8051-1
-
Upload
mukul-shukla -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
0
Transcript of 8051-1
-
7/28/2019 8051-1
1/5
MICROCONTROLLER
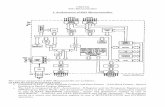
BLOCK DIAGRAM OF IC-AT89C51
The AT89C51 is a low-power, high-performance CMOS 8-bit Amicrocomputer
with 4Kbytes of Flash programmable and erasable read only memory
(EPROM). The device is manufactured using Atmels high -density nonvolatile
memory technology and is compatible with the industry-standard MCS-51
instruction set and pin layout. Fig.shows the block diagram of AT89C51.
The on-chip Flash allows the program memory to be reprogrammed in-system or by a
conventional nonvolatile memory programmer. By combining a versatile 8-bit CPU with
Flash on a monolithic chip, the Atmel AT89C51 is a powerful microcomputer which
provides a highly-flexible and cost-effective solution to many embedded control
applications.
FIG.4.1 Block Diagram of AT89C51
-
7/28/2019 8051-1
2/5
PIN CONFIGURATION
The AT89C51 provides the following standard features: 4K bytes of Flash, 128 bytes of
RAM, 32 I/O lines, two 16-bit timer/counters, five vector two-level interrupt architecture,
a full duplex serial port, on-chip oscillator and clock circuitry.
In addition, the AT89C51 is designed with static logic for operation down to zero
frequency and supports two software selectable power saving modes. The Idle Mode stops
the CPU while allowing the RAM, timer/counters, serial port and interrupt system to
continue functioning. The Power-down Mode saves the RAM contents but freezes the
oscillator disabling all other chip functions until the next hardware reset.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
31
P1.0
P1.1
P1.2
P1.3
P1.4
P1.5
P1.6
RST
(RXD) P3.0
(TXD) P3.1
(INT0) P3.2
(INT1) P3.3
(T0) P3.4
(T1) P3.5
(WR) P3.6
XTAL 2
XTAL 1
GND
Vcc
P0.0(AD0)
P2.0(A8)
P2.1(A9)
P2.2(A10)
P2.3(A11)
P2.4(A12)
P2.5(A13)
P2.6(A14)
P2.7(A15)
PSEN
ALE/PROG
EA/VPP
P0.6(AD6)
P0.7(AD7)
P0.5(AD5)
P0.4(AD4)
P0.3(AD3)
P0.2(AD2)
P0.1(AD1)
(RD) P3.7
P1.7
(Serial)
interrupt
Timer
Ex M W/R
clock
Ext
MemoryAddress
Ext Memo
Access Con
Ext Memory
Address
8051
Fig Pin Diagram (AT89C51)
-
7/28/2019 8051-1
3/5
PIN DESCRIPTION
4.3.1 PORT 1(Pin 1-8)
Port 1 is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pullups. The Port 1 output buffers can
sink/source four TTL inputs. When 1s are written to Port 1 pins they are pulled high by the
internal pullups and can be used as inputs. As inputs, Port 1 pins that are externally being
pulled low will source current because of the internal pullups. Port 1 also receives the low-
order address bytes during Flash programming and verification
4.3.2 RST (Pin 9)
Reset input. A high on this pin for two machine cycles while the oscillator is running resets
the device.
4.3.3 PORT 3 (Pin 10-17)
Port 3 is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-ups. The Port 3 output buffers can
sink/source four TTL inputs. When 1s are written to Port 3 pins they are pulled high by the
internal pull-ups and can be used as inputs.
TABLE 4.1 Alternate Functions of Port 3
-
7/28/2019 8051-1
4/5
As inputs, Port 3 pins that are externally being pulled low will source current because of the
pull-ups. Port 3 also serves the functions of various special features of the AT89C51 as listed
below: Port 3 also receives some control signals for Flash programming and verification.
4.3.4 XTAL2 (Pin 18)
It is output of the inverting oscillator amplifier.
4.3.5 XTAL1 (Pin 19)
Input to the inverting oscillator amplifier and input to the internal clock operating circuit.
4.3.6 GND (Pin 20)
It is ground pin.
4.3.7 PORT 2(Pin 21-28)
Port 2 is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pullups. The Port 2 output buffers can
sink/source four TTL inputs. When 1s are written to Port 2 pins they are pulled high by the
internal pullups and can be used as inputs. As inputs, Port 2 pins that are externally being
pulled low will source current because of the internal pullups. Port 2 emits the high-order
address byte during fetches from external program memory and during accesses to externaldata memory that uses 16-bit addresses. In this application, it uses strong internal pull-ups
when emitting 1s. During accesses to external data memory that uses 8-bit addresses; Port 2
emits the contents of the P2 Special Function Register. Port 2 also receives the high-order
address bits and some control signals during Flash programming and verification.
4.3.8 PSEN (Pin 29)
Program Store Enable is the read strobe to external program memory. When the AT89C51 is
executing code from external program memory, PSEN is activated twice each machine cycle,
except that two PSEN activations are skipped during each access to external data memory.
4.3.9 ALE/PROG (Pin 30)
Address Latch Enable output pulse for latching the low byte of the address during accesses to
external memory. This pin is also the program pulse input (PROG) during Flash programming.
In normal operation ALE is emitted at a constant rate of 1/6 the oscillator frequency, and may
be used for external timing or clocking purposes. Pulse is skipped during each access toexternal Data Memory. If desired, ALE operation can be disabled by setting bit 0 of SFR
-
7/28/2019 8051-1
5/5
location 8EH. With the bit set, ALE is active only during a MOVX or MOVC instruction.
Otherwise, the pin is weakly pulled high. Setting the ALE-disable bit has noeffect if the
microcontroller is in external execution mode.
4.3.10 EA/VPP (Pin 31)
External Access Enable. EA must be strapped to GND in order to enable the device to fetch
code from external program memory locations starting at 0000H up to FFFFH. Note, however,
that if lock bit 1 is programmed, EA will be internally latched on reset. EA should be strapped
to VCC for internal program executions. This pin also receives the 12-volt programming
enable voltage (VPP) during Flash programming, for parts that require 12-volt VPP.
4.3.11 PORT0 (Pin 32-39)
Port 0 is an 8-bit open-drain bi-directional I/O port. As an output port, each pin can sink
eight TTL inputs. When 1s are written to port 0 pins, the pins can be used as high
impedance inputs. Port 0 may also be configured to be the multiplexed low order. Address
/data bus during accesses to external program and data memory. In this mode P0 has
internal pull ups. Port 0 also receives the code bytes during Flash programming andoutputs the code bytes during program verification. External pull ups are required during
program verification.
4.3.12VCC(40)
It is supply voltage.











![8051- Intro to Hardware[1]](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/577d2e991a28ab4e1eaf7e72/8051-intro-to-hardware1.jpg)



![Writing C Code for the 8051[1]](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/577dae281a28ab223f900c36/writing-c-code-for-the-80511.jpg)