1 Chapter 7 Respiratory Drugs. 2 Ventilation Refers to the movement of air in and out of the lungs...
-
Upload
phoebe-heath -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
4
Transcript of 1 Chapter 7 Respiratory Drugs. 2 Ventilation Refers to the movement of air in and out of the lungs...

11
Chapter 7 Chapter 7 Respiratory DrugsRespiratory Drugs

22
VentilationVentilation
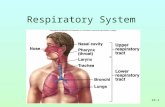
Refers to the movement of air in and out of Refers to the movement of air in and out of the lungs through a series of air passages.the lungs through a series of air passages. NoseNose MouthMouth TracheaTrachea Bronchial treeBronchial tree
The upper portion of the respiratory system The upper portion of the respiratory system is mainly responsible for conditioning is mainly responsible for conditioning inhaled air from the environment. inhaled air from the environment.

33
To maintain normal ventilatory function, it To maintain normal ventilatory function, it is critical that the upper respiratory is critical that the upper respiratory system adjust the temperature and system adjust the temperature and humidify the inhaled air as well as humidify the inhaled air as well as provide filtration of the contaminants in provide filtration of the contaminants in the ambient air. the ambient air.

44
Filtration of inspired air occurs mainly as Filtration of inspired air occurs mainly as the inhaled air passes over the mucus the inhaled air passes over the mucus lined epithelium of the trachea. lined epithelium of the trachea.
The branches of the bronchial tree are The branches of the bronchial tree are lined with smooth muscle, which adjusts lined with smooth muscle, which adjusts the constriction and dilation of the the constriction and dilation of the airways in response to the needs of the airways in response to the needs of the body. body.

55
Respiratory SystemRespiratory System
In the respiratory system, receptor In the respiratory system, receptor specificity is a very important issue and specificity is a very important issue and has prompted a continued development has prompted a continued development in many of the agents discussed in this in many of the agents discussed in this chapter.chapter.

66
One of the major systems regulating the One of the major systems regulating the respiratory system is the autonomic respiratory system is the autonomic nervous systemnervous system A main function of the autonomic nervous A main function of the autonomic nervous
system is to regulate smooth muscle tone in system is to regulate smooth muscle tone in the respiratory system and thereby maintain the respiratory system and thereby maintain the balance between bronchoconstriction the balance between bronchoconstriction and bronchodilation. and bronchodilation.

77
AsthmaAsthma
Millions of people in the United States Millions of people in the United States have asthma and billions of dollars are have asthma and billions of dollars are spent annually on the care of these spent annually on the care of these individuals. individuals.
Asthma is a condition of the respiratory Asthma is a condition of the respiratory system involving narrowing system involving narrowing (bronchoconstriction) and inflammation of (bronchoconstriction) and inflammation of the small air passages of the lower the small air passages of the lower respiratory system.respiratory system.

88
Technically, asthma, exercise induced Technically, asthma, exercise induced asthma (EIA), and exercise induced asthma (EIA), and exercise induced bronchoconstriction (EIB) are separate bronchoconstriction (EIB) are separate conditions and treated differently. conditions and treated differently.
True asthma is characterized by both True asthma is characterized by both bronchoconstriction and inflammation in bronchoconstriction and inflammation in the respiratory tract.the respiratory tract.

99
Exercise is a trigger for approximately Exercise is a trigger for approximately 80% to 90% of individuals with asthma.80% to 90% of individuals with asthma.
Individuals with EIA, must have excellent Individuals with EIA, must have excellent control of their underlying asthma in control of their underlying asthma in order to be able to prevent asthma order to be able to prevent asthma exacerbations during physical activityexacerbations during physical activity

1010
Exercise-induced bronchoconstriction Exercise-induced bronchoconstriction without active inflammation is technically without active inflammation is technically not exercise induced asthma. not exercise induced asthma.
Exercise-induced bronchoconstriction Exercise-induced bronchoconstriction occurs in approximately 11% of occurs in approximately 11% of individuals without asthma and the rate individuals without asthma and the rate may be as high as 50% for elite athletes. may be as high as 50% for elite athletes.

1111
In asthmatic reaction, inflammatory In asthmatic reaction, inflammatory response = increase in mucus production response = increase in mucus production to protect bodyto protect body
Excess coating can lead to air-flow Excess coating can lead to air-flow restrictionrestriction
Another mechanism to protect body is Another mechanism to protect body is bronchoconstrictionbronchoconstriction

1212
The classic signs of an acute asthma The classic signs of an acute asthma exacerbation are: exacerbation are: Shortness of breathShortness of breath Wheezing following exerciseWheezing following exercise
Other signs and symptoms include:Other signs and symptoms include: CoughCough HeadacheHeadache Stomach crampsStomach cramps Pain or tightness in the chestPain or tightness in the chest NauseaNausea

1313
These signs and symptoms typically start These signs and symptoms typically start 6 to 8 minutes after the onset of 6 to 8 minutes after the onset of strenuous exercise but may not reach strenuous exercise but may not reach maximum severity until up to 15 minutes maximum severity until up to 15 minutes after the cessation of exercise. after the cessation of exercise.
Typically, spontaneous return to baseline Typically, spontaneous return to baseline respiratory function occurs within a 20- to respiratory function occurs within a 20- to 60-minute period following onset of 60-minute period following onset of symptoms. symptoms.

1414
Asthma Treatment Asthma Treatment OptionsOptions
Certified athletic trainers often interact with Certified athletic trainers often interact with athletes who use an inhaler, or more formally athletes who use an inhaler, or more formally known as metered dose inhalers (MDIs). known as metered dose inhalers (MDIs).
Most true asthma exacerbations have both Most true asthma exacerbations have both an inflammatory and bronchoconstriction an inflammatory and bronchoconstriction component.component. The use of medications to control and treat The use of medications to control and treat
asthma may address one or both of these asthma may address one or both of these problems. problems.

1515
Currently, the most widely accepted Currently, the most widely accepted approach to asthma treatment is to initially approach to asthma treatment is to initially control the inflammatory process control the inflammatory process associated with the trigger and thus prevent associated with the trigger and thus prevent bronchoconstriction onset. bronchoconstriction onset.
This approach is reflected in the switch This approach is reflected in the switch from heavy dependence on “rescue” from heavy dependence on “rescue” inhalers to the increased use of controlling inhalers to the increased use of controlling agents. agents.

1616
With respect to exercise-induced asthma, With respect to exercise-induced asthma, the athlete typically experiences little or the athlete typically experiences little or no active inflammatory process and the no active inflammatory process and the primary complication is the primary complication is the bronchoconstriction associated with the bronchoconstriction associated with the exercise trigger. exercise trigger.
The treatment for asthma and EIA are The treatment for asthma and EIA are different. different.

1717
Asthma exacerbations are categorized based Asthma exacerbations are categorized based on the severity and the frequency of the on the severity and the frequency of the symptoms. symptoms.
In general, asthma is broken down into four In general, asthma is broken down into four categories: (Table 7-1, pg 95)categories: (Table 7-1, pg 95) mild intermittentmild intermittent mild persistentmild persistent moderate persistentmoderate persistent severe persistentsevere persistent

1818
Commonly Used Drugs Commonly Used Drugs for Asthma Controlfor Asthma Control
Numerous pharmacological approaches are Numerous pharmacological approaches are used to treat asthma. used to treat asthma.
Some factors that influence the choice of Some factors that influence the choice of approach are severity and frequency of the approach are severity and frequency of the exacerbations, as well as the convenience of exacerbations, as well as the convenience of using the drug. using the drug.
The drugs used to treat asthma can be The drugs used to treat asthma can be classified into two groups: classified into two groups: bronchodilators and anti-inflammatory agents bronchodilators and anti-inflammatory agents
(steroids and non-steroids).(steroids and non-steroids).

1919
It is generally accepted that anyone with It is generally accepted that anyone with persistent asthma should utilize a persistent asthma should utilize a controlling agent for the inflammatory controlling agent for the inflammatory component in conjunction with a “rescue” component in conjunction with a “rescue” inhaler for the bronchoconstriction.inhaler for the bronchoconstriction.
The role of corticosteroids in asthma, and The role of corticosteroids in asthma, and respiratory care in general, is to combat respiratory care in general, is to combat inflammation of the airways associated inflammation of the airways associated with certain respiratory conditions. with certain respiratory conditions.

2020
Corticosteroids indirectly prevent Corticosteroids indirectly prevent inflammation-mediated inflammation-mediated bronchoconstriction through the inhibition bronchoconstriction through the inhibition of prostaglandins and leukotrienes.of prostaglandins and leukotrienes.
In addition, corticosteroids reverse In addition, corticosteroids reverse vascular permeability associated with the vascular permeability associated with the inflammation process.inflammation process.

2121
Oral nonsteroidal asthma medications are an Oral nonsteroidal asthma medications are an attractive alternative to the use of inhaled attractive alternative to the use of inhaled steroids in the control of asthma.steroids in the control of asthma.
In addition, there is no fluctuation in delivery In addition, there is no fluctuation in delivery of the medication due to improper use of the of the medication due to improper use of the MDI.MDI.
It is important to note that all individuals who It is important to note that all individuals who use either steroids or nonsteroidals still need use either steroids or nonsteroidals still need access to a “rescue” inhaler in the event of access to a “rescue” inhaler in the event of an asthma exacerbationan asthma exacerbation

2222
Rescue InhalersRescue Inhalers Table 7-2, pg 96Table 7-2, pg 96
Exercise-induced AsthmaExercise-induced Asthma Causes: Causes:
water loss water loss heat exchange cooling the airwaysheat exchange cooling the airways Increased sodium intakeIncreased sodium intake
Must have formal diagnosisMust have formal diagnosis

2323
Adverse Effects of Adverse Effects of Asthma MedicationsAsthma Medications
MDIs have less serious adverse effectsMDIs have less serious adverse effects Localized delivery of the medication Localized delivery of the medication
The adverse effects of beta-2 agonists are The adverse effects of beta-2 agonists are relatively minor.relatively minor. Common adverse effects include Common adverse effects include
nervousness, restlessness, trembling, throat nervousness, restlessness, trembling, throat irritation, and potential airway hypersensitivity. irritation, and potential airway hypersensitivity.

2424
Inhaled steroids, have localized side Inhaled steroids, have localized side effects, such as throat irritation and effects, such as throat irritation and hoarseness. hoarseness.
The inhaled steroid residue present in the The inhaled steroid residue present in the mouth alters the bacterial environment, mouth alters the bacterial environment, thus allowing for opportunistic yeast thus allowing for opportunistic yeast infections in the mouth.infections in the mouth.
To limit this problem, users are To limit this problem, users are encouraged to rinse their mouth and brush encouraged to rinse their mouth and brush their teeth after each use of an inhaler.their teeth after each use of an inhaler.

2525
Oral steroids short-term and long-term Oral steroids short-term and long-term adverse effects. adverse effects. Short term Short term –– increased appetite, acne, poor increased appetite, acne, poor
wound healing, fluid retention, and insomnia wound healing, fluid retention, and insomnia Long-term Long-term –– avascular necrosis, osteoporosis, avascular necrosis, osteoporosis,
glaucoma, and decreased muscle massglaucoma, and decreased muscle mass

2626
Adverse effects of inhaled nonsteroidal Adverse effects of inhaled nonsteroidal asthma medicationsasthma medications Bitter taste in mouthBitter taste in mouth Throat irritationThroat irritation Dry mouthDry mouth HeadacheHeadache Skin rashSkin rash

2727
AllergiesAllergies
Are the result of some adverse Are the result of some adverse environmental stimulusenvironmental stimulus
Two classes of drugs are used for the Two classes of drugs are used for the treatment of allergies:treatment of allergies: Antihistamines Antihistamines Corticosteroids (nasal sprays). Corticosteroids (nasal sprays).

2828
HistaminesHistamines
Histamine causes blood vessel dilation Histamine causes blood vessel dilation and subsequently an inflammatory and subsequently an inflammatory response in the area affected.response in the area affected. Results in an inflammatory response noted by Results in an inflammatory response noted by
the classic allergy symptoms, such as runny the classic allergy symptoms, such as runny nose, itchy and watery eyes, and sneezing.nose, itchy and watery eyes, and sneezing.

2929
AntihistaminesAntihistamines
Antihistamines produce three general Antihistamines produce three general effects on the body:effects on the body: Alteration of histamine actionAlteration of histamine action SedationSedation Anticholinergic activity (decreased salivation, Anticholinergic activity (decreased salivation,
dry mouth, and constipation)dry mouth, and constipation)

3030
Currently there are first- and second-Currently there are first- and second-generation antihistaminesgeneration antihistamines
The major differences between the two The major differences between the two generations are:generations are: The time they are activeThe time they are active
1st generation = 4 to 6 hrs1st generation = 4 to 6 hrs 2nd generation = up to 12 hrs2nd generation = up to 12 hrs
The extent to which they promote drowsinessThe extent to which they promote drowsiness 2nd generation are less sedating2nd generation are less sedating

3131
Antihistamine drugsAntihistamine drugs
Halt increased vascular permeabilityHalt increased vascular permeability Decrease smooth muscle constriction of the Decrease smooth muscle constriction of the
airwaysairways First-generation antihistamines cross the blood First-generation antihistamines cross the blood
brain barrier and cause sedationbrain barrier and cause sedation Use a first-generation antihistamine during the Use a first-generation antihistamine during the
evening (less expensive) and nighttimeevening (less expensive) and nighttime Switch to a second-generation antihistamine Switch to a second-generation antihistamine
during the daytimeduring the daytime

3232
Antihistamines result in decreased Antihistamines result in decreased symptoms and increased patient comfort. symptoms and increased patient comfort. Their use is sometimes questioned. Their use is sometimes questioned.
Impeding these effects is not always a Impeding these effects is not always a good thing. good thing. The body produces mucus in an effort to The body produces mucus in an effort to
protect the respiratory system. protect the respiratory system. Decreasing these functions may slow Decreasing these functions may slow
recovery.recovery.

3333
Antihistamines may not be effective in Antihistamines may not be effective in decreasing nasal blockage.decreasing nasal blockage.
Second-generation antihistamines are Second-generation antihistamines are available with a decongestant. available with a decongestant. Claritin-D and Allegra-D Claritin-D and Allegra-D
A decongestant will assist with the A decongestant will assist with the resolution of the runny nose and head resolution of the runny nose and head congestion.congestion.

3434
Adverse effects of antihistaminesAdverse effects of antihistamines Mucous membrane drynessMucous membrane dryness Cardiac stimulationCardiac stimulation Blurred visionBlurred vision Urinary retentionUrinary retention

3535
Steroid Nasal SpraySteroid Nasal Spray
Nasal steroid medications are specifically Nasal steroid medications are specifically used for allergic rhinitis. used for allergic rhinitis. They are not for symptoms of the common They are not for symptoms of the common
cold. cold.
Drugs are delivered locally.Drugs are delivered locally. Potential for nasal irritation, dryness, and Potential for nasal irritation, dryness, and
epistaxisepistaxis

3636
Coughs and Colds Coughs and Colds
Runny nose, mild sore throat, and watery Runny nose, mild sore throat, and watery eyes are similar in both the common cold eyes are similar in both the common cold and allergic reactions. and allergic reactions.
Common cold refers to a nonbacterial Common cold refers to a nonbacterial infection of the upper respiratory system. infection of the upper respiratory system.

3737
Cough and Cold Cough and Cold MedicationsMedications
DecongestantsDecongestants vasoconstriction resulting in mucosal drying vasoconstriction resulting in mucosal drying
AntihistaminesAntihistamines combat increased histamine = nasal congestion combat increased histamine = nasal congestion
and mucosal irritationand mucosal irritation ExpectorantsExpectorants
facilitate the removal of mucous from the facilitate the removal of mucous from the respiratory systemrespiratory system
AntitussivesAntitussives work to suppress coughingwork to suppress coughing

3838
Medications may contain a combination Medications may contain a combination of decongestant, antihistamine, of decongestant, antihistamine, expectorant, and antitussive agentsexpectorant, and antitussive agents Vicks NyQuil contains:Vicks NyQuil contains:
Acetaminophen Acetaminophen Pseudoephedrine, a decongestant, Pseudoephedrine, a decongestant, Dextromethorphan, a cough suppressant Dextromethorphan, a cough suppressant AntihistamineAntihistamine

3939
Decongestants Decongestants Prolonged use of decongestants:Prolonged use of decongestants:
Headache Headache Nausea Nausea Dry mouth and nose Dry mouth and nose DizzinessDizziness Nervousness Nervousness
Prolonged application of nasal spray (topical) Prolonged application of nasal spray (topical) Can cause a rebound effect vasodilatation after Can cause a rebound effect vasodilatation after
the initial vasoconstriction decreasesthe initial vasoconstriction decreases

4040
Common decongestants Common decongestants Pseudoephedrine (Sudafed) Pseudoephedrine (Sudafed) Tetrahydroziline (Visine) Tetrahydroziline (Visine) Oxymetazoline (Afrin)Oxymetazoline (Afrin)

4141
Expectorants Expectorants
Cough syrup to relieve the coughing Cough syrup to relieve the coughing linked to cold symptomslinked to cold symptoms
Cough syrups can contain Cough syrups can contain Antitussive (cough suppressant) Antitussive (cough suppressant) Expectorant (promotes mucus clearance)Expectorant (promotes mucus clearance)
If the coughing linked with a cold is If the coughing linked with a cold is “nonproductive,” eliminate the “nonproductive,” eliminate the nonproductive coughingnonproductive coughing

4242
Mucus removal produced by the body Mucus removal produced by the body during the common cold needs to be thin during the common cold needs to be thin and mobile for the coughing to be and mobile for the coughing to be productive. productive.
Expectorants are available in two forms: Expectorants are available in two forms: Mucolytic Mucolytic Stimulant Stimulant

4343
Antitussives Antitussives
Antitussives suppress the cough.Antitussives suppress the cough. Use a central or a local mechanism.Use a central or a local mechanism.
Used for short periods of time.Used for short periods of time. Used to inhibit a cough via a central Used to inhibit a cough via a central
mechanism. mechanism. Cough center located in the medulla is Cough center located in the medulla is
targeted. targeted.

4444
Dextromethorphan (DM) is the most common Dextromethorphan (DM) is the most common ingredient in OTC suppressing agents.ingredient in OTC suppressing agents. Robitussin products, Tylenol cold products, and Robitussin products, Tylenol cold products, and
NyQuil medications.NyQuil medications. Physician can prescribe a narcotic Physician can prescribe a narcotic
antitussive. antitussive. Codeine or hydrocodone.Codeine or hydrocodone. Addictive property of narcotics. Addictive property of narcotics. Duration of the prescription does not exceed 1 Duration of the prescription does not exceed 1
week.week.

4545
Adverse EffectsAdverse Effects
OTC cold and allergy medications OTC cold and allergy medications relatively show few serious adverse relatively show few serious adverse effects. effects.
Participating in a sport while in a state of Participating in a sport while in a state of drowsiness could be dangerous.drowsiness could be dangerous.
Antihistamines (1st generation) can result Antihistamines (1st generation) can result in significant drowsiness even after the in significant drowsiness even after the drug’s half-life is complete. drug’s half-life is complete.

4646
Antihistamines may cause anticholinergic Antihistamines may cause anticholinergic effects such as effects such as Mucus membrane drynessMucus membrane dryness Cardiac stimulationCardiac stimulation Decreased gastrointestinal activity Decreased gastrointestinal activity Urinary retentionUrinary retention
Decongestants can promote Decongestants can promote Excessive drying of the nose and throatExcessive drying of the nose and throat Tachycardia and restlessnessTachycardia and restlessness

4747
Guaifenesin (cough syrups)Guaifenesin (cough syrups) DizzinessDizziness HeadacheHeadache NauseaNausea
Antitussives (Dextromethorphan)Antitussives (Dextromethorphan) Mild dizzinessMild dizziness DrowsinessDrowsiness NauseaNausea Stomach crampsStomach cramps