4.1 Chemical Energy & ATP 4.2 Overview of Photosynthesis 4.3 Photosynthesis in Detail CELL ENERGY.
4.3 Photosynthesis
description
Transcript of 4.3 Photosynthesis

4.3 PHOTOSYNTHESIS

PHOTOSYNTHESIS IN PLANTS
What is the simple word equation for photosynthesis?

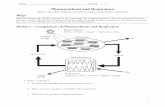
CHLOROPLASTSThylakoids are a phospholipid bilayer membrane-bound compartment. A granum is a stack of thylakoids folded on top of one another. The stroma is the fluid space within the chloroplast. The lumen is the fluid filled space within a thylakoid.
An average green plant cell has between 10 – 50 chloroplast

CHLOROPHYLL
Chlorophyll is actually made up of 5 pigments
Chlorophyll a & b Carotenoids
(carotene and xanthophyll)
Phaeophytin (a grey breakdown product of the others)

There are 2 distinct chlorophyll complexes Photosystem I (PSI) Photosystem II (PSII)
Each system has a different combination of pigments
They therefore absorb light in different areas of the spectrum
PSI absorbs around 700 nm PSII absorbs around 680 nm
Each system has a different role in photosynthesis

BIOCHEMISTRY OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS
Photosynthesis is a two stage process involving a series of reactions.
Light-dependent stage can only take place during daylight.
It produces products which are used by the light-independent stages.
The whole process occurs all the time during daylight hours. But the light-independent stage can also occur in the dark.

LIGHT-DEPENDENT Takes place on thylakoid membranes 2 functions:
Produce ATP Split water in a photochemical reaction providing
hydrogen ions to reduce CO2 and make carbohydrates
Light is made of photons, photons hit chlorophyll and excite them (give them more energy)
excited electrons are picked up by electron acceptors
ATP can then be made by photophosphorylation via an electron transport chain.

CYCLIC PHOTOPHOSPHORYLATION

NON-CYCLIC PHOTOPHOSPHORYLATION
Electron
transpo
rt chain
NADP (electron acceptor)
Reduced NADP (used in light-independent reaction)
+2H+

LIGHT-INDEPENDENT STAGE
Ribulose bisphosphat
e (RuBP)
6C
2 GP (glycerate 3 phosphate)
2 GALP (glyceraldyd
e 3 phosphate)
Glucose
CO2
RUBISCO
Calvin Cycle