3.5.5: Discuss the relationship between one gene and one polypeptide.
description
Transcript of 3.5.5: Discuss the relationship between one gene and one polypeptide.

One gene may code for multiple polypeptides due to alternative splicing (Post transcriptional modification)
3.5.5: Discuss the relationship between one gene and one polypeptide.
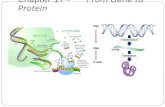
mRNA from one gene
Introns are transcribed but not translatedExons are transcribed and translated

Post-transcriptional modification, splicing (joining) exons in various combinations example: lymphocyte production of antibodies:millions of different antibody proteins are produced from just a few genes
Some genes do not code for polypeptides at all
some genes code for tRNA (transfer RNA) not translated into protein transports amino acids to ribosomes
some genes code for rRNA (ribosomal RNA) not translated into protein a component of ribosome structure and function
tRNA molecule
rRNA molecule