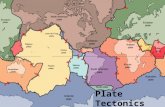
4.2 The Theory of Plate Tectonics Tectonics – ( Greek ) meaning “construction” Tectonics: The...
-
Upload
garey-fowler -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
1
Transcript of 4.2 The Theory of Plate Tectonics Tectonics – ( Greek ) meaning “construction” Tectonics: The...

4.2 The Theory of Plate TectonicsTectonics – (Greek) meaning “construction”
Tectonics:The study of the formation of features in the earth’s crust
Two types of crust:• Oceanic crust• Continental crust
Open textbook to p. 72

Lithosphere & AsthenosphereLithosphere – made up of the crust and the rigid upper mantle
The lithosphere is broken into separate plates that ride on the
denser asthenosphere.
Asthenosphere – layer of plastic rock; a solid rock that slowly flows(like putty) when under pressure.

Plate BoundariesDivergent boundaries –
where plates move away from each other

Plate BoundariesConvergent boundaries – where plates collide (3 types)
1. Ocean & Continent – forms a subduction zone; usually forms an ocean trench and mountains on land

Plate BoundariesConvergent boundaries – where plates collide
2. Two Continental plates – neither plate is subducted, so both are crumpled and
uplifted

Plate BoundariesConvergent boundaries – where plates collide 3. Ocean & Ocean – forms deep ocean trench when one plate is
subducted; subducted plate melts and forms volcanic chain(Island Arc)

Plate Boundaries
Transform fault boundaries – forms where two plates are grinding past each other.
Can you think of an example?

San Andreas Fault

Causes of Plate Motion
Convection Currents – cycle of warm matter rising and cool matter sinking

Theory of Suspect Terranes
3 identifying characteristics:1. Terrane contains rock and fossils that differ from the rocks
and fossils of neighboring terranes.
2. There are major faults at the boundaries of a terrane.
3. The magnetic properties of a terrane do not match those of neighboring terranesSee Figure 4-9 on p. 77
Continents are a patchwork of terranes, each with its own distinct geologic history.