumar -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
79 -
download
3
Transcript of Abdominal wall defects
EmbryologyEmbryology Normal 2wk embryo is a flat disc that contains Normal 2wk embryo is a flat disc that contains
ectoderm, endoderm & mesodermectoderm, endoderm & mesoderm Intraembryonic coelom divides mesoderm into Intraembryonic coelom divides mesoderm into
sphlancnoplueric & somatoplueric mesodermsphlancnoplueric & somatoplueric mesoderm
4 folds appear4 folds appear
Cephalic fold: thoracic & epigastric wallCephalic fold: thoracic & epigastric wall
Caudal fold: hindgut, bladder & hypogastric wallCaudal fold: hindgut, bladder & hypogastric wall
Lateral folds: lateral abdominal wall.Lateral folds: lateral abdominal wall.
Four folds meet to form the umbilical ring by Four folds meet to form the umbilical ring by 4rth week4rth week
Physiological herniation of gut during the 6 Physiological herniation of gut during the 6 – 10th week.– 10th week.
Small defects at umbilicus: probably Small defects at umbilicus: probably failure of intestine to return into the failure of intestine to return into the peritoneal cavityperitoneal cavity
Large defects: Failure of development of Large defects: Failure of development of body wall.body wall.
ExomphalosExomphalos
GastroschisisGastroschisis
Extrophy bladderExtrophy bladder
ExomphalosExomphalos
Central defect at the site of the umbilical Central defect at the site of the umbilical ringring
Eviscerated contents are covered by a sac Eviscerated contents are covered by a sac formed by peritoneum, whartons jelly & formed by peritoneum, whartons jelly & amnionamnion
Size 4 – 12cmsSize 4 – 12cms
Umbilical cord is inserted onto the sacUmbilical cord is inserted onto the sac
Contents: Usually small & large bowel, Contents: Usually small & large bowel, sometimes stomach & liversometimes stomach & liver
Abdominal muscles are well developed, Abdominal muscles are well developed, coelom not well developedcoelom not well developed
Congenital hernia of the cord:Congenital hernia of the cord: Less than 4 cms diameterLess than 4 cms diameterContain few loops of intestineContain few loops of intestineMay be missed at birthMay be missed at birthCareless clamping may result in injuryCareless clamping may result in injury
Giant omphalocoeles:Giant omphalocoeles: Massive sac containing most of the Massive sac containing most of the
abdominal viscera including liver, abdominal viscera including liver, spleen, gall bladder, gonads, spleen, gall bladder, gonads, intestines.intestines.
GastroschisisGastroschisis::
Smooth edged defect located Smooth edged defect located adjacent to a normal umbilical cord. adjacent to a normal umbilical cord. Ocassionaly separated from the Ocassionaly separated from the cord by a strip of skin.cord by a strip of skin.
Almost always to the right of the Almost always to the right of the umbilicusumbilicus
Size 2-5 cms, often dangerously Size 2-5 cms, often dangerously small compared to the size of the small compared to the size of the eviscerated organs.eviscerated organs.
Stomach, small & large intestine are Stomach, small & large intestine are commonly herniated.commonly herniated.
There is no sac, hence exposed to There is no sac, hence exposed to amniotic fluid. amniotic fluid.
Exposed bowel often foreshortened, Exposed bowel often foreshortened, edematous, covered by thick edematous, covered by thick exudates. May be ischemic.exudates. May be ischemic.
Associated anomalies:Associated anomalies:
Pentalogy of Cantrell Pentalogy of Cantrell
( defect of cephalic fold)( defect of cephalic fold)
OmphalocoeleOmphalocoele
Anterior diaphragmatic Anterior diaphragmatic herniahernia
Sternal cleftSternal cleft
Ectopia cordisEctopia cordis
Cardiac anomaliesCardiac anomalies
Lower midline defect:Lower midline defect:
Bladder / cloacal Bladder / cloacal extrophyextrophy
ARMARM
MMCMMC
Sacral vertebral Sacral vertebral anomaliesanomalies
Major congenital anomalies are often seen
ManagementManagement
Immediate post natal :Immediate post natal :
NG aspirationNG aspiration IV Fluid managementIV Fluid management CatheterisationCatheterisation Maintain body temperatureMaintain body temperature Dressing Dressing
Surgical managementSurgical management Could be in single / multiple stagesCould be in single / multiple stages
Exomphalos: Exomphalos:
Excise the sacExcise the sac
Put the contents back into the Put the contents back into the abdomen after inspectionabdomen after inspection
Measure abdominal pressureMeasure abdominal pressure
If pressure lower than 20cms of HIf pressure lower than 20cms of H220 0 proceed with primary repair of the proceed with primary repair of the defectdefect
If pressure is high, close only the If pressure is high, close only the skin to make a ventral hernia for skin to make a ventral hernia for repair laterrepair later
If peritoneal cavity is small & not If peritoneal cavity is small & not
accepting contents, apply prosthetic accepting contents, apply prosthetic closureclosure
Single running suture is applied at the top Single running suture is applied at the top of the sac. Suture reapplied everyday and of the sac. Suture reapplied everyday and contents are gradually reduced over a contents are gradually reduced over a period of 8 – 10 days. Then defect is period of 8 – 10 days. Then defect is repairedrepaired..
Dacron reinforced Dacron reinforced silastic sheet is used as a silastic sheet is used as a prosthetic sac.prosthetic sac.
It is sutured to the fascia It is sutured to the fascia around the circumference around the circumference of the defect.of the defect.
Extrophy – Epispadias ComplexExtrophy – Epispadias Complex
Abnormal over-development of cloacal Abnormal over-development of cloacal membrane preventing migration of membrane preventing migration of mesenchymal tissue and development mesenchymal tissue and development of lower abdominal wall.of lower abdominal wall.
Incidence: 1 in 20,000 live births.Incidence: 1 in 20,000 live births.
AnatomyAnatomy
Musculoskeletal defect:Musculoskeletal defect: Outward rotation of iliac bones Outward rotation of iliac bones
results in wide pubic diastasis. Pelvic results in wide pubic diastasis. Pelvic diaphragm is open (divergent) and diaphragm is open (divergent) and incompetent. High incidence of rectal incompetent. High incidence of rectal prolapseprolapse
Urinary defectsUrinary defects
Anterior wall of bladder absentAnterior wall of bladder absent
Mucosa of posterior wall , trigone, ureteric Mucosa of posterior wall , trigone, ureteric orifices & bladder neck exposedorifices & bladder neck exposed
Bladder plate may be large & elastic or Bladder plate may be large & elastic or small, fibrosed & unelastic.small, fibrosed & unelastic.
Mucosa may be normal, polypoid or undergo Mucosa may be normal, polypoid or undergo squamous metaplasia.squamous metaplasia.
Upper tracts & kidneys are usually normal.Upper tracts & kidneys are usually normal.
Anorectal:Anorectal:Perineum is short & broad. Anus displaced Perineum is short & broad. Anus displaced
anteriorlyanteriorly
Male genital defect:Male genital defect:
Severe - EpispadiasSevere - Epispadias
Phallus is foreshortened because of wide Phallus is foreshortened because of wide separation of crural attachmentseparation of crural attachment
Prominent dorsal chordeeProminent dorsal chordee
Short urethral grooveShort urethral groove
External sphincter deficientExternal sphincter deficient
Female genital defectFemale genital defect
Short vagina. Stenosis commonShort vagina. Stenosis common
Clitoris is bifid and labia divergentClitoris is bifid and labia divergent
Problems in managementProblems in management Bladder plate may be inadequateBladder plate may be inadequate
Large fascial defect on bladder closure. Difficult Large fascial defect on bladder closure. Difficult to repair inspite of osteotomiesto repair inspite of osteotomies
Chances of continence after surgery is poorChances of continence after surgery is poor
Extremely difficult to attain cosmetically Extremely difficult to attain cosmetically satisfying reconstruction of genitaliasatisfying reconstruction of genitalia
Fertility poor.Fertility poor.