Nucleic acids are polymers of monomers called nucleotides 2 types of nucleic acid – DNA & RNA ...
-
Upload
lenard-cook -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
2
Transcript of Nucleic acids are polymers of monomers called nucleotides 2 types of nucleic acid – DNA & RNA ...


Nucleic acids are polymers of monomers called Nucleic acids are polymers of monomers called nucleotidesnucleotides
2 types of nucleic acid – DNA & RNA2 types of nucleic acid – DNA & RNA Each nucleotides composed of 3 parts :Each nucleotides composed of 3 parts :
- A - A nitrogenous basenitrogenous base pyrimidines pyrimidines purinespurines
- A - A pentosepentose (5-C sugar) (5-C sugar)- - Phosphate groupPhosphate group
Nucleic acidsNucleic acids

Nitrogenous baseNitrogenous base

A, G, C found as both RNA and DNAA, G, C found as both RNA and DNA U is found as RNAU is found as RNA T is found as DNAT is found as DNA

PENTOSE SUGARPENTOSE SUGAR
In ribonucleotides, the In ribonucleotides, the pentose is ribosepentose is ribose
In deoxyribonucleotide (or In deoxyribonucleotide (or deoxynucleotides) the deoxynucleotides) the sugar is 2’-deoxyribose – sugar is 2’-deoxyribose – the carbon at position 2’ the carbon at position 2’ lacks a hydroxyl grouplacks a hydroxyl group


In a nucleic acid polymer/polynucleotide, In a nucleic acid polymer/polynucleotide, nucleotides are joined by covalent bonds = nucleotides are joined by covalent bonds = phosphodiester linkagephosphodiester linkage (between (between phosphate of one nucleotides and the phosphate of one nucleotides and the sugar of the next)sugar of the next)

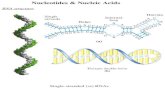
Nucleic acid structureNucleic acid structure Nucleotides can be joined to each other to form RNA and Nucleotides can be joined to each other to form RNA and
DNA. DNA.
The nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides whose The nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides whose phosphates bridge the 3' and 5' positions of neighboring phosphates bridge the 3' and 5' positions of neighboring ribose units ribose units
The phosphates of these The phosphates of these polynucleotides polynucleotides are acidic, so are acidic, so at physiological pH, nucleic acids are polyanions. at physiological pH, nucleic acids are polyanions.
The linkage between individual nucleotides is known as a The linkage between individual nucleotides is known as a phosphodiester bondphosphodiester bond. .

Each nucleotide that has been incorporated into Each nucleotide that has been incorporated into the polynucleotide is known as a the polynucleotide is known as a nucleotide nucleotide residue. residue.
The terminal residue whose C5' is not linked to The terminal residue whose C5' is not linked to another nucleotide is called the another nucleotide is called the 5' end5' end
The terminal residue whose C3' is not linked to The terminal residue whose C3' is not linked to another nucleotide is called the 3' another nucleotide is called the 3' end. end.
By convention, the sequence of nucleotide By convention, the sequence of nucleotide residues in a nucleic acid is written, left to right, residues in a nucleic acid is written, left to right, from the 5' end to the 3' end.from the 5' end to the 3' end.

Nucleic acid structureNucleic acid structure

DefinitionsDefinitions
DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. It is DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. It is the genetic code molecule for most the genetic code molecule for most organisms.organisms.
RNA stands for ribonucleic acid. RNA RNA stands for ribonucleic acid. RNA molecules are involved in converting the molecules are involved in converting the genetic information in DNA into proteins. genetic information in DNA into proteins. In retroviruses, RNA is the genetic In retroviruses, RNA is the genetic material.material.

DNA structure : Watson and CrickDNA structure : Watson and Crick Watson and Crick 1953 1Watson and Crick 1953 1stst
proposed the proposed the double helixdouble helix as 3-D as 3-D structure of DNAstructure of DNA
Two polynucleotide chains wind Two polynucleotide chains wind around a common axis to form a around a common axis to form a double helixdouble helix. .
The two strands of DNA are The two strands of DNA are antiparallelantiparallel, but each forms a , but each forms a right-handed helix. right-handed helix.
The bases occupy the core of the The bases occupy the core of the helix and sugar-phosphate chains helix and sugar-phosphate chains run along the periphery, thereby run along the periphery, thereby minimizing the repulsions between minimizing the repulsions between charged phosphate groups.charged phosphate groups.

DNA consist of 2 polynucleotide strands DNA consist of 2 polynucleotide strands wound around each other to form a right-wound around each other to form a right-handed double helixhanded double helix

Nucleotides are linked each other by Nucleotides are linked each other by 3’-5’ 3’-5’ phosphodiester bondsphosphodiester bonds (join 5’-hydroxyl group of (join 5’-hydroxyl group of deoxyribose sugar of one nucleotide to the 3’-deoxyribose sugar of one nucleotide to the 3’-hydroxyl group of deoxyribose of another hydroxyl group of deoxyribose of another nucleotide)nucleotide)
Hydrogen bond formHydrogen bond form between the nitrogenous between the nitrogenous base of 2 antiparallel polynucleotide strandsbase of 2 antiparallel polynucleotide strands
TWOTWO types of base pairs in DNA : types of base pairs in DNA :
1) 1) adenineadenine (purine) pairs with (purine) pairs with thyaminethyamine (pyrimidine)(pyrimidine)
2) 2) GuanineGuanine (purine) pairs with (purine) pairs with cytosinecytosine (pyrimidine)(pyrimidine)

If 1 strand has the base sequence If 1 strand has the base sequence AGGTCCG, so the other strand must have AGGTCCG, so the other strand must have sequence TCCAGGCsequence TCCAGGC
These hydrogen bonding interactions, a These hydrogen bonding interactions, a phenomenon known as phenomenon known as complementary complementary base pairingbase pairing, , result in the specific result in the specific association of the two chains of the double association of the two chains of the double helix.helix.


Dimension of DNA :Dimension of DNA :
1) one turn of double helix span 3.4nm 1) one turn of double helix span 3.4nm consist 10.4 base pairs.consist 10.4 base pairs.
2) diameter of double helix is 2.4nm2) diameter of double helix is 2.4nm
3) distance between adjacent base pairs is 3) distance between adjacent base pairs is 0.34nm. 0.34nm.

Noncovalent bondingNoncovalent bonding in DNA structure : in DNA structure :
1) Hydrophobic interactions1) Hydrophobic interactions. Electron between . Electron between stacked purine & pyrimidine bases is nonpolar. stacked purine & pyrimidine bases is nonpolar. the clustering of bases component of nucleotide the clustering of bases component of nucleotide within double helix stabilize structure, because it within double helix stabilize structure, because it minimize their interaction with water.minimize their interaction with water.
2) Hydrogen bond2) Hydrogen bond. Base pairs, on close . Base pairs, on close approach form hydrogen bond, approach form hydrogen bond, threethree between between GC pairs and GC pairs and two two between AT.between AT.

3) Base stacking3) Base stacking. Stacking interactions are a form . Stacking interactions are a form of van der waals interaction. Interaction between of van der waals interaction. Interaction between stacked G and C bases are greater than those stacked G and C bases are greater than those between stacked A and T bases, which largely between stacked A and T bases, which largely accounts for the greater thermal stability of accounts for the greater thermal stability of DNAs with a high G+C contentDNAs with a high G+C content
4) Electrostatic interaction4) Electrostatic interaction. DNA external surface, . DNA external surface, sugar-phosphate backbone possesses –ve sugar-phosphate backbone possesses –ve charged phosphate group. charged phosphate group.

The DNA helixThe DNA helixThe geometry of DNAThe geometry of DNA
The biologically most common form of DNA is known as The biologically most common form of DNA is known as B-DNA, - structural features first noted by Watson and B-DNA, - structural features first noted by Watson and Crick together with Rosalind Franklin and other. Crick together with Rosalind Franklin and other.
DNA is flexible molecule. It can assume several distinct DNA is flexible molecule. It can assume several distinct structural depending on the structural depending on the solvent compositionsolvent composition and and base base sequencesequence. The major structural variants of DNA are . The major structural variants of DNA are A-A-DNADNA and and Z-DNAZ-DNA. .
Under dehydrating conditions, B-DNA undergoes a Under dehydrating conditions, B-DNA undergoes a reversible conformational change to A-DNA which forms a reversible conformational change to A-DNA which forms a wider and flatter right-handed helix than does B-DNA. wider and flatter right-handed helix than does B-DNA.


A-DNAA-DNA
When DNA become partially dehydrated, it When DNA become partially dehydrated, it assumes the assumes the A formA form..
The base pairs no longer at right angleThe base pairs no longer at right angle They tilt 20° away from the horizontalThey tilt 20° away from the horizontal Distance between adjacent base pairs slightly Distance between adjacent base pairs slightly
reduced (11bp helical turn instead or 10.4bp reduced (11bp helical turn instead or 10.4bp found in B form)found in B form)
Each turn of double helix occur in 2.5nm, instead Each turn of double helix occur in 2.5nm, instead of 3.4nmof 3.4nm
Diameter swell to 2.6nmDiameter swell to 2.6nm

Z-DNAZ-DNA
Named for it zigzag conformationNamed for it zigzag conformation Diameter = 1.8nm, slimmer than B-DNADiameter = 1.8nm, slimmer than B-DNA Twisted into left-handed spiral with 12bp Twisted into left-handed spiral with 12bp
per turnper turn Each turn occur in 4.5nmEach turn occur in 4.5nm

RNARNA Ribonucleic acid is a class of polynucleotidesRibonucleic acid is a class of polynucleotides In In contrast, RNA occurs primarily as contrast, RNA occurs primarily as single single
strandsstrands, which usually form compact structures , which usually form compact structures rather than loose extended chains rather than loose extended chains
Nearly all involve in some aspect of protein Nearly all involve in some aspect of protein synthesissynthesis
RNA molecules are synthesized in a process RNA molecules are synthesized in a process called called TRANSCRIPTIONTRANSCRIPTION
New RNA mol. are produced by mechanism New RNA mol. are produced by mechanism similar to DNA, through complementary base similar to DNA, through complementary base pair formationpair formation

New RNA mol. Are produced by mechanism New RNA mol. Are produced by mechanism similar to DNA, through complementary base similar to DNA, through complementary base pair formation (A=U G=C)pair formation (A=U G=C)
Eg. DNA sequence 5’-CCGATTACG-3’ is Eg. DNA sequence 5’-CCGATTACG-3’ is transcribe into RNA sequence transcribe into RNA sequence
3’-GGCUAAUGC-5’3’-GGCUAAUGC-5’

Differences between DNA & RNADifferences between DNA & RNA
RNARNA DNADNA
Sugar moiety is Sugar moiety is riboseribose Sugar moiety is Sugar moiety is deoxyribosedeoxyribose
Nitrogenous base Nitrogenous base Adenine, Adenine, Urasil, Urasil, Guanine, CytosineGuanine, Cytosine
Nitrogenous baseNitrogenous base
Adenine, Adenine, Thyamine,Thyamine,
Guanine, CytosineGuanine, Cytosine
Exist in Exist in single strandsingle strand Exist in Exist in double helixdouble helix
Content of A and U, as Content of A and U, as well as G and C are well as G and C are equalequal
Content of A and T, as Content of A and T, as well as G and C are well as G and C are equalequal

Secondary structure of RNASecondary structure of RNA RNA exist as single strand.RNA exist as single strand. RNA can coil back on itself and form a unique RNA can coil back on itself and form a unique
secondary structuresecondary structure The shape of these structures determined by The shape of these structures determined by
complementary base pairing by specific RNA complementary base pairing by specific RNA sequence, as well as base stackingsequence, as well as base stacking

Types or RNATypes or RNA Types of RNA = transfer RNA, ribosomal Types of RNA = transfer RNA, ribosomal
RNA, messenger RNARNA, messenger RNA
Transfer RNATransfer RNA tRNA transport amino acids to ribosomes tRNA transport amino acids to ribosomes
for assembly into protein for assembly into protein Average length of tRNA = 75 nucleotidesAverage length of tRNA = 75 nucleotides


Ribosomal RNARibosomal RNA rRNA is the most abundant RNA in living cellsrRNA is the most abundant RNA in living cells rRNA is the component of ribosomesrRNA is the component of ribosomes Ribosomes = cytoplasmic structures that Ribosomes = cytoplasmic structures that
synthesized proteinssynthesized proteins
Messenger RNAMessenger RNA mRNA is the carrier of genetic information from mRNA is the carrier of genetic information from
DNA for the synthesis of proteinDNA for the synthesis of protein mRNA is transcribed from a DNA template, and mRNA is transcribed from a DNA template, and
carries coding information to the sites of protein carries coding information to the sites of protein synthesis: the ribosomessynthesis: the ribosomes


Denaturation and renaturation of Denaturation and renaturation of DNADNA
Unique properties of nucleic acids- under certain Unique properties of nucleic acids- under certain conditions DNA duplexes reversibly melt (separate) and conditions DNA duplexes reversibly melt (separate) and reanneal (base pair to form duplex again)reanneal (base pair to form duplex again)
Binding forces that hold the DNA double helix can be Binding forces that hold the DNA double helix can be disrupteddisrupted
This process = denaturation, promoted by :This process = denaturation, promoted by :
- heat (most common denaturing method)- heat (most common denaturing method)- low salt concentrations- low salt concentrations- extremes in pH- extremes in pH

- Renaturation DNA can be prepared by maintain the temp. - Renaturation DNA can be prepared by maintain the temp. below denaturing temp.below denaturing temp.- requires some time because the strands - requires some time because the strands explore various configurations until they achieve the most explore various configurations until they achieve the most stable onestable one

Nucleic acid methodsNucleic acid methods
Most of technique used in nucleic acid research Most of technique used in nucleic acid research are based on differences in molecular weight or are based on differences in molecular weight or shape, base sequences, or complementary base shape, base sequences, or complementary base pairingpairing
Some of the most useful nucleic acid fractionation Some of the most useful nucleic acid fractionation procedure are:procedure are:
ChromatographyChromatography ElectrophoresisElectrophoresis UltracentrifugationUltracentrifugation

Ruptured bacterial cells or isolate eukaryotic nucleusRuptured bacterial cells or isolate eukaryotic nucleus
- to expose the nucleic acid- to expose the nucleic acid
- done by grinding or sonicating the sample- done by grinding or sonicating the sample Removing membrane lipids by adding a detergent or Removing membrane lipids by adding a detergent or
enzyme lysozymeenzyme lysozyme Removing proteins by adding a proteaseRemoving proteins by adding a protease Precipitating the DNA with an alcohol Precipitating the DNA with an alcohol
- usually ice-cold ethanol or isopropanol. Since DNA is - usually ice-cold ethanol or isopropanol. Since DNA is insoluble in these alcohols, it will aggregate together, insoluble in these alcohols, it will aggregate together, giving a giving a pelletpellet upon centrifugation. This step also upon centrifugation. This step also removes alcohol-soluble salt removes alcohol-soluble salt
Nucleic acid extraction protocol

Chromatography Chromatography Many of the chromatographic techniques that are Many of the chromatographic techniques that are
used to separate proteins also apply to nucleic used to separate proteins also apply to nucleic acidsacids
ObjectivesObjectives : purify nucleic acid of interest or : purify nucleic acid of interest or isolation of individual nucleic acid sequencesisolation of individual nucleic acid sequences
A type of column chromatography that uses a A type of column chromatography that uses a calcium phosphate gel calledcalcium phosphate gel called hydroxyapatite hydroxyapatite been been used in nucleic acid researchused in nucleic acid research
Hydroxyapatite bind tightly to double-stranded Hydroxyapatite bind tightly to double-stranded nucleic acid than single-stranded nucleic acid nucleic acid than single-stranded nucleic acid moleculesmolecules
So dsDNA can be effectively separate from So dsDNA can be effectively separate from ssDNA, RNA or other protein contaminants by this ssDNA, RNA or other protein contaminants by this methodmethod

dsDNA can be rapidly isolated by passing a cell dsDNA can be rapidly isolated by passing a cell lysate through a hydroxyapatite columnlysate through a hydroxyapatite column
wash the column with a low concentration of wash the column with a low concentration of phosphate buffer to release only the ssDNA, RNA phosphate buffer to release only the ssDNA, RNA and proteinand protein
Elute the column with a concentrated phosphate Elute the column with a concentrated phosphate buffer tp collect dsDNAbuffer tp collect dsDNA
hydroxyapatiteRNA + protein dsDNA

Affinity chromatography is used to isolate Affinity chromatography is used to isolate specific nucleic acids. specific nucleic acids.
For example, most eukaryotic messenger RNAs For example, most eukaryotic messenger RNAs (mRNAs) have a poly (A) sequences or cellulose (mRNAs) have a poly (A) sequences or cellulose to which poly (U) is covalently attached. The to which poly (U) is covalently attached. The poly(A) sequences specifically bind to the poly(A) sequences specifically bind to the complementary poly(U) in high salt and low complementary poly(U) in high salt and low temperature and can later be released by temperature and can later be released by altering these condition.altering these condition.

ElectrophoresisElectrophoresis
Gel electrophoresis separate nucleic acids on Gel electrophoresis separate nucleic acids on the basis of molecular weight and 3-D structure the basis of molecular weight and 3-D structure in an electric fieldin an electric field
The technique involves drawing DNA molecules, The technique involves drawing DNA molecules, which have an overall negative charge, through which have an overall negative charge, through a semisolid gel by an electric current toward the a semisolid gel by an electric current toward the positive electrode within an electrophoresis positive electrode within an electrophoresis chamber.chamber.
The used gel is typically composed of a purified The used gel is typically composed of a purified sugar component of agar called agarose. sugar component of agar called agarose.

Electrophoresis Electrophoresis Nucleuic acids mixture Nucleuic acids mixture
placed in wellplaced in well Nucleic acids are -ve Nucleic acids are -ve
charge (phosphate group)charge (phosphate group) Nucleic acid migrate to Nucleic acid migrate to
anodeanode Rate of migration are Rate of migration are
proportional to molecular proportional to molecular sizesize

In genetic engineering, scientists use the In genetic engineering, scientists use the technique to isolate fragments of DNA technique to isolate fragments of DNA molecules that can then be inserted into molecules that can then be inserted into vectors, multiplied by PCR, or preserved in vectors, multiplied by PCR, or preserved in a gene library. a gene library.

Southern blottingSouthern blotting
Enable researcher to detect and analyze Enable researcher to detect and analyze particular DNA sequenceparticular DNA sequence
The basis of detecting specific sequence : The basis of detecting specific sequence : nucleic acids hybridization nucleic acids hybridization
Hybridization can be used to locate and/ or Hybridization can be used to locate and/ or identify specific genes or other sequenceidentify specific genes or other sequence
Eg. ssDNA from two diff sources (tumor Eg. ssDNA from two diff sources (tumor cell and normal cell) can be screened for cell and normal cell) can be screened for sequence differencessequence differences

Southern blott technique Southern blott technique
1) restriction fragment preparation1) restriction fragment preparation DNA samples to be tested are treated with DNA samples to be tested are treated with
restriction enzymes that cut at specific nucleotides restriction enzymes that cut at specific nucleotides sequences to produce a restriction fragmentssequences to produce a restriction fragments
2) electrophoresis2) electrophoresis The mixture of restriction fragments from each The mixture of restriction fragments from each
sample are separated by electrophoresis according sample are separated by electrophoresis according to their sizeto their size
Each sample forms a characteristic patterns of bandEach sample forms a characteristic patterns of band The gel soaked with 0.5M NaOH to convert dsDNA The gel soaked with 0.5M NaOH to convert dsDNA
to ssDNAto ssDNA

Southern blot
technique

3) Blotting3) Blotting The DNA fragments are transferred to The DNA fragments are transferred to
nitrocellulose filter paper by placing them on a wet nitrocellulose filter paper by placing them on a wet sponge in a tray with a high salt buffer sponge in a tray with a high salt buffer (nitrocellulose bind strongly to ssDNA)(nitrocellulose bind strongly to ssDNA)
As buffer is drawn through the gel and filter paper As buffer is drawn through the gel and filter paper by capillary action, the DNA is transferred and by capillary action, the DNA is transferred and become permanently bound to nitrocellulose filterbecome permanently bound to nitrocellulose filter
4) hybridization with radioactive probe4) hybridization with radioactive probe Nitrocellulose filter is exposed to radioactively Nitrocellulose filter is exposed to radioactively
labeled probe, which bind to ssDNA with a labeled probe, which bind to ssDNA with a complementary sequencecomplementary sequence

4) hybridization with radioactive probe4) hybridization with radioactive probe Nitrocellulose filter is exposed to a solution Nitrocellulose filter is exposed to a solution
containing radioactively labeled probe.containing radioactively labeled probe. The probe is ssDNA complementary to The probe is ssDNA complementary to
DNA sequence of interest, and it attaches DNA sequence of interest, and it attaches by base pairing to restriction fragment of by base pairing to restriction fragment of complementary sequencecomplementary sequence

5) Autoradiography5) Autoradiography Rinse away unattached probeRinse away unattached probe Autoradiograph showing hybrid DNA Autoradiograph showing hybrid DNA
fragmentfragment


UltracentrifugationUltracentrifugation
Equilibrium density gradient ultracentrifugation in Equilibrium density gradient ultracentrifugation in CsCl is one of the most commonly used DNA CsCl is one of the most commonly used DNA separation procedures. separation procedures.
At high speeds, a linear gradient of CsCl is At high speeds, a linear gradient of CsCl is established.established.

Mixture of DNA, RNA and protein migrating Mixture of DNA, RNA and protein migrating through this gradient separate into discrete through this gradient separate into discrete bands at position where their densities are bands at position where their densities are equal to density of CsCl.equal to density of CsCl.
DNA mol. with high Guanine and Cytosine DNA mol. with high Guanine and Cytosine content are content are more densemore dense than those with a than those with a higher proportion of adenine and thyamine.higher proportion of adenine and thyamine.
The difference helps separate heterogenous The difference helps separate heterogenous mixtures of DNA fragmentsmixtures of DNA fragments
Single stranded DNA denser than the double Single stranded DNA denser than the double stranded DNA, so the two can be separated by stranded DNA, so the two can be separated by equilibrium density gradient ultracentrifugation. equilibrium density gradient ultracentrifugation.