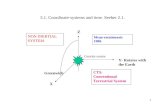
2.1 control systems
-
Upload
momina-mateen -
Category
Business
-
view
1.618 -
download
8
description
Transcript of 2.1 control systems

Back to Control Systems
Control SystemsMomina
Hyper linking

Back to Control Systems
What is a control system?
It uses microprocessors to control physical conditions. This is done by :
1. Keeping them the same over a period of time 2. Vary them according to the preset values + lengths
of time.
Physical conditions can include: Temperature Pressure Humidity Light Moisture.

Process Control
Medical Applications
Central-heating systems
Car Manufacture
Air-conditioning systems
Cl ick for more>>>
Refrigeration

Back to Control Systems
Air-Conditioning Systems
How does an Air-Conditioning System work?
Keep in mind that the ‘gas’ that is being used is called refrigerant. There is a reason why refrigerant is used and that reason is that it has the ability to be easily converted to a gas and back to a liquid again.

Back to Control Systems
How does an Air-conditioning System work?
The room cools down
As liquid changes to gas, it absorbs heat from the inside of the building.
Fan blows air across metal fins (which have chilled as a result of heat being absorbed)
Liquid flows through the expansion valve
It evaporates into a cool low-pressure gasGas moves through the condenser outside the building
Gas cools down into a liquid
Compressor
Cool low-pressure gas into hot high-pressure gas

Back to Control Systems
Refrigeration
• The principle of how refrigeration works is the same as that of the Air conditioning system.
• Main inputs are:1. Temperature sensor: Monitors the
temperature inside the refrigerator2. Contact switch/ pressure sensor: for the door3. Number pad: input required temperature
So what happens now?

Back to Control Systems
Refrigeration
The microprocessor compares the data from the sensor to the preset values. Then?
If the temperature is higher than the preset value, the microprocessor will activate an actuator which will then turn on the compressor.
If the temperature is lower than the preset values, the microprocessor will turn the switch to the compressor off.
Are there any other outputs from the fridge?

Back to Control Systems
Refrigeration
1. Light –emitting diodes (LED): this allows the user to know what the current temperature is inside fridge.
2. Warning Buzzer: this sounds when the door is left open, in order to alert someone to close it.

Back to Control Systems
Central Heating Systems
What are the main parts of a central heating system?
1. Boiler2. Hot-water cylinder3. A pump4. Radiator
So how does it all work?

Back to Control Systems
Central Heating Systems
Boiler used to heat the water
Water from the boiler flows into
hot-water cylinder
Pump causes heated water
from the cylinder to flow round the
system to the radiators
What happens in a micro-processed controlled central-heating system?

Back to Control Systems
Central Heating System
• An ADC (Analogue to Digital Converter) is used.
• The microprocessor controls separate actuators:
1. Opens the valves2. Switches the pump
on

Back to Control Systems
Car Manufacture
• The robots used in the manufacture of cars use actuators in the form of electric motors.
• A DC motor spins quickly when an electric current is applied to it. It spins the opposite way when the current flowing through it is reversed.
What is a stepper motor? More popular type of motor for robotics. As the name suggests; it does its actions in
steps. This is then easier for a computer to control.

Back to Control Systems
What do they use in industries and why?∞ They use robot arms∞ It consists of seven metallic sections with six
joints.∞ Each joint is controlled by a separate stepper
motor.How does the computer control the movement
of the arm?It uses different ‘end effectors’. This allows for a
variety of jobs to be done. The ‘end effectors’ are attached at the end of a robot arm.

Back to Control Systems
What types of end effectors are used in car manufacture?
1. Cameras in order to inspect work2. Welding guns3. Grippers which allow for parts to be picked up
easily. They have built-in pressure sensors.4. Vacuum cups i.e. electrical parts5. Drills6. Screwdrivers7. Spray guns8. Sanders
NOTE: the end effector can have any of the mentioned attachments BUT if the end effector is changed you also need to change the programming.
For example: you can’t have the robot that was spray painting then to be used as a screwdriver head without changing the programming.

Back to Control Systems
What are industrial robots?
• Their purpose is to perform the same task again and again.
What does a robot do on a car production line?1. Painting car bodies2. Putting on car wheels3. Drilling holes in car bodies4. Fixing rivets to car bodies5. Tightening the bolts6. Assembling electric circuits in cars7. Inserting car engines.

Back to Control Systems
How does a robot know what to do?
• Initially the programmer guides the arm step by step. This is usually done be actually physically holding the arm.
• These arms contain sensors which allow them to transmit data back to the computer.
• The computer then stores the exact order of movements as a program in its memory.
• You could also move the robotic arm by using a remote control.

Back to Control Systems
Why are robots used rather than humans?
• A robot arm is much more accurate than a human
• The running costs are comparatively lower• Robotic arms do not get tired• Robots can be used continuously

Back to Control Systems
Medical Applications
There are two major medical applications of ICT:
1- Intensive care2- Surgery

Back to Control Systems
Intensive Care
The patient is monitored by sensors. These sensors measure:
1. Blood pressure2. Pulse rate3. Body temperature
The computer it pre-set with values. So the sensors take in the above mentioned variables and compare them to the pre-set values, if the
measured value is outside the pre-set value range, an alarm is set off by the computer.
The computer allows the doctor to monitor several patients at the same time.

Back to Control Systems
Surgery• It involves robotic arms + cameras inside the
patient’s body.• These robot arms and cameras are much
smaller than normal. • Usually the end effector is a scalpel.• The surgeon wears a type of goggles which
allow him to see inside the patients body. The surgeon then controls their hand by putting their hands into a console. Their hand movement is then imitated by the robotic arms.

Back to Control Systems
What are the benefits of robots in surgery?
• The work is done more accurately• The patients recover more quickly because
large scale operations are not necessary.• The patient does not occupy the hospital bed
for long.

Back to Control Systems
Process Control
• This is when computers/microprocessors are used to control a process.
Few examples:× Oil refining× Chemical processing× Car manufacture× Temperature control
Types of Process Control

Back to Control Systems
1. Batch Control Process
2. Continuous Process Control
3. Discrete Process Control

Back to Control Systems
Batch Control Process
• This is used when a specific amount of raw materials are combined together + mixed for a certain length of time
For example:- In pre-packed meals: the amount of each
ingredient that is added is controlled by a computer. The length of time it cooks for and the temperature is also computer controlled.
- It is used to produce relatively small amounts of product per year.

Back to Control Systems
Continuous Process Control
• This is a process that never appears to end.For example:Maintaining the temperature of a confined
environment.Paper machines with continuous paper output
onto rolls.
It is used to produce very large quantities of product per year.

Back to Control Systems
Discrete Process Control
• This is only used when a specific item is produced. It is like an on/off process.
For example:Manufacturing of cars; computer control used
when fitting the wheel.The wheel is fitted, next car comes and the
same robot fits the wheel in the same position.

Back to Control Systems
What are most process controls overseen by?
• By a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC)• It is the type of computer that is only used for
one purpose.• It can accept both analogue and digital Inputs.• Then a set of logic statements are used to
compare the input with the input pre-set value. Dependent on the result the output device is activated.
• It is usually found in industrial processes.• Once it has been programmed; there is no
further input from the user.

Back to Control Systems
How can you program a PLC?
• By using a Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) algorithm.
• They are used with closed-loop systems.What is a close-loop system?• It is a system in which a physical variable is
continuously being monitored.• The purpose of the PLC is to make the input
value equal to the pre-set one.• PID is the BEST way to do this. It is found in
many versions of control systems. For example washing machines.

Back to Control Systems
What does PID do?
• It calculates the difference between the input value and the pre-set value.
• It then causes the PLC to make the appropriate changes to the output so that the pre-set value is eventually reached.

Back to Control Systems
EWT: Embedded Web Technology
• This technology combines the Internet, the worldwide web and the real time systems into one technology for controlling embedded systems.
What is an embedded system?It is an integration of microprocessors, input
sensors, output actuators and the software needed to control them.
The embedded software enables the user to adjust and control oven temperatures using a mobile phone or PDA or laptop computer.