Wireless Training Wireless Basics DHCP Basics Wireless Network Topology and the LAN Wireless...
-
Upload
damian-wilkins -
Category
Documents
-
view
222 -
download
1
Transcript of Wireless Training Wireless Basics DHCP Basics Wireless Network Topology and the LAN Wireless...

Wireless TrainingWireless Training• Wireless Basics
• DHCP Basics
• Wireless Network Topology and the LAN
• Wireless Configuration Parameters
• Operating System Configuration.• Panther• Tiger• Windows
• AP Behavior
• Troubleshooting Techniques
• Airespace ACS Training

The Frequency SpectrumThe Frequency Spectrum802.11 in Relation to the Spectrum
Walkie/Talkie
Cell phones
Pagers
Cordless Phones
Garage Door openers
Radio controlled toys
Access Points
Blue Tooth Transmitters
Microwave Ovens
Cell phones
Cordless Phones
Howstuffworks.com
802.11 (ISM)• Unlicensed/Regulated Frequency Band
• FCC Regulates• Frequency open to public use - no license required• Max Power Requirements

Radio Frequency RFRadio Frequency RFThe Signal 802.11 Standard
Howstuffworks.com
FCC provides gives 90Mhz of spectrum for use2.41GHz 2.5GHz
22 Mhz per Channel
11 Channels
2.41GHz 2.5GHz
1 6 119

Interference Interference
Any RF Device Transmitting in 2.46GHz Frequency Range Can Interfere
•Microwave Oven
•Cordless Phone
•Another Access Point
•Bluetooth Telephones
Signal / Noise. dB
Signal High / Noise Higher Signal High / Noise LowAP Close To Unwanted Devices in the room
Signal Low / Noise High AP is Far and Unwanted Transmitters Close
-108dBm
-10dBm
Not so good Good

The Standard 802.11The Standard 802.11What The Heck Is 802.11 Anyway
The following IEEE Standards and task groups exist within the IEEE 802.11 working group:
* IEEE 802.11 - The original 1 Mbit/s and 2 Mbit/s, 2.4 GHz RF and IR standard (1999)
* IEEE 802.11a - 54 Mbit/s, 5 GHz standard (1999, shipping products in 2001)* IEEE 802.11b - Enhancements to 802.11 to support 5.5 and 11 Mbit/s (1999) * IEEE 802.11c - Bridge operation procedures; included in the IEEE 802.1D standard (2001) * IEEE 802.11d - International (country-to-country) roaming extensions (2001) * IEEE 802.11e - Enhancements: QoS, including packet bursting (2005) * IEEE 802.11F - Inter-Access Point Protocol (2003) Withdrawn 2005
* IEEE 802.11g - 54 Mbit/s, 2.4 GHz standard (backwards compatible with b) (2003) * IEEE 802.11h - Spectrum Managed 802.11a (5 GHz) for European compatibility (2004) * IEEE 802.11i - Enhanced security (2004) * IEEE 802.11j - Extensions for Japan (2004) * IEEE 802.11k - Radio resource measurement enhancements * IEEE 802.11l - (reserved, typologically unsound) * IEEE 802.11m - Maintenance of the standard; odds and ends.
* IEEE 802.11n - Higher throughput improvements * IEEE 802.11o - (reserved, typologically unsound) * IEEE 802.11p - WAVE - Wireless Access for the Vehicular Environment (such as ambulances and passenger cars) * IEEE 802.11q - (reserved, typologically unsound, can be confused with 802.1Q VLAN trunking) * IEEE 802.11r - Fast roaming * IEEE 802.11s - ESS Mesh Networking * IEEE 802.11T - Wireless Performance Prediction (WPP) - test methods and metrics * IEEE 802.11u - Interworking with non-802 networks (e.g., cellular) * IEEE 802.11v - Wireless network management * IEEE 802.11w - Protected Management Frames * IEEE 802.11x - reserved * IEEE 802.11y - Contention Based Protocol

Connection Speeds Vs RangeConnection Speeds Vs Range
Range and Connection Speeds are Directly Related
50Ft54/23Mbps Trans/Actual
300Ft2/1Mbps Trans/Actual
100Ft22/12Mbps Trans/Actual
175Ft11/6Mbps Trans/Actual
Dynamic Shift Rate Maximum speeds are 54, 22,11,5.5, 2, 1Divide the speeds roughly in Half for Actual Speeds
Facility Construction materials can chang the speeds dramatically even when close to the AP
Glass - Best PenetrationPlastic - Good Penetration
Wood - Ok Penetration Concrete - Limited Penetration
Metal- Worst Penetration
200Ft5.5/ 2 Mbps Trans/Actual
375 FT >1/.6Mbps Trans/Actual

Wired VS Wireless ConnectionsWired VS Wireless Connections
Wired Connection Wireless Connection
10/100/1000 Mbps 802.11 WIFI1 Mbps to 54 Mbps2.46Ghz b=11Mbps g=54Mbps5 Ghz a=54Mbps
Connection speed is fixed Connection speed varies
Dedicated connection Shared connection
Slow Talkers Effect all users Connected to the APs and neighboring APs
Fixed physical connection Mobility
Requires physical access Passes through walls
Standardized QOS No standard QOS (yet)
Managed by SNMP Managed by guesswork
Wireless is NOT a replacement for wired

Slow TalkersSlow TalkersSlow Talkers Effect all Users
Connected to the Access Points and Neighboring APs
Both Aps were running at 54 Mbps. Slow Talker Reduced Both APs to
22 to wait for slow talker
802.11b 11b Mbps
Fast Talkers 54 Mbps
Slow Talker
Fast Talkers 54 Mbps
APs Listen to each other

Dynamic Load BalancingDynamic Load Balancing
Solving Performance & Capacity problems in high density areas (e.g. conference rooms, cafeteria, carts
Labs)…

Real - Time RF ManagementReal - Time RF Management
Dynamic Channel AssignmentDynamic Power Optimization
RF channel “6”
RF channel “1”
RF channel “11”

DHCP BasicsDHCP Basics
Overview
•What is DHCP?•Why use it?•How does it work?
What is DHCP?
DHCP allows a host to learn its configuration parameters from a server. It automates IP configuration, making it much easier to connect to a network. It allows re-use of IP addresses.
Why use DHCP?•Visitor convenience•Speeds setup of new machines•Simplifies conference room connections•Allows roaming laptops•Centralizes IP management

DHCP BasicsDHCP BasicsHow does DHCP work?1. Server discovery
• Client DHCPDISCOVER packet asking “Who can give me DHCP information?” Hello
2. Servers make an offer• All servers on the subnet unicast a DHCPOFFER packet saying “I can supply you with DHCP information, if you like.” What Do You need
3. Client requests•The client selects one of the responses, and broadcasts a DHCPREQUEST packet saying “I choose server XYZ. Server XYZ, here’s my MAC address, what’s my IP address?” Give Me An Address•The unchosen servers treat this as a rejection.•The request can specify a preferred IP address, if the client has a preference.•The request can ask for additional information.
4. Server responds Here It is and for How long•The server responds with a DHCPACK packet saying “Here is your IP address. It’s good for 24 hours.”•The response can contain additional information, if the client asked for it.•The server records that the IP address is in use.
5. Client releases You Can Have it Back•The client finishes it’s work, and send a DHCPRELEASE packet saying “I’m done with the IP address.”•The server records that the IP address is not in use.

DHCP BasicsDHCP Basics
Clients refresh leases• When half the lease time has expired, a client broadcasts another DHCPREQUEST packet saying “I choose server XYZ. Server XYZ, I want IP address N. Can I have it?”. The server responds yes or no.
Servers can refuse• If a server can’t supply an unused IP address, or if the server can’t supply an IP address that matches the client’s MAC address, the server sends a DHCPNAK packet saying “you can’t have an IP address”. The client is then free to make another request.
Clients preserve addresses• A client can remember its last-used IP address in non-volatile memory. When it boots, it can request the address from the server. This improves the chances that a client will retain the same IP address over long periods of time.

DHCP BasicsDHCP Basics
What DHCP can provide•IP address and lease time•subnet mask•default route•DNS, NIS, LPR, NTP, logging server(s)•WINS NBNS node type•More
Static vs. dynamic addresses•DHCP servers manage two kinds of IP addresses: o Static IP addresses, which the server gives to clients based on the client’s MAC address o Dynamic IP addresses, which the server gives to clients as requested. These come from a “pool” of addresses in a subnet, set aside for this purpose
Network Parameters
IP AddressTracking Management
Exclusion Area
Scope sizeLease Times
Reservations

DHCP BasicsDHCP Basics
Client Address Leases

DHCP BasicsDHCP Basics
Typical Client Parameters Provided
Typical DHCP Properties

DHCP BasicsDHCP Basics
Reservations
Exclusion Areas

Elementary/Middle/High Primary Wired VLAN:Elementary/Middle/High Primary Wired VLAN:
10.x.192.1 10.x.128.1 10.x.193.255 10.x.129.255
10.x.194.1 10.x.130.1 10.x.198.255 10.x.134.255
10.x.199.1 10.x.135.1 10.x.199.254 10.x.135.255
Static IP Addresses (510 Addresses)
DHCP Wireless Clients (1020 Addresses)
Elementary/Middle/High Primary Wireless (176) VLAN: Elementary/Middle/High Primary Wireless (176) VLAN:
10.x.176.1 10.x.112.110.x.176.255 10.x.112.255
10.x.177.1 10.x.113.110.x.188.255 10.x.125.255
10.x.189.1 10.x.126.110.x.191.254 10.x.127.254
Backup DHCP Server (764 Addresses)
Static Printers and Servers (255Addresses)
DHCP Wired Clients (3060 Addresses)
Reserved Network Equipment (255 Addresses)
SBBC Dynamic Host Control Protocol (DHCP) Network Standard
Elementary Schools without VLANs) :Elementary Schools without VLANs) :ETS will eventually establish Wireless VLANS in all Elementary Schools. ETS will eventually establish Wireless VLANS in all Elementary Schools.

Elementary Primary Wired LAN: DHCP Lease 60 Days 510 DHCP Ip AddressesElementary Primary Wired LAN: DHCP Lease 60 Days 510 DHCP Ip Addresses
10.x.192.1 10.x.128.1 10.x.196.255 10.x.132.255
10.x.197.1 10.x.133.1 10.x.198.255 10.x.134.255
10.x.199.1 10.x.135.1 10.x.199.254 10.x.135.255
Static IP Addresses (1530 Addresses)
DHCP Wireless Clients (510 Addresses)
Middle/High Primary Wireless (176) VLAN: DHCP Lease 60 Days 3060 Ip AddressesMiddle/High Primary Wireless (176) VLAN: DHCP Lease 60 Days 3060 Ip Addresses
10.x.176.1 10.x.112.110.x.176.255 10.x.112.255
10.x.177.1 10.x.113.110.x.188.255 10.x.125.255
10.x.189.1 10.x.126.110.x.191.254 10.x.127.254
Backup DHCP Server (764 Addresses)
Static Printers and Servers (255Addresses)
DHCP Wired Clients (3060 Addresses)
Reserved Network Equipment (255 Addresses)
SBBC Dynamic Host Control Protocol (DHCP) Network Standard
Middle/High Non-Standard DHCP Scope VLAN (192 Subnet) :Middle/High Non-Standard DHCP Scope VLAN (192 Subnet) :1.1. Micro scopes were created on Hard Wired Networks to support Wireless Media Center ProjectMicro scopes were created on Hard Wired Networks to support Wireless Media Center Project
• ETS have authorized the continuation of these micro scopes at the Tech’s requestETS have authorized the continuation of these micro scopes at the Tech’s request
2.2. Various scopes created by Site Techs Prior to Refresh Initiative have remained at Sites RequestVarious scopes created by Site Techs Prior to Refresh Initiative have remained at Sites Request

Wireless Network TopologyWireless Network TopologyPhysical Connection
School LAN
DHCPServer
Wan
ETS AirespaceControl System
RAirespace Switch
ApplicationServer
AP
AP
AP
•APs are connected to a rack anywhere in the facility.•APs are powered up using Power Over Ethernet. •AP Cart plug into any Data Quad and power up from any power source.
No AppletalkOver Wireless

Wireless Network TopologyWireless Network TopologyVirtual ConnectionVirtual Connection
School LAN
DHCPServer
Wan
ETS
AirespaceControl System
R
Airespace Switch
ApplicationServer
AP
AP
AP
1. Access Points Seek out and finds the Airespace switch using a special tunneling protocol called LWAP.
2. Using parameters from the switch, it boots up and operates in 30 seconds.
3. Every access point is the same throughout the LAN.
•WLAN service delivery•RF management• Encryption/authentication•Wireless prevention/protection• Location tracking•Capacity Management•Centralized management•Dynamic Control

Wireless Network TopologyWireless Network TopologyWireless Client PerspectiveWireless Client Perspective
School LAN
DHCPServer
ApplicationServer
10.x.192/176.1
SBBC WEP
Airespace Switch
BCPS 802.1x
Guest Web auth
1. The switch can be programmed with many Network names. All access points transmits these network names.
2. Network Name (SSID) Closed Broadcast ( Cant See the Network Name under the “Available Wireless Networks” Window.
3. Authentication:
• WEP authentication encrypts data going across the airwaves so intruders can not snoop and reconstruct the packets intelligibly.
• WEP is either set to be shared or can run open mode.
• Open (Airespace): If user gets SSID right but WEP wrong a connection will be displayed but access will not be provided.
• Shared (Apple Basestation): User must have both correct to show a connection.
• 128 Bit Vs 40 bit.
• 128 Bit 13 Characters (ASCII) 26 Characters Hex
• 40 Bit 5 Characters (ASCII) 10 Characters Hex
• 802.1x: Uses a Key loaded in each client device and in a special server (RADIUS) located at the site. Wireless Switch checks the network name and sends client information to RADIUS server to compare the key for authentication then checks the client’s username and password for authenticity.
• Web Authentication: Passwords are added to the switch. Users must load the appropriate network name, then open a browser to authenticate the password list on the switch.
Future

Wireless Network TopologyWireless Network TopologyKiosk
One or Two Cells of coverage in a small area such as the media center will provide bandwidth managed connectivity exactly where it is
needed.

Wireless Network TopologyWireless Network TopologyOverlay
Overlapping Cells of coverage spread out throughout the building to connect entire buildings wirelessly. Services roaming clients.
Generally 10 – to 15 devices per AP with low bandwidth needs.

Wireless Network TopologyWireless Network TopologyOne-To-One
When the airespace switch
detects high loads on one access point it will
transfer some clients to other AP to share the
load.
Overlapping Cells of coverage installed in close proximity and mounted throughout all rooms the facility and servicing users
with medium to high bandwidth needs.

Wireless Network TopologyWireless Network TopologyBest Practices
2 floaters can be used in areas where there is no infrastructure supported and heavy bandwidth
requirements are needed.
Ceiling Mount
1 Floater
2 Floaters
Ceiling Mount will share the work load with floater on cart. When floater is pulled out of the room ceiling mount still provides connectivity to teachers
staff and students

Wireless ConfigurationWireless ConfigurationDevice Configuration
See the local LAN AdministratorSee the local LAN Administrator
http://Web/wireless Instructions:

Apple Wireless OS/10.3xApple Wireless OS/10.3x
Configuration of PantherStudent Setup
Specific Setup
Step 1. System preferencesStep 2. Network Preferences
Step 3 Click on location dropdown
Step 4 Select new location
Step 5 Type in the name

Configuration of PantherStudent Setup
Specific Setup
Step 6. Select Airport Tab
Step 7. Select “by defaultJoin by” in dropdown box
Step 8. Enter “SBBC” inNetwork name box and the password in the passwordBox
Step 9. Deselect “Allow thisComputer to create networks”
Apple Wireless OS/10.3xApple Wireless OS/10.3x

Configuration of Panther cont’d
Student Setup
Specific Setup
Step 10. Click on TCP/IPStep 11. Enter the Ip Parameters as per siteRequirements dictate
Step 12. Click on ProxiesTabStep 13. UseSite specific proxySettings
Apple Wireless OS/10.3xApple Wireless OS/10.3x

Configuration of Panther Cont’d
Staff SetupAutomatic Setup
Step 1. System preferencesStep 2. Network Preferences
Step 3 Click on location dropdown
Step 4 Select new location
Step 5 Type in the name
Apple Wireless OS/10.3xApple Wireless OS/10.3x

Configuration of Panther Cont’d
Staff Setup
Automatic Setup
Step 6. Select Airport Tab
Step 7. Select “Automatic”in dropdown box
Step 8 Deselect “Allow thisComputer to create networks”
Apple Wireless OS/10.3xApple Wireless OS/10.3x

Configuration of Panther Cont’d
Staff Setup
Automatic Setup
Step 9: Click on the
Airport Icon.
Step 10: Toggle down and click on Other. The Closed network
box appears.
Step 11: Select the Wireless Security Drop down box and check
WEP 40 / 128-bit ASCIIIf you have version O/S 10.2. x Select 128 ASCII bit encryption
Step 12: Enter the Network Name in the Network Name Box and type in the Password in the Password Box. If you don’t know the network parameters contact your site tech and Service Desk for details
Apple Wireless OS/10.3xApple Wireless OS/10.3x

Configuration of Panther Cont’d
Staff Setup
Automatic Setup
Step 14: Click OK
Step 13: Enter the Network Name in the Network Name Box and type in the Password in the Password Box. If you don’t know the network parameters contact your site tech and Service Desk for details
Step 15: Check the wireless Icon to be sure it appears bolded with at least three bars. 5 bars is the best signal. 1 bar indicates poor signal strength.
Apple Wireless OS/10.3xApple Wireless OS/10.3x

Configuration of Panther Cont’d
Staff Setup
Automatic Setup
Step 16. Click on TCP/IPStep 17. Enter the Ip Parameters as siteRequirements dictate
Step 18. Click on ProxiesTabStep 19. Entertssproxy.broward.k12.fl.usType 8888In the second box
Apple Wireless OS/10.3xApple Wireless OS/10.3x

Apple Wireless TrainingApple Wireless Training
Configuration of Tiger
Summary: Configure wireless client devices based upon the user.
• Student Cart Laptop setup1. Configure devices for the wireless
cart AP. It could be the SBBC network or a site specific AP.
2. Set a specific network name and password and set up one location setting.
3. DHCP is site specific. ETS is handling all DHCP transitions.
• Staff1. Configure devices with multiple
locations2. Where ever possible use automatic
configuration. Uses the Plist file in preferences folder

Apple Wireless TrainingApple Wireless Training
Configuration of Tiger Cont’d
Student SetupSpecific Setup
Step 1. System preferencesStep 2. Network Preferences
Step 3 Click on location dropdown
Step 4 Select new location
Step 5 Type in the name

Apple Wireless TrainingApple Wireless Training
Configuration of Tiger Cont’d
Student Setup
Specific Setup
Step 6. Select Airport Tab
Step 7. Select “by defaultJoin by” in dropdown box
Step 8 Enter “SBBC” inNetwork name box and the password in the passwordBox
Step 9 Select ‘Options’to set require admin password

Apple Wireless TrainingApple Wireless Training
Configuration of Tiger Cont’d
Student Setup
Specific Setup
Step 10. Click on TCP/IPStep 11. Enter the Ip Parameters as per siteRequirements dictate
Step 12. Click on ProxiesTabStep 13. UseSite specific proxySettings web
broward.k12.fl.us

Apple Wireless TrainingApple Wireless Training
Configuration of Tiger Cont’d
Staff SetupAutomatic Setup
Step 1. System preferencesStep 2. Network Preferences
Step 3 Click on location dropdown
Step 4 Select new location
Step 5 Type in the name

Apple Wireless TrainingApple Wireless Training
Configuration of Tiger Cont’d
Staff Setup
Automatic Setup
Step 6. Select Airport Tab
Step 7. Select “Automatic”in dropdown box
Step 8 Select ‘Options’To set admin password

Apple Wireless TrainingApple Wireless Training
Configuration of Tiger Cont’d
Staff Setup
Automatic Setup
Step 9: Click on the
Airport Icon.
Step 10: Toggle down and click on Other. The Closed network
box appears.
Step 11: Select the Wireless Security Drop down box and check
WEP 40 / 128-bit ASCII

Apple Wireless TrainingApple Wireless Training
Configuration of Tiger Cont’d
Staff Setup
Automatic Setup
Step 13: Click OK
Step 12: Enter the Network Name in the Network Name Box and type in the Password in the Password Box. If you don’t know the network parameters contact your site tech and Service Desk for details
Step 14: Check the wireless Icon to be sure it appears bolded with at least three bars. 5 bars is the best signal. 1 bar indicates poor signal strength.

Apple Wireless TrainingApple Wireless Training
Configuration of Tiger Cont’d
Staff Setup
Automatic Setup
Step 15. Click on TCP/IPStep 16. Enter the Ip Parameters as siteRequirements dictate
Step 17. Click on ProxiesTabStep 18. Entertssproxy.broward.k12.fl.usType 8888In the second box
webbroward.k12.fl.us

Step 1. Open Directory Access in the utilities directory. Step 2. If your not logged on with Admin privileges click the “lock” in the bottom left corner of the Directory Access window and enter in the Admin user name and password of the local machine. Click OK
Apple Directory AccessApple Directory AccessConfigure SMB Configure SMB

Step 3. Make sure SMB is CheckedStep 4. Highlight SMB and click configure.Step 5. In the workgroup drop down box, select ETS.Step 6. In the wins server Box type, in 10.251.192.91Step 7. Click on OK.Step 8. Click Apply and click the lock to prevent further changesStep 9. Close the Directory Access window.
Directory AccessDirectory AccessConfigure SMBConfigure SMB

Step 10. Click on the Desktop or Finder IconStep 11. Click on Go in the menu and select Connect to Server
Directory AccessDirectory AccessConnect to the NetworkConnect to the Network

Step 12. Click on the Desktop or Finder IconStep 13. Click on Go in the menu and select to Server. The “Connect to Server” Window Will Appear. Step 14. Click Browse, the Network Icon will appear.Step 15. Click on the Network Icon in the Network WindowStep 16. Scroll through the domain Name list to find your resources.
Directory AccessDirectory AccessConnect to the NetworkConnect to the Network

Summary: IP printing is the ability for a printer to use TCP/IP protocols (such as LPD/LPR, IPP, or Socket or Jet Direct) to make itself accessible to your computer. If the printer you want to use is not listed when you print, you can add it to your list of available printers. To add an printer using IP, you need to know its IP address or DNS name. See your network administrator for assistance.
OSX 10.x OSX 10.x IP Printing ConfigurationIP Printing Configuration
Step 1. Open System Preferences on the Doc or Blue Apple and click the Print & Fax Icon.
Step 2. Click Printing tab, and then click the Set Up Printers button.
Step 3. Click the Add Printer Icon in the printer list.
Step 4. Choose IP Printing from the pop-up menu.
Step 5. Select Internet Printing protocol from the Printer Type pop-up menu.
Step 6. Type the IP address for the printer in the Printer Address field. If the printer IP address is not marked ask your Tech Specialist.
Step 7. Type in a recognizable name into the Queue Name field.

OS 10.x OS 10.x IP Printing ConfigurationIP Printing Configuration
Step 8. Choose the brand of printer appropriate for your printer from the Printer Model pop-up menu, then select your printer in the Model Name list.
Step 9. Click Add. The printer appears in the Printer List as the default printer (in bold type). It also appears in the Printer pop-up menu when you print a document.

Summary: Windows XP wireless client utility offers the same interface regardless of the vendor. Service Pac1 has a slightly different interface than Service Pac2. Windows is able to do this by defaulting the setup to use the Windows client utility as the Wireless Configuration manager.
Step 1: Double click on the Wireless Icon at the bottom of the systems tray or left click on the icon to bring up the menu and click open utility. This brings up the wireless network connections properties box.
Step 2. Make sure that you are in the WirelessNetworks properties Tab window
Step 3: Click the Add button.
WindowsXPWindowsXPWEP Wireless Client ConfigurationWEP Wireless Client Configuration
SP2SP2

Step 4: Type in the appropriate Network name in the Network Name box. See your network administrator or contact the ETS Service Desk for Details.
Step 5: Select “Open” in the “Network Authentication” drop down box.
Step 6: Deselect the Box “ The Key is provided for me automatically”.
WindowsXPWindowsXPWEP Wireless Client ConfigurationWEP Wireless Client Configuration
SP2SP2
Step 4
Step 5
Step 6

Step 7: Select “WEP” in the “Data encryption” drop down box
Step 8: Type in the “WEP” Network Key and confirm. Contact your administrator or ETS Service Desk if you don’t know the password.
Step 9: Be sure that “Key Index” is set to “1”
Step 10: Click “OK”
WindowsXPWindowsXPWEP Wireless Client ConfigurationWEP Wireless Client Configuration
SP2SP2
Step 7
Step 8
Step 9
Step 10

Step 11: Check the systems tray to be sure that both the Wireless network Icon indicator and the Wireless signal strength icon are active. Bright blue and the absence of the red “X” indicates that the network is active. The Wireless signal strength indicates how strong you are receiving the Nearest Access point..
Wireless Network Icon
Wireless Signal Strength Icon
WindowsXPWindowsXPWEP Wireless Client ConfigurationWEP Wireless Client Configuration
SP2SP2

Step 1: Double Click the Wireless Utility Icon in the Systems Tray. The “Dell Wireless WLAN Card Utility” window will appear. Note the icon may be dark meaning it is not connected to a wireless network.
Step 2: click Add. The “connection settings” window appears
Wireless Network Icon Utility
Windows XPWindows XPConfigure Using the Dell Config ToolConfigure Using the Dell Config Tool
Step 3:Type “SBBC” in the Network Name SSID box.
Step 4: Select Open in the Network Authentication dropdown box
Step 5: Select the network tab and enter the “Br0wardC0unty: in the Network key and retype in the Confirmation box.
Step 6: Select key index “1”
Step 7: Click the OK button

Step 1: Look for the SBBC Icon in the preferred network window.
Step 2: Select link status tab to visually see the connection strength.
Step 3. Click the OK button.
Windows XPWindows XPConfigure Using the Dell Config ToolConfigure Using the Dell Config Tool

Summary: Unlike WindowsXP, Windows2000 wireless client utilities are different from vendor to vendor and even within versions of a vendor’s client utility. To that end this instruction document will cover the ETS recommended Client Card (Dell True Mobile and Proxim ABG Client Card) and discuss differences in the District’s most popular client software.
•In most cases the Client card will come embedded on the laptop and pre configured for a Default setting. •Configuration is all that will need changing. In cases where there is no client card pre installed, ETS recommends the Proxim ABG combo Card. •In this case both the drivers and Client software will need to be installed. •***** Important**** Never insert the card in the laptop until the software is loaded. •If you do insert the card first and continue through the load procedures, you will need to uninstall the device driver from “Windows 2000’s Device Driver window located in the Control Panel by double clicking on the “System” Icon.
Both the True Mobile and Proxim ABG Client Card configuration tool are similar in appearance and can be accessed by double clicking on the wireless icon in the systems tray or through [Start-Programs-Dell True Mobile or Orinoco Wireless Client]
Windows2000 Windows2000 WEP Wireless Client ConfigurationWEP Wireless Client Configuration
Proxim ABG CardProxim ABG Card

Step 1: Follow the instruction to load the Proxim Client PC card using the instructions provided by Proxim.Step 2. Double click on the Wireless Icon in the systems tray or click on Start-Programs-Orinoco wireless client and select the Client Utility icon.Step 3. Click on the profile management tab.
Windows2000 Windows2000 WEP Wireless Client ConfigurationWEP Wireless Client Configuration
Proxim ABG CardProxim ABG Card

Step 4: Highlight the Default icon and Click on Modify Button
Step 5: Enter in the profile name meaningful to the user as to where the profile will connect to.Step 6: Client Name will default to the Computer name and should remain.
Windows2000 Windows2000 WEP Wireless Client ConfigurationWEP Wireless Client Configuration
Proxim ABG CardProxim ABG Card

Step 7: Select the Security Tab. Current security requirements for the district wireless is Pre-shared Key (open) in Key 1Step 8: Select the Pre-shared Key radio button.Step 9: Click on configure.
Windows2000 Windows2000 WEP Wireless Client ConfigurationWEP Wireless Client Configuration
Proxim ABG CardProxim ABG Card

Step 10: Select ASCII text radio buttonStep 11: Click the WEP Key1 radio button and enter the password in the encryption window. Step 12: Select the 64 bit radio button. The password is 5 digits long or the 128 bit radio button if the password is 13 digits long.
Step 13: Click the OK button.
Windows2000 Windows2000 WEP Wireless Client ConfigurationWEP Wireless Client Configuration
Proxim ABG CardProxim ABG Card

Step 14: Click on the Advanced TabStep 15: Make sure that Open is highlighted in the 802.11 Authentication ModeStep 16: Click on OK
Windows2000 Windows2000 WEP Wireless Client ConfigurationWEP Wireless Client Configuration
Proxim ABG CardProxim ABG Card

Step 17: The Profile Management Details will show the network name in SSID 1 and the Profile icon will indicate that it is connected to the network.
Note. Open WEP Key architecture will depict that the client device is connected to the network even though the WEP password is incorrect. If the client can not access the network for any reason, double check the password was entered correctly.
Windows2000 Windows2000 WEP Wireless Client ConfigurationWEP Wireless Client Configuration
Proxim ABG CardProxim ABG Card

AP BehaviorAP BehaviorBoot-up/ Update Sequences
Normal Operation
Green-amber-orange
Solid lights
Downloading CodeGreen-amber-orangeFlashing Lights
Searching for switchGreen-amber-orangeLights flash in sequence
FaultRed light on only
Access Point LED Description

Client Trouble Shooting Client Trouble Shooting Flow Chart
http://web/wireless/support.htm

Client Trouble Shooting Client Trouble Shooting Overview
1. Techs can look to determine if clients are experiencing broad issues across the network or isolated connection configuration problems
To Access https://10.x.199.200 Https://10.x.135.200
User Name TLCPassword readonly

Client Trouble Shooting Client Trouble Shooting Overview
To Access Step 1 enter https://10.x.199.200
Https://10.x.135.200 in a browseStep 2. Click LoginStep 3. Enter User Name TLC
And Password “readonly”
Step 4. Click Clients

Client Trouble Shooting Client Trouble Shooting Overview
To Access Step 5. Look in the AP name to determine the AP clients are connected Step 6. Status and Auth column to determine if your clients are Authenticated and Associated to the network
Clients Trouble ConditionsProblem: Associated but Auth “NO” 1. Client has Network name correct but: 2. Has the WEP Password wrong or does not have an IP address. Both problems are related.Solution: 1. Check DHCP settings or proper IP address or proper static IP address 2. Reenter WEP encryption password again
Problem: DHCP not delivering to any clientsSolution: 1. Check the AP to be sure it is connected to a live port and powered on. 2. Check to be sure there is a nearby AP

ACS TrainingACS TrainingOverview
1. Techs and Network Support at ETS have a single solution for tracking the health of the wireless network.
2. Techs have capability to monitor user activity, track users around their site and monitor and take action against unauthorized access to the network.
To Access Web/wireless/support.htm
User Name TLCPassword readonly

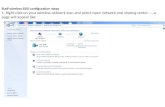
ACS TrainingACS TrainingACCESS
To Access Step 1. Web/wireless/support.htm Step 2. Select the appropriate Link
Step 3.Click the Logon Button
Step 4 Enter “tlc” for User Name “readonly” for the password
tlc
readonly
Home Display

ACS TrainingACS TrainingLOCATE SITE
To Locate Site Step 1. Select “Monitor” DropdownStep 2. Click on “Maps”Step 3 If site is displayed on the first page of the list Click on the name link otherwise type your site in the search area to the left.
Search for your site if not displayed on the first page1. Select all maps in the “search for” dropdown2. Type in the Site. “ use Capital “ for first letter in name3. Click “Search” Button 4. Any location with that search criteria is returned5. Select what is applicable
Step 5. For Cart data select Building, AP’s mounted in Ceilings select CampusStep 4. Book Mark This Link for future use.
Maps

ACS TrainingACS TrainingUtilization Management
Step 1. Click on The Appropriate Building if looking for AP cediling mount information. Select Campus for cart data
Step 2. Click on the Floor
Step 3 . Select FilterStep 4. Select DisplayStep 5. Select Utilization
Techs can review the overall health of the network by looking at the utilization levels to determine how user impact.
RED and Yellow indicates 50-90% utilization levels

Questions ??????????????Questions ??????????????