1. What is the job of DNA? 2. What does DNA look like? 3. Fill in the blank with the missing...
-
Upload
sara-caldwell -
Category
Documents
-
view
213 -
download
1
Transcript of 1. What is the job of DNA? 2. What does DNA look like? 3. Fill in the blank with the missing...

DO NOW1. What is the job of DNA?2. What does DNA look like?3. Fill in the blank with the missing
nucleotideT A C __ T ___ G ____
4. T A _ T C G G ___ A T T

ANNOUNCEMENTS
You’re getting a copy of your progress report today.
THEY AREN’T PRETTY!!!
You will fail if you fail your tests and then don’t retake.
We have a lab at the end if we can get through everything today.


TODAY Finish the material from yesterday. Talk about how DNA replicates using RNA Exit ticket
Bad news I couldn’t find the flavored marshmellows, so we aren’t doing the lab today.
HOWEVER!!! WE STILL HAVE OUR LAB TOMORROW!
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PZW6dPvIC0g&feature=related

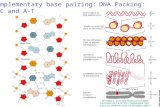
REPLICATION The act of making an exact copy of the
DNA. During replication DNA strands are as
templates used to make copies of new strands. Here is how it happens:
1. The DNA molecule opens up, separating into two strands.
2. Nucleotides match up and join to the open DNA strands.
3. Two identical DNA molecules are formed.

GUIDED PRACTICE:P1 Turn to Page C137 and C138. Draw the diagram labeled replication at
the bottom of the page. Make sure you label it.
You have 10 minutes. Hint: replication means to “repeat”

GUIDED PRACTICE With a partner, answer the following
question
Describe the differences among DNA, genes and Chromosomes.
How are they related?
Once you are done:Turn to page C137 and C138 and copy the
pictures and label them in your notes. (25 pts)

ANSWERS: Genes are units of heredity that are
located in DNA. DNA-molecules that stores information
(about your genetic make up) Chromosomes- this is the form that DNA
takes when cells divide. (DNA coils up into chromosomes)

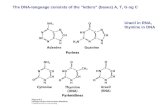
INDEPENDENT PRACTICE1. Describe the shape of the DNA
molecule and how the nucleotide bases fit into that structure.
2. What is a protein and what is it made of?

RNA• In order to make proteins DNA needs
help “translating” the genetic code using another molecule.
• RNA carries information from DNA to a ribosome where the amino acids are brought together to form a protein.
• The only difference between RNA and DNA is the sugars that make them. RNA-ribose, DNA-deoxyribose.

TYPES OF RNA There are 3 different types of RNA that
are used to make proteins. Messenger RNA (mRNA) Ribosomal RNA(rRNA) Transfer RNA (tRNA) In prokaryotes- RNA and protein is made
in the cytoplasm. In eukaryotes-DNA is copied in the
nucleus, then RNA moves to the cytoplasm, where proteins are made.

TRANSCRIPTION The process of transferring information
from DNA to RNA. The structure is very similar to DNA. They have 4 base pairs just like DNA. The 3 bases that make up DNA are the
same:Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Cytosine (C). The fourth base is different- Uracil (U)
instead of Thymine.

HOW TRANSCRIPTION TAKES PLACE During transcription, DNA is used as a
template to make RNA. DNA opens up along a gene. Nucleotides of RNA match up and join to
open up the DNA strand. The completed RNA strand is released
and moves into the cytoplasm. Only one strand of DNA is transcribed.
So only one new RNA strand is made

TRANSLATION Ribosomes attach to an mRNA molecule
at the beginning of a coding region. Transfer RNA (tRNA) match up and joins
to the mRNA strand. As the ribosome moves along the mRNA
strnd, it attaches one amino acid to another.
tRNA molecule is released after the amino acid has been attached.
Once the ribosome reaches the end of the coding region, a completed chain of amino acids are released.

GUIDED PRACTICE 1. Identify 3 types of RNA involved in
protein synthesis. 2. What might happen if the wrong amino
acid is put on a tRNA molecule?

GUIDED PRACTICE ProteinBased on the video clip answer the
following questions:1. Give 2 examples of protein being used
by the body.2. How can a lack of protein prevent
someone from being able to maintain homeostasis?
3. Do athletes need more protein than others? Why or why not.
4. How does RNA work to help the body to build more proteins.

DOMINANT AND RECESSIVE GENES A dominant gene is the gene that
will be expressed if one of the parents has the trait.
A recessive gene must have two recessive genes in order to be expressed.

LOOK INTO THE FUTURE Next week we will begin using Punnet
Squares. Punnet Squares are used to help
determine dominant and recessive genes.

BACK ON TRACK Today! We are going to be making a 3-D model of a
DNA Molecule.
You will need: 2 pieces of licorice 12 toothpicks 9 pink marshmallows 9 yellow marshmallows 9 green marshmallows 9 orange marshmallows 5 paperclips Masking Tape

EXIT TICKET Adenine matches with __________________.
A. Thymine B. Cytosine C. Guanine D. Uracine
Cytonine matches with _________________. A. Thymine B. Adenine C. Guanine D. Uracine
What’s the job of DNA?