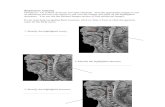
Wrist and Hand Anatomy. Bone Anatomy Scapoid Lunate Triquetrium Pisiform Trapeziod Trapezium...
-
Upload
ami-peters -
Category
Documents
-
view
220 -
download
2
Transcript of Wrist and Hand Anatomy. Bone Anatomy Scapoid Lunate Triquetrium Pisiform Trapeziod Trapezium...
Hand and Wrist Anatomy
• 14 phalanges– 2 sesamoid bones (thumb)
• 5 metacarpals• 8 carpal bones• Distal Radius– Forms small ulnar notch to accept the ulnar head– Radial styloid process
• Distal Ulna– Ulnar styloid process arises from medial surface– Ulnar head
Articulations
• Distal Radioulnar– Formed by ulnar head and ulnar notch– Allows 1 degree freedom of movement• Pronation/supination
– Radius glides around the ulna
• Radiocarpal joint– Reinforced by ligamentous thickening– Formed by distal radius articulating with scaphoid,
lunate and triangular fibrocartilage disk(TFCC)– Ellipsoid joint (2 degrees freedom)• Flexion/extension• Radial/ulnar deviation
• Midcarpal Joints– Proximal/distal carpal row separated by a single
joint cavity with small fibrous projections connecting the rows
– Limited mobility in flex/ext, radial/ulnar deviation
• Carpometacarpal Joint (CMC)– MC1/trapezium– MC2/trapezoid– MC3/capitate– MC4and 5/hamate (forms 1 articulation)
• 1st CMC (thumb)– Saddle joint• 2 degrees of freedom(3)
– Flexion/extension– Abduction/adduction
• Accessory rotation– Allows for opposition
• 2-4 CMC– Plane/synovial joint– 1 degree freedom• Flexion/extension
• 5th CMC– 2 degree freedom• Flexion/extension• Abduction/adduction
• Metacarpophalangeal Joint (MCP)– Two degrees freedom of movement• Flexion/extension• Abduction/adduction
– Thumb can abduct at any point/fingers only when extended
– Collateral ligaments• Varus/valgus force
– When fingers are in flexion they tighten and limit abduction/adduction
Ligament Support
• Volar Carpal Ligaments– Volar Radiocarpal
Ligament• Three bands
– Volar Ulnocarpal Ligament
– Scapholunate Interosseous Ligament
– Lunotriquetral Ligament
Ligament Support
• Dorsal Carpal Ligaments– Dorsal Radiocarpal
Ligament– Dorsal Intercarpal
Ligament– Radial Collateral
Ligament– Ulnar Collateral
Ligament
Carpal Tunnel
• Fibro-osseous structure– Floor is proximal carpal bones– Roof is transverse carpal ligament
• Tunnel contains 10 structures– Median n., flexor pollicis longus tendon, 4 slips of flexor
digitorium superficialis, 4 flexor digitorium profundus
• Compression results in paresthesia 2-4 fingers and decrease grip
• Wrist flexors (median n.)– Superficial
• Flexor carpi radialis• Palmaris longus• Flexor carpi ulnaris• Flexor digitorium superficialis• Pronator teres
– Deep• Flexor digitorium profundus• Flexor pollicis longus• Pronator quadratus
• Palmar (intrinsic)– Thenar• Abductor pollicis brevis• Flexor pollicis brevis• Opponens Pollicis• Tendon FPL• Adductor pollicis
• Central– Tendons FDS/FDP
• Superficialis (PIP)• Profundus (DIP)
• Lumbricales– Radial side profundus tendon(extensor hood)
• Flex MP/ext PIP/DIP
• Palmar aponeurosis• Interossei– 4 palmar/4 dorsal
Extensor Indicis
• O– Dorsal surface lower ½ body
of ulna– Interosseus membrane
• I – Ulnar side of index finger’s
EDC tendon
• N– Radial (posterior interosseus)
• F– MCP and IP Ext of 2nd digit
Extensor Pollicis Longus
• O– Posterior 1/3 ulna– Interosseus membrane
• I– Posterior surface of base of
thumb distal phalanx
• N – Radial (posterior interosseus)
• F– CMC, MCP and IP Ext of 1st
digit
Extensor Pollicis Brevis
• O– Dorsal 2/3 of radius
• I– Dorsal surface of base of
proximal 1st phalanx
• N– Radial (posterior interosseus)
• F– CMC & MCP Ext of thumb– CMC ABD of thumb
Abductor Pollicis Longus
• O– Posterior distal 2/3 of ulna– Posterior middle 1/3 of radius– Interosseus membrane
• I– Radial side of base of 1st
metacarpal
• N– Radial (posterior interosseus)
• F– CMC ABD & Ext of thumb
Flexor Pollicis Longus
• O – Anterior middle ½ of radius– Interosseus membrane
• I – Palmar surface of base of
distal 1st phalanx
• N– Median (anterior interosseus)
• F– IP Flexion of thumb
Extensor Digiti Minimi
• O– Lateral epicondyle of
humerus• I– Extensor expansion of 5th
digit• N– Radial (posteior
interosseus)• F– MCP and IP extension of
5th digit
Flexor Digitorum Superficialis• O
– Medial epicondyle of humerus
– Coronoid process– Middle ½ anterior radius
• I– Four tendons separating into
two parts that insert into sides of bases of middle 2-5 phalanxes
• N– Median
• F– MCP flexion digits 2-5– PIP flexion digits 2-5
Flexor Digitorum Profundus
• O– Anteriomedial surface of ulna– Interosseus membrane
• I– Four tendons inserting into
distal phalanxes of digits 2-5
• N– Media 2-3 digits– Ulna 4-5 digits
• F– DIP flexion of 2-5 digits
Abductor Pollicis Brevis
• O– Scaphoid tuberosity– Trapezium ridge– Transverse carpal ligament
• I– Lateral base f proximal 1st
phalanx
• N– Median
• F– CMC & MCP ABD of thumb
Flexor Pollicis Brevis• O
– Superficial head – trapezium– Deep head – trapezoid,
capitate and palmar ligaments of distal carpal bones
• I– Base of prximal 1st phalanx on
radial side– Extensor expansion
• N– Superficial – median– Deep – Ulnar
• F– CMC & MCP Flexion of thumb
Opponens Pollicis
• O– Trapezium– Transverse Carpal
Ligament• I– Radial side of 1st
metacarpal shaft• N– Median
• F– Opposition
Abductor Digiti Minimi
• O– Pisiform
• I– Ulnar side base of 5th
proximal phalanx
• N– Ulnar
• F– MCP ABD of 5th digit
Opponen Digiti Minimi
• O– Hook of hamate– Transverse carpal ligament
• I– Ulnar border of entire 5th
metacarpal bone
• N– Ulnar
• F– MCP flexion & rotation of 5th
digit
Flexor Digiti Minimi
• O– Hamate bone– Transverse carpal
ligament• I– Ulnar side of proximal 5th
phalanx• N– Ulnar
• F– MCP Flexion of 5th digit
Adductor Pollicis• O
– Oblique Head• Capitate bone• Bases of 2-3 metacarpals
– Transverse Head• Proximal 2/3 of palmar
surface of 3rd metacarpal
• I– Ulnar side of base of 1st
proximal phalanx• N
– Ulnar• F
– CMC ADD of thumb
Palmar Interossei• O
– 1st – ulnar side base of 1st metacarpal bone
– 2nd – ulnar side of 2nd MC bone– 3rd – radial side of 4th MC bone– 4th – radia side of 5th MC bone
• I– Extensor expansion of 2,4 and
5th digits• N
– Ulnar• F
– ADD of 1st, 2nd, 4th and 5th digits toward midline of hand
Dorsal Interossei• O
– 1st lateral head – ulnar side of 1st metacarpal bone
– 1st medial head – radial side of 2nd metacarpal bone
– 2nd, 3rd, 4th space between metacarpal bones
• I– 1st – radial side 2nd proximal
phalanx– 2nd – radial side of 3rd
– 3rd – ilnar side of 3rd
– 4th – ulnar side of 4th
• N– Ulnar
• F– ABD of 2nd, 3rd, and 5th finger
from midline
Lumbricales
• O– Tendons of FDP
• I– Extensor expansion on dorsal
aspect of each digits radial side
• N– 1 and 2 – median– 3 and 4 – ulnar
• F– MCP flexion 2-5 digits– DIP & PIP ext 2-5 digits
Palmaris Brevis
• O– Flexor retinaculum
• I– Palmar surface skin on
ulnar side of hand• N– Ulnar
• F– Wrinkles skin of hand on
ulnar side
Cords Give off Branches!! (in axilla)
• Lateral Musculocutaneous
Median
• Medial Ulnar
• Posterior RadialAxillary
(thoracodorsal)(subscapular)
Innervation by Posterior Cord• Radial Nerve (largest branch)– Course: Through arm, around humerus, around lateral
epicondyle, then divides– Innervates: all posterior muscles of arm and forearm• Triceps brachii, anconeus, supinator, brachioradialis
– Divides in forearm: • Superficial = skin of arm and dorsolateral surface of hand• Deep = extensor muscles of forearm (eg E. carpi radialis L + B)
– Damage to Radial Nerve = wristdrop• Inability to extend the hand, st inability to fully extend forearm
Innervation by Posterior Cord (continued)
• Axillary Nerve (runs w/ humeral circumflex a.)– Innervates: • Deltoid and Teres minor (motor inn)• Capsule of shoulder, skin of shoulder (sensory inn)
• Subscapular Nerve {branches of C5 + C6 rami}
– Innervates: Subscapularis, Teres major
• Thoracodorsal Nerve (runs w/thoracodorsal a+v)– Innervates: Latissimus dorsi
Innervation by Lateral Cord• Musculocutaneous– Course: branches to arm, distal to elbow becomes
cutaneous for lateral forearm skin– Innervates• Biceps brachii, brachialis, coracobrachialis (motor inn)• Skin distal to elbow (sensory)
• Suprascapular (runs w/suprascapular a+v) {C5, C6}– Innervates: Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus
Innervation by both Lateral and Medial Cords
• Median– Course: middle of brachial plexus, does not branch in arm, distal
to elbow provides many branches to most forearm flexors, passes through carpal tunnel to hand to lateral palmar intrinsics
– Innervates: most muscles of anterior forearm (motor inn)• (eg) most flexors, some intrinsics (thumb)
– Innervates: skin of lateral 2/3 hand on palm side, dorsum of fingers 2+3 (sensory inn)
– Nerve Damage = “Ape” Hand• Inability to Oppose Thumb
Innervation by Medial Cord
• Ulnar– Course: runs along medial side of arm, behind medial
epicondyle, superficial to carpal tunnel into hand, branches to supply intrinsics and skin
– Innervates: • FCU and part of FDP, most intrinsics (motor inn)• Skin of medial 2/3 of hand A+P (sensory inn)
– Nerve Damage: Clawhand• Inability to extend fingers at interphalangeal joints,
results in permanent flexion = claw
Ulnar Nerve
Brachial Artery
Median Nerve
Ulnar NerveMedian Nerve
Radial Artery
Musculocutaneous Nerve UlnarArtery
Where’s Radial Nerve?