With Microsoft ® Excel 2010 2e © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall1 Excel...
-
Upload
nevaeh-grattan -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
0
Transcript of With Microsoft ® Excel 2010 2e © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall1 Excel...
with Microsoft® Excel 2010 2e © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 1
Excel 2010 Chapter 9Creating a Worksheet and Charting Data
1
with Microsoft® Excel 2010 2e © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 2
Objectives
• Create, Save, and Navigate an Excel Workbook
• Enter Data in a Worksheet• Construct and Copy Formulas and
Use the SUM Function
with Microsoft® Excel 2010 2e © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 3
Objectives
• Format Cells with Merge & Center and Cell Styles
• Chart Data to Create a Column Chart and Insert Sparklines
• Print, Display Formulas, and Close Excel
with Microsoft® Excel 2010 2e © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 4
Objectives
• Check Spelling in a Worksheet• Enter Data by Range• Construct Formulas for Mathematical
Operations• Edit Values in a Worksheet• Format a Worksheet
with Microsoft® Excel 2010 2e © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 5
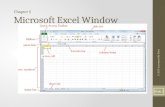
Create, Save, and Navigate an Excel Workbook
• Workbook– Excel Document
• Worksheet– Individual spreadsheet, part of a workbook– Vertical columns (letters) and horizontal
rows (numbers)• Cell
– Intersection of a row and a column
with Microsoft® Excel 2010 2e © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 6
Create, Save, and Navigate an Excel Workbook
with Microsoft® Excel 2010 2e © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 7
Create, Save, and Navigate an Excel Workbook
with Microsoft® Excel 2010 2e © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 8
Create, Save, and Navigate an Excel Workbook
with Microsoft® Excel 2010 2e © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 9
Enter Data in a Worksheet
• Cell content– Anything entered into a cell– Constant values
• Text values (label)• Number values
– Formulas• Equations that perform calculations on values
in the worksheet
with Microsoft® Excel 2010 2e © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 10
Enter Data in a Worksheet• Active cell
– Selected by clicking on the cell– Cell is outlined in black– Column and row number are highlighted– Cell reference displays in Name Box
with Microsoft® Excel 2010 2e © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 11
Enter Data in a Worksheet
with Microsoft® Excel 2010 2e © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 12
Enter Data in a Worksheet
• Auto Fill – Generates and extends a series of values
• Fill handle– Used to drag the contents of the selected
series
with Microsoft® Excel 2010 2e © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 13
Enter Data in a Worksheet
• Ranges– Two or more cells that are adjacent or
nonadjacent– A range colon (:), appearing between two
cell references, includes all cells between the two cell references • EX: B3:D3 is a range including B3, C3, and D3
with Microsoft® Excel 2010 2e © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 14
Enter Data in a Worksheet
with Microsoft® Excel 2010 2e © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 15
Construct and Copy Formulas and Use the SUM Function
• Construct formulas– Type formula with the equal sign (=)
• May be typed in the cell or the formula bar• Use the plus sign (+) to add numbers• Press enter and the cell will display the results
and the formula will appear in the formula bar
• Use the Excel SUM function• Copy formulas using the fill handle
with Microsoft® Excel 2010 2e © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 16
Construct and Copy Formulas and Use the SUM Function
with Microsoft® Excel 2010 2e © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 17
Construct and Copy Formulas and Use the SUM Function
with Microsoft® Excel 2010 2e © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 18
Format Cells with Merge & Center and Cell Styles
• Merge & Center– Joins selected cells into one larger cell and
centers content– Select range, then click Merge & Center
• Cell Styles– Defined set of formatting characteristics– Font, font size, font color, cell borders, and
cell shading
with Microsoft® Excel 2010 2e © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 19
Format Cells with Merge & Center and Cell Styles
• Formatting numbers– Accounting Number Format and
Comma Style• Use comma separator where appropriate• Apply two decimal places• Use parentheses for negative numbers
– Differences• Accounting Number Format—dollar sign ($)• Comma Style—no dollar sign
with Microsoft® Excel 2010 2e © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 20
Chart Data to Create a Column Chart and Insert Sparklines
• Chart– A graphic representation of data– Easier to read than a table of numbers
• Sparklines– Tiny charts embedded in a cell to give a
visual summary alongside data
with Microsoft® Excel 2010 2e © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 21
Chart Data to Create a Column Chart and Insert Sparklines
with Microsoft® Excel 2010 2e © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 22
Chart Data to Create a Column Chart and Insert Sparklines
with Microsoft® Excel 2010 2e © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 23
Chart Data to Create a Column Chart and Insert Sparklines
with Microsoft® Excel 2010 2e © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 24
Chart Data to Create a Column Chart and Insert Sparklines
with Microsoft® Excel 2010 2e © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 25
Print, Display Formulas, and Close Excel
• Page Layout view– See edges of the paper of multiple pages,
margins, and rulers– Insert headers and footers
• Backstage view– Select the File tab (upper left corner)– Shows document properties, and print and
print preview options
with Microsoft® Excel 2010 2e © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 26
Print, Display Formulas, and Close Excel
with Microsoft® Excel 2010 2e © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 27
Print, Display Formulas, and Close Excel
with Microsoft® Excel 2010 2e © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 28
Switch Views & Page Setup for Printing
• Open the spreadsheet• Data view v. formula
view• Switch: Formulas tab –
Formula Auditing group – Show Formulas
• Quick Switch: Ctrl ~
Page Setup for printing1. File – Print – Page Setup
2. Orientation: check Landscape
3. Scaling: check Fit to 1 page
4. Sheet tab: check Gridlines box
5. Save your page setup
Note: You only need to do the setup once for both data and formula views.
with Microsoft® Excel 2010 2e © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 29
Check Spelling in a Worksheet
with Microsoft® Excel 2010 2e © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 30
Enter Data by Range
• Time-saving technique for entering numbers– Select the range of cells where numbers
are to be entered.– Press Enter after each entry and the active
cell will move within the selected range.– This technique works for multiple columns.
with Microsoft® Excel 2010 2e © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 31
Construct Formulas for Mathematical Operations
• Excel formulas begin with an equal sign and include cell references and arithmetic operators.
Symbols Used in Excel for Arithmetic OperatorsOperator Symbol Operation
+ Addition
- Subtraction (also negation)
* Multiplication
/ Division
% Percent
^ Exponentiation
with Microsoft® Excel 2010 2e © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 32
Construct Formulas for Mathematical Operations
• Copying formulas in Excel– A formula copied in Excel changes cell
references relative to the cell with the formula.• Example: Copying =C4+D4 from cell E4
to cell E5 will result in =C5+D5
– To force Excel to keep a cell reference use absolute addressing to fix the formula reference by inserting a dollar sign ($) before the row and/or column.
with Microsoft® Excel 2010 2e © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 33
Construct Formulas for Mathematical Operations
with Microsoft® Excel 2010 2e © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 34
Edit Values in a Worksheet
• Changing cell contents– Making changes to numbers will result in
re-calculating any formulas that reference the cell that was changed.• This is a powerful and useful feature of Excel.
• Formatting cells– Formatting cells will result in a different
appearance but will not impact the calculations.
with Microsoft® Excel 2010 2e © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall 35
Format a Worksheet
• Formatting– Specifying appearance of cells and overall
layout of the worksheet– Inserting and deleting rows and columns
• Existing data is moved and formulas automatically adjusted
– Adjusting column widths and wrapping text• Wrap text displays the contents of a cell on
multiple lines, thus increasing the cell height