· PDF file1) What is Acupuncture ? 4 . 2) Meridians in Acupuncture. 6 . 3) Effects of...
Transcript of · PDF file1) What is Acupuncture ? 4 . 2) Meridians in Acupuncture. 6 . 3) Effects of...

Index

1) What is Acupuncture ? 4
2) Meridians in Acupuncture. 6
3) Effects of Acupuncture. 8
Units Used in Acupuncture 9
4) Classification of Acupuncture points. 11
5) Five Elements and Acupuncture 14
6) Yin Yang 16
7) Organ Clock. 18
8) 14 Meridians of Acupuncture. 22
1) Lung Channel 22
2) Large Intestine Channel 30
3) Stomach Channel 41
4) Spleen Channel 57
5) Heart Channel 68
6) Small Intestine Channel 74
7) Urinery Bladder Channel 83
8) Kidney Channel 103
9) Pericardium Channel 113
10) Tripple Warmer Channel 119
11) Gall Bladder Channel 129
12) Liver Channel 145
13) Governing Vessel Channel 153
14) Conceptional Vessel Channel 163

9) Extra ordinary Points 170
10) Un-numbered Extra Points 186
11) The New Acupuncture Points 189
12) Nose, Hand and foot Acupuncture 211
13) Scalp Acupuncture 222
14) Auricule Acupuncture 228
15) Eight Extraordinary Channel 241
16) Selection Technique of Acupuncture Points 251
17 ) Clinical Acupuncture
1) Brain and Nervous System Disorders 274
2) Respiratory Disorders 277
3) Heart and Cardio Vascular Disorders 279
4) Blood Disorders 281
5) Stomach and Gastro Intestinal system Disorders 282
6) Hepatic, Biliary, Splenic and Pancreatic Disorders 286
7) Genito Urinary Disorders 288
8) Ear Disorders 290
9) Eye Disorders 292
10) Endocrine Disorders 296
11) Psychiatric Disorders 297

12) Disorder of Children 299
13) Acute Disorders 300
14) Gynaecological Disorders 304
15) Locomotor Disorders 308
16) Skin Disease 311
18) Analysis of Acupuncture Points According to
Chinese Image Meaning 314
104 Meeting Point 318
19) Acuyoga 324
Acuyoga For 14 Channel 336
Acuyoga Therapy 345
Acumeridian Tooth organ Relationship 355
Eye and Lip Micro-acupuncture system 356
Face Acupuncture 357
Acuyoga For Beautiful Face 359
Index of Acu-Points with English Meanings. 373
ACUPUNCTURE POINTS ON SPECIFIC AREA 388 Index of Acu-Points with Chinese alphabet 389
Index Of Disease And Prescription 407 Entry Exit Point 416 Reference Books & website 417
Warning :

All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced or utilised in any form or by means, electronic or mechanical, including photo copying, recording or by any information storage and retrieval system, without permission in writing from auther.
Note to Reader :
This book in intended as an informational guide. The remedies, approches and
techniques described herein are meant to supplement and not to be substitute for,
professional medical care or treatment. They should not be used to treat a serious
ailment without prior consultation with qualified health care professional.
Preface :
From last 10 years the patients who benefits the Laser Acupuncture Therapy & other patients from my country & abroad, motivated me to write the book in detail, because the books on these Acupuncture, acupressure, acuyoga, in any language are in just brief. Acupuncture is discovered with the battle of archery i.e. Bow & Arrow. Soldier was injured on leg with arrow and his eyesight was improved, thus the many other acupuncture point was discovered.
In this book I added almost all acupuncture point’s with Chinese Images & their meanings which found rarely in other books. Figures include Each Channel of separate organ & it’s internal relationship with related organ. Each points separate figure, International name, Chinese Image, it’s meanings, Location, Indication, Needling ( Puncture ), Acupressure, Laser, Acuyoga. The book include total points on channel including left & right side 670, Extra ordinary points left & right side are 75, unnumbered acupuncture points 42, Recent discovered points 96.
This book include Micro system Acupuncture Ear-acupuncture ( Auricular-acupuncture Total No of points including left and right 200), Nose acupuncture, Hand Acupuncture, Foot Acupuncture, Scalp Acupuncture with detail figure, & treatment. On Nose 34 Points, On both hands 34 Points, On both feet 32 Points.
In this book I added different techniques of point selection, use of analgesic points, use of specific points for specific diseases, use of combination points, use of five element theory & it’s rule, use of 60 command points, use of tonification & sedation points & other many techniques.
In Clinical acupuncture, Disorders of Brain & Nervous System, Heart & Blood vessels disorders, Diseases of Stomach & Intestine, Genito-urinary disorders, Sensory organ’s disorders (i.e. Ear, Nose, Eye, Skin), Psychological disorders, Diseases of respiratory system, Gynecological & obstetrics diseases, Diseases of bones, joints, & connective tissues, diseases of Gall Bladder & Liver, Skin (Dermatology) & Cosmetology etc. are describe in brief and simple language.

Acuyoga the combination of acupressure and yoga is described in detail with figure. Daily self acupressure practice, Acuyoga and self acupressure for different diseases are described in brief with figures. For looking young and beautiful face with natural face lifting, more than sixty facial acupressure and facial yoga are described in detail with other health benefits including detail figures.
DR. Sakhare M.S.
1 What is Acupuncture? Acupuncture is the Latin word. Acus means needle and puncture with needle means Acupuncture or Acuate means sharp pointed apparatus by which puncture is done means Acupuncture.
In most of religion Ear Piercing in the centre of lobe is Ceremony on twelfth day after the birth of child. In Auriculo-Acupuncture Eye point is in the centre of lobe, above the eye point there is brain point, It is believed that by piercing ear the health of child is improved, behind this there is scientific reason of ear acupuncture.
In Islam Religion before prey ( Namaz ) each must clean their ear ( Wujoo). In Ear acupuncture there are more than 200 points. Piercing ear in different points, massaging ear, pinching ear, twisting or wringing ear our health is improved.
Wearing gold and silver ornament on different body part, wearing bangles, applying kumkum or smooth paste of sandalwood or other scented powder, at the centre of eyebrows, applying ash ( Bhasma ), wearing necklace etc. is related to acupuncture different points and benefits as per point.
Nerves end on palm and sole. Clapping 15 minutes daily while praying, motivating players, playing different games, working in kitchen, churning curd with churning staff by hand, grinding chutney or spices on stone slab and grinder by hand, daubing yard or courtyard by hand, draw water from well with rope palms are stimulated. Walking bare foot sole is stimulated. Revolving around temple with bare feet sole is stimulated. Nowadays polished pavements, marble are all over in temples, mashids, churches, so there is no stimulation to our sole and we think that we are not receiving blessings of God.
There are different types of hand postures (Mudra) in different religions while praying, different types of dance (Kathhak, Bharat Natyam, Mohini Attam, Ballet, other classical dance etc.) acupressure is done naturally.

Massaging oil on head and body of child, Massaging oil and scrubbing with smooth scented herbal powder before bath is the acupressure to different points of body. Tapping by hand to children while slipping, they sleep soundly because the points of sedation are behind ear. We also take our hand by folding in elbow underneath ear naturally while sleeping.
Hot stamping on body (Tapt Mudra), Cauterizing, Tattoo painting, Ear piercing etc. are done in different types of community. Behind all these conventional acupressure and acupuncture science is there.
Most of female wear Necklace. As Necklace rest on the 7th
cervical spine they have least possibility of neck pain. The pendant of specific shape if placed near neck and neck is pressed downward it improves thyroid function. Now a day female have low backache because they forget to wear silver belt which was used few years ago. Knee pain is common in females because they do work in kitchen by standing. While working in front of Kitchen Katta weight of body is not divided same on both legs in the centre of knee joint. In rural region those females who are cooking in sitting position are free from knee pain and low backache. Long time sitting on chair hamstring muscle are contracted and become short.

2 Acupuncture Meridians The route on which Chi flows in the body is known as Meridian or Channel. These routes originate from various vital organs of the body and known as per name of particular organ. E.g. Route originated from Heart is known as Heart Meridian. Heart Meridian is denoted by the symbol H and first or starting point is denoted by H-1 and so on.
There are twelve paired Meridians and two single Meridians means total fourteen main Meridians.
Six Meridians are on Hand. Six Meridians are on Leg. Six Meridians are Yang ( Positive ). Six Meridians are Yin ( Negative ). Six Meridians are Ascending. Six Meridians are Descending.
Name of Meridian Symbol Polarity No of Points
LUNG LU YIN 11
LARGE INTESTINE LI YANG 20
HEART H YIN 09
SMALL INTESTINE SI YANG 19
PERICARDIUM P YIN 09
TRIPLE WARMER TW/SJ YANG 23
STOMACH ST YANG 45

SPLEEN SP YIN 21
URINARY BLADDER UB YANG 67
KIDNEY K YIN 27
GALL BLADDER GB YANG 44
LIVER LIV YIN 14
GOVERNING VESSEL GV/DU ------ 28 CONCEPTIONAL VESSEL CV/REN ------ 24
On the above table 1 to 6 Meridian’s pairs are on hand and 7 to 12 Meridian’s pairs are on leg and 13 and 14 single Meridian are on body’s posterior mid line and anterior midline.
Origins and Direction of Meridians :
The direction of the channel is depending upon the direction of flow of Chi of particular organ. Three Yin channels on the hand start from chest and descend on medial side of hand towards fingers and meet Yang channels.
Three Yang ascends from fingers on lateral side of arm and goes to head and meet three yang channels of leg.
Three yang channels of leg start from head and descend on leg’s toe from front, back and lateral side of leg and meet three yin channel of leg.
Three yin channels of leg ascend from medial side of leg and go to the chest and meet the three yin channel of hand.

3 Effects Of acupuncture Effects of acupunctures are Subjective and Objectives. Subjective Effects feel patient
while objective effect knows doctors only.
Subjective Effects :
Pain: Patient feels pain while pricking needle. In Laser acupuncture there is no pain.
Numbness: Patient feels numbness after pricking needle. In Laser acupuncture there is no numbness.
Heaviness: Patient feels heaviness after pricking needle. In Laser acupuncture there is no heaviness.
Soreness: Skin around the needle becomes a sore.
Distention: Patient feels something moving from both end of channel where we prick the needle.
Objective Effects :
Analgesic : Some acupuncture points relieves pain of patients.
Sedation : Some acupuncture points have sedation or tranquilizing effects.
Immunity Improvement : Some acupuncture points improve immunity.
Homeostatic Effect : Due to acupuncture blood purifies, removes blockage of breathing, regulates heart beats, body temperature, many biochemical reactions, other many life saving parameters are regulated.
Motor Gate Theory : Due to acupuncture rain and nerves are stimulated and movements starts at particular place.

Endorphin Theory : Acupuncture stimulates endorphin hormone which has pleasure analgesic effect.
Unit used in Acupuncture:
There is separate unit to measure the length and deepness of point. It is known as Chun or Cun. 1.Width of one finger = 0.5 Chun. 2.Width of thumb = 1 Chun. 3. Width Of two finger = 1.5 Chun. 4.Width of three finger = 2 Chun. 5. Width of four finger = 3 Chun.


4 Classification of Acupuncture Points A spot on body which becomes red, tender, swell and painful at the point at the time of disease that spot known as Acupuncture point.
Meridian or Channel Points :
The points which are situated on the classical line of Meridians are known as Meridian Points.
Extra Points or Extraordinary Points :
The points which are not on the classical line of Meridians and are situated all over body are known as Extra points.
Recent Acupuncture Points :
These points are recently discovered by physicians and scientists.
Yuan Source Points :
These points have maximum energy of channel and they are useful in chronic diseases. Every channel has one Yuan Source Point. These all points are situated on the wrist and ankle. e.g. LU-9, LI-4, ST-42, SP-3, HT-7, SI-4, UB-64, K-3, P-7, TW-4, GB-40, LIV-3.
Alarm Points :
These points work as alarm signal. Every channel has one alarm point. In the time of diseases of particular channel or organ they become red, tender, painful or swell. These are useful for diagnosis , prognosis and treatment. These points are MU-FRONT and BACK-SHU Points.
Jing Well Point :
These points are used in medical emergency like shock, coma, unconsciousness, feats, severe headache, hyper paraxia, and in chronic diseases. Every channel has one jingwell point either at the starting point or end point. These all points are situated on the nail root of the finger except GV-26 and K-1 e.g.LU-9, LI-1, P-9, TW-1, H-9, SI-1, SP-1, ST-45, Liv-1, GB-44, K-1, UB-67.
Influential Points :

There are eight important tissues in our body and for each tissue there is one specific point which is useful foe treatment for that particular tissue.
Influential Point Related Tissue
CV- 12 Hollow Organs or Fu organs.
LIV-13 Solid organs of Zang organs.
CV-17 Lungs and respiratory tissues.
UB-17 Blood.
UB-11 Bone and Cartilage.
GB-34 Muscle and tendon.
UB-39 Bone Marrow.
LU-9 Vascular System or blood vessels.
8. Aha Shi Points or Floating Points : As per name these points has no particular location . It can come out at the time of disease of particular organ. At the time of disease they become tender, swell and painful. After cure of disease they will disappear e.g. Large Intestine ST-37, Stomach ST-36, Triple Warmer UB-39, Gall Bladder GB-34, Small Intestine ST-39, Urinary Bladder UB-40.
9. Dangerous Points : Some acupuncture points situated near internal and external important vital organs. Inexperienced and careless needling can harm particular organ. These points are dangerous points, needling to these points must be done carefully and after sufficient experience. In Laser acupuncture these points can be treated without harm to any organ.
10. Luo Connecting Points : These points connects link between two connected channels or two same channel of both side. These are only points which can treat a diseases of two connecting channel or the channel of both sides e.g. LU-7, LI-6, ST-40, SP-4, H-5, SI-7, UB-58, K-4, P-6, TW-5, GB-37, LIV-5.
11. Distal Points : The points which acts on particular organ from long distance are known as Distal Points.

Distal points Related Area
LI – 4 Face, Forehead, Neck and five sense organs.
LU – 7 Back of head, Neck, Back, Lungs.
P – 6 Front of chest, diaphragm, Upper half of abdomen.
UB – 40 Low back, urogenital organs.
ST – 36 Stomach, Internal organs of abdomen.
SP – 6 Perineum, external genital, pelvic organs.
12. Tonification Point : These points are useful to increase the energy of channel. Each channel has one tonification point. These points are also called as Mother Point, Reinforcing Point, Tonifying Point e.g. LU-9, LI-11, ST-41, SP-2, H-9, SI-3, UB-67, K-7, P-9, TW-3, GB-43, LIV-8.
13. Sedation Point : These points are useful to sedate the excess energy of channel. Each channel has one sedation point. These points are also called as Son Point, Reducing Point, Sedating Point e.g. LU-5, LI-2, LI-3, ST-45, SP-5, H-7, SI-8, UB-65, K-1, K-2, P-7, TW-10, GB-38, GB-34, LIV-2.
14. Local Points : The points situated near the affected organs are known as Local Points. These points may be Meridian Points or Extra Points.
Xi-Cleft Points : These points used to treat acute diseases of channel and pertaining internal organs. Each of twelve channels have one Xi-Cleft Point LU-6, LI-7, ST-34, SP-8, H-6, SI-6, UB-63, K-5, P-4, TW-7, GB-36, LIV-6.
Point on extraordinary channel K-8, K-9, UB-58, GB-35.

5 Five Element And Acupuncture In Ayurved there are five elements like Fire, Earth, Water, Air, Space. Like this in Acupuncture Fire, Earth, Metal, Water, Wood.

In above diagram there are two types of Cycles. 1. Creative Cycle or Constructive Cycle or Generative Cycle, KO Cycle. 2. Destructive Cycle or SHEN Cycle
Creative Cycle :
In Creative Cycle Fire is fed by Wood, the ashes formed become Earth, Metal is formed in earth, Water springs from Metal ( Fluidity arises from solid state ) and water nourishes trees and which becomes Wood and complete the cycle.
Destructive Cycle :
In destructive cycle Fire melts Metals, Metal cuts Wood, and Wood covers the Earth and Earth dams Water. The five elements are therefore not independent entities but exist in an intimate relation to each element which governs and is governed by another element. In Acupuncture each channel has one element and the same element is for that organ. Each Channel has each element’s point. So above cycles can use in the treatment.

6 Yin And Yang The principle of Yin and Yang is every object has its opposite side, in Chinese Positive
and Negative sides are related with each thing. In Acupuncture each organ and meridians are divided in Yin and Yang.
Yin Yang
Lung Large Intestine Heart Small Intestine Pericardium Triple Warmer Spleen Stomach Kidney Urinary Bladder Liver Gall Bladder
Yin Yang Yin Yang Yin Yang
Female Male Night Day Cold Hot
Valley Hill Moon Sun West East
In Out Dark Light Winter Summer
Water Fire Descending Ascending Colds Hot
Bone Skin Front Back Interior Exterior
Yin and Yang principle body’s functions are balanced. If any principle of yin or yang is imbalanced we get sick. Nothing is completely yin or completely yang. In every yin there is small amount of yang and in every yang there is small amount of yin. This yin and is symbolized by dividing a circle with letter S in two parts Black and White colour. In the White part there is a small black spot show that in yang there is yin and in black part there is a small white spot show that in yang there is small yin.


7 Organ Clock According to Noon-Midnight law (tsu wu) Vital energy (Chi) flows through the twelve
channels in 24 hour cycle. In each channel it is about 2 hours. The table is given below.
Meridian Time Horary Point
Lung 3.00 a.m. to 5.00 a.m. LU-8
Large Intestine 5.00 a.m. to 7.00 a.m. LI-1
Stomach 7.00 a.m. to 9.00 a.m. ST-36
Spleen 9.00 a.m. to 11.00 a.m. SP-3
Heart 11.00 a.m. to 1.00 p.m. H-8
Small Intestine 1.00 p.m. to 3.00 p.m. SI-5
Urinary Bladder 3.00 p.m. to 5.00 p.m. UB-66
Kidney 5.00 p.m. to 7.00 p.m. K-10
Pericardium 7.00 p.m. to 9.00 p.m. P-8
Triple Warmer 9.00 p.m. to 11.00 p.m. TW-6
Gall Bladder 11.00 p.m. to 1.00 a.m. GB-41
Liver 1.00 a.m. to 3.00 am LIV-1
From above chart the energy tide enters the Lung Channel at 3.00 a.m. and leaves it to enter the succeeding Large Intestine Channel at 5.00 a.m. The vital energy flows in this manner successively through the twelve Channels till it leaves the Liver Channel and re-enter the Lung Channel at 3.00 a.m. of the following day. This flow of energy in this time sequence is known as “Organ Clock”
Horary Points are used during appropriate period of Organ Clock. When treating with disorder of Lung the Horary Point LU-8 may be used during the period 3.00a.m. to 5.00 a.m. It is not possible to treat within this period we can treat diametrically opposite to it in Organ Clock i.e. Urinary Bladder Channel at 3.00 p.m. to 5.00 p.m. at the point UB-66.
Horary point is a point on channel which have element of that channel. It is also called Element Point. These points are in fact included among Sixty Command Points.




8 14 Meridians of Acupuncture
1 Lung Meridian
The Hand Greater Yin (Tai Yin) 1 Element : Metal. 2 Total No of Points : 11. 3 Polarity : Yin, Negative, -ve. 4 Pathway :Descending Yin. 5 Maximum Energy Time : 3 to 5 AM 6 Related Organ : Lung. 7 Related Couple Organ : Large Intestine. 8 Related Sense Organ : Nose. 9 Related Tissues : Skin & Body Hair.
Pathway : As shown in fig. channel starts from the first point LU-1 in the depression in front of shoulder below clavicle it ascends up to clavicle, from here it descends on upper arm from front & middle aspect lateral to bicep up to elbow crease. Then it descends on lower arm from front & middle aspect then it take turn & goes the radial side of arm up to lateral end of wrist crease, then it run away on two colour skin junction line of thumb & end on the nail root of thumb lateral corner.
Indication of Channel : 1. All Lung Diseases, Asthma, Bronchitis, Pleurisy, Pneumonia. 2. Diseases of URT ( Upper Respiratory Track ) i.e. Rhinitis, Common Cold, Sinusitis. 3. Diseases along the pathway ie. Shoulder & Upper arm pain. 4. Occipital Headache & Neck Pain.
1) Lu-1 "Central Residence" 中府 Zhongfu
IMAGE: As the Front Mu point for the Lung, this is the central storage place or "residence" of the Lung Qi.
Location : 6 cun lateral to anterior midline level with the 1st intercostals space, 1 cun below LU- 2. Caution: needle oblique to avoid lungs.
Indication : Cough, dyspnea, pain in the chest, shoulder & back pain, pulmonary tuberculosis, etc.

2) Lu-2 "Cloud's Door" 云 门 Yunmen
IMAGE: The "cloud" refers to upper body or heaven's energy. The Qi of heaven and earth meet at the clouds. Cloud is also a name for the many small connecting channels of the Lung which meet here, and for the Kong Qi which enters the chest from the outside air.
Location : 6 cun lateral to the anterior midline below the clavicle in the depression medial to the coracoids process. Needle oblique to avoid lungs. Indication : Cough ,asthma, pain in the chest, shoulder & back pain, fullness of chest.
3) Lu-3 "Heaven's Residence" 天府 Tianfu
Speciality : Window of Sky
IMAGE: Tian fu is a name for the breasts. This point is said to touch the nipple when the arm is folded in toward the chest.
Location : 3 cun inferior to the anterior axillary fold on radial side of biceps brachii muscle.
Indication : Asthma, epistaxis, pain in the medial aspect of palm.
4) Lu-4 "Gallantry" 俠白 Xiabai

IMAGE: Also known as "Clamp White" or "Protect White." The Lung ("white" or "metal") is said to be "clamped" between the two arms.
Location : 4 cun inferior to the anterior axillary fold, 1 cun inferior to LU-3 on radial side of biceps brachii muscle. Indication : Cough, shortness of breath, pain in the chest, pain in medial aspect of upper arm.
5) Lu-5 "Cubit Marsh" 尺泽 Chize
Speciality : Sedation Point, He Sea Point, Water Point.
IMAGE: "Cubit" is a term for the elbow, and "Marsh" is a description of the Qi as it spreads out at this point, and a reminder that this is the water point on the Lung channel. "Chi" is also a Chinese measurement, about a foot long. The ulna is called "chi bone" (as it is that long) and the elbow is also sometimes referred to as "chi."
Location : On the cubital crease, in the depression lateral to biceps brachii tendon.
Indication : Cough ,asthma, hemoptysis, tonsillitis, pain & swelling of elbow & arm, skin disease.
6) Lu-6 "Opening Maximum" 孔最 Kongzui
Speciality : Xi Cleft Point.
IMAGE: Also translated as "Collection Hole", "Extreme Aperture", or "Biggest Hole" A reference to the Xi Cleft point's function of storing excess channel Qi, & this point's ability to accommodate it. "Hole" may also be a reference to the throat and Lu 6's ability to treat diseases of the throat.
Location : 7 cun above the transverse crease of the wrist.
Indication : Cough, asthma, hemoptysis, tonsillitis, pain and swelling of elbow & arm.

7) Lu-7 "Broken Sequence" 列缺 Lieque
Speciality : Luo point, Confluent point of Conception Vessel, Exit point.
IMAGE: "Broken Sequence" refers to a disturbance in the flow of Qi, which is broken because the luo channel begins here. "Lieque" is also an ancient name for lightning, a reference to the strong sensation of Qi at this point when needled correctly.
Location : 1.5 cun above the transverse crease of the wrist, superior to the styloid process of the radius.
Indication : Headache, stiff neck, cough, asthma, facial paralysis.

33) St-33 "Yin's Market" 阴市 Yinshi
IMAGE: Qi and Blood are said to meet at St-33, in much the same way as food and goods are brought together at a market. "Yin" may also be a reference to the fact that the stomach channel passes through the yin (front) part of the torso.
Location : 3 cun above the superior lateral border of the patella on line connecting the ASIS found with knee flexed. Indication : Pain and paralysis of lower extremities, knee joint.
34) St-34 "Ridge Mound" 梁丘 Liangqiu
Speciality : Xi Cleft Point.
IMAGE: Also translated as "Grain Mound," a reference to the stomach being the "granary" of the body and a reference to the "mound" of the rectus femoris muscle, through which the Stomach channel Qi passes
Location : 2 cun above the superior lateral border of the patella on line connecting the ASIS found with knee flexed. Indication : Gastralgia, diarrhea, mastitis, disorder of knee joint

11. RECENT ACUPUNCTURE POINTS HEAD AND NECK
1.Shanken : Location : On the nose midway between the inner canthus of two eyes. Indication : Headache, blurring of vision.

2. Shangying Hsiang : Location : 0.5 cun below the medial angle of eyes. Indication : Rhinitis, nasal polyp.

3. Chenming : Location : Inferior border of orbit on its inner aspect. Indication : Cataract, optic atrophy, night blindness.
4. Piliu : Location : On the outer nostril, in the of the line connecting the septum nasi and ala nasi. Indication : Acute rhinitis, facial nerve paralysis.
5. Piting : Location : At the upper end of nasobial sulcus. Indication : Rhinitis ,nasal furuncle.
6. Houtinghui (Back of listening conference) : Location : 0.5 cun above TW 17 at the level of GB 2. Indication : Vertigo, deafness, tinnitus.
7. Ting such (Listening Point) : Location : In the the middle of the line joining SI-19 with GB-2. Indication : Deafness, deaf mutism.
8. Ting Chung (Listing Clever) : Location : 0.2 cun distal to GB-2. Indication : Deafness, deaf mutism.
Acuyoga Therapy
1) Diseases of Brain and Nervous system

Disorders in these main treatment points are GV-20 and EX-6. For these point, head stand or half head stand should be done.
1) Sit on both knees. Place the hand on front floor and raise the Lumber.
Place the elbows on floor and interlace the hand. Place the head near the palms. Increase the pressure on the elbows and raise the Lumber then transfer slowly weight on the head. Slide the head forward and backward direction the left to right, with this acupressure is done on different points on head.

2) Nerves ends from brain on Palms and sole. Sit on floor with legs straight or on the chair Exhale and clench the fist of both hands and feet. Inhale and open the fist of hand and feet and stretch the fingers & toe wide. Exhale and clench fist of hands and feet. Do this 20 to 30 times as per capacity. On the centre of palm there is point P-8 and on the sole there is point. K-1. It benefits chest pain, Coma, fainting, feats, treamer in hands, psychological disorders, Stomatitis etc.
2) Diseases of Respiratory track In these the diseases are asthma, common cold, Bronchitis.
Do the acuyoga of Conceptional Vessel, Lung. Lie on the back by folding knees bring the legs near the Lumber, Clench the fist and hold behind the neck. Bend the fist from wrist contact both wrist. Inhale slowly and Lift the lumber. Exhale and down the lumber to floor. This is Bridge pose or Setubandhasan. With this exercise the points on hands LI-4, LI-3 and point on the neck GB-20, GV-14,15 UB-10 and UB-11 are pressed. It benefits Asthma, Bronchitis, Common cold sore throat, headache, menses problem, & fever etc.
Do the steps 5 & 6 in acuyoga and make nose hot.

9) Locomotors Disorders Do the acuyoga of Governing Vessel, Urinary Bladder, Spleen and step No. 27 of acuyoga Lumber traction
a) Lie on the back near wall, by folding knees place the toes on the wall. Keep hands on the floor. Inhale and by pressing hands on floor and pressing toes on the wall lift the lumber away from floor, exhale and slowly down the lumber. Repeat this 5 to 15 times as per capacity. Due to this exercise pressure on the Lumber spine decreases and relief pain.

b) Lie on back straight Raise both legs straight from Lumber at right angle. Hold this position for 10 seconds. Due to this exercise Lumber spines touch the floor and they got relief. (Ardha Halasana)
c) Lie on back, fold the knees on stomach hold it with both hands and rock left & right then forward and backward.

d) Do the step No. 29 in Acuyoga punching the sacrum.
e) Take medicine ball of 5 to 7 inch diameter underneath the lumber region and move lumber over it left right.





Acuyoga for Beautiful face 1) First do the steps 1 to 10 in acuyoga. in the fig. the points on face are shown. first with the ring finger massage circularly on the point Ex-1. It benefits that it is the brow chakra. At this level there is pituitary gland in the centre of brain. Pituitary gland controls all glands. This massage benefits vertigo, headache, common cold, psychological disorders etc.
2) With both hands index finger UB-1 and middle finger UB-2 massage circularly 10 to 30 seconds this benefits for eye disorders, facial paralysis etc.
3) With both hands ring finger massage the point Extra-3 circularly. This benefits eye disorders, eye pain, facial paralysis, ptosis.
On this points with both hands ring finger press downwards same time stretch eyebrow upward direction. Repeat this for 10 times. This benefits wrinkles on eyelids and look broad eyes.

18 Analysis of Acupuncture Points According to Chinese Image Meaning
Chinese Characters ( Script ) are in the image form. Traditionally the knowledge of Chinese medicine was handeled from father to son or teacher to student. Memorization of skill was required and the point name containing mnemonic symbols aided the retentation of information about the point. The point names or image also contain hidden meanings only known to student of particular master. This way the the point names helped to keep a master’s secrets safe from other practioners and thus protected his income.
With the time and study the points names become more than lables, they become guides to understanding the points and system of medicine that named the point. The inherent ambiguity of the point names lent an air of mystery to the healing arts and aided in preserving the secrets of the masters. In addition the point name revealed important information about the points and imbuled them with poetic spirit that become multitude of valuable associations.
Acupuncture Points are generally analysed as per their Functions, Location, Five Elements , Five Phases, Relation with Yin and Yang, Trlation with Channel.

According to function of Points :
ST-1 means Tear Container.
ST-2 means Four Whites
According to Different Types of Point :
H-6 means Yin Cleft or Cleft-Xi. This is the Xi-Cleft point of Heart Channel.
LIV-5 means Wood Worm Canal. This is the Luo Connecting point of Liver Channel.
According to the location of point :
SI-8 means wrist bone, thus denotes the location of that point.
ST-32 means crounching Rabit , this denotes the shape of anterior of thigh muscle ( Rectus femoris Muscle )
According to relation with Yin and Yang :
UB-59 means tarsal Yang or Fu Yang. This point is on the yang side of lateral malleolus.
According toFive Phase :
K-5 means water spring.
According to five element :
LU-4 means Gallantry white or Xia Bai . Here White colour denotes the metal element of Lung Chanel.
Certain points denotes the functions to the acupuncturist.e.g. ST-4 means Earth Granary.Stomach is related Granery and Earth is the Element of the Stomach Channel.
LU-1 means Central Mension or Central Treasury. Here at this point the Lung Channel meets the Stomach Channel. Stomach is the Centrel channel and Lung is the treasury Qi’s treasury.
Certain points are dangerous for acupuncture. LI-13 means Arm Five Finger Inside. Here improper needling harms the Qi.
Some points shows Double meaning. TW-21 means Ear Gate this shows the point’s location and it’s function on ear disorders. H-9 Yin Cleft.This shows the point is in the yin side of the hand or the polarity of nthe Heart Channel is Yin and it is the Xi-Cleft poit of Heart Channel.
Following are examples of Acupuncture points as per categorization
Yin Yin’s Intersection or Junction of Yin REN-7

Yin’s Market ST-33
Yang Yang’s Intersection GB-35
Yang’s Tomb Spring GB-34
Yang Valley SI- 5
Five Phases Yellow Emperor (Grandfather’ Grandson) SP-4
Lesser Shang (Lesser Metal’s Note) LU-11
Organ’ name Heart Shu UB-15
Gall Bladder Shu UB-19
Qi or Chi Sea Of Qi Ren-6
Hinge at the Source or Origin Pass Ren-4
Blood Sea Of Blood SP-10
Path of
Channel Eyebrow’s Pouring (Ascension) UB-3
Intersection Three Yin Intersection SP-6
of channel Three Yang Intersection TW-8
Hundred Point Meeting DU-20
Channel Name Girdling Vessel GB-26
Point Function
Wind Pool GB- 20
Bright Eyes UB-1
Bright Eyesight GB-37
Anatomical Location
Breast Centre ST-17

Middle of Naval REN-8
Jade Pillow UB-9
Knee’s Yang Hinge GB-33
Location Hint Basket’s Door ( Winnower Gate) SP-11
Standing By White LU-4
Body Measurement
Cubit Marsh Or Cubitum Elbow LU-5
Leg Three Measure ST-36
Arm’s Three Measure LI-10
Astronomic Sun & Moon GB-24
Celestial Pivot (Heaven’s Axis) ST-25
Meterologic Wind Mansion (Wind’s Dwelling) DU-16
Cloud’s Gate (Cloud’s Door) LU-2
Geographic Support the Mountain UB-57
Outer Mound ST-26
Water Relation
Branch Ditch TW-6
Shining Sea K-6
Name of Historical Place
Metal Gate (Golden Door) UB-63
Shang Hill or Metal Mound
or Mound of Commerce SP-5
Numerical Second Place (Between Two) LI-2
Fifth Place UB-5
Architectural Structure

Gate Tower Great Gate Tower REN-14
Palace Purple Palace Ren-19
Store Room Store Room ST-14
Storehouse Stomach Granary (Storehouse) UB-50
Abode Qi Abode ST-11
Bowel Abode SP-13
Hall Jade Hall Ren-18
Chamber Will Chamber UB-52
Corridor Corridor Walk K-22
Court Spirit Court DU-24
Cout Yard Central Court Yard REN-16
Window Eye Window GB-16
Celestial Window SI-16
Gate Wind Gate UB-12
Spirit Gate H-7
Door Qi Door ST-13
Space Unyielding Space (Between Strength) DU-18
Second Space (Second Interval) LI-2
Town Planning
Metropolises Great Metropolis SP-2
Yin Metropolis K-19
Market Wind Market GB-31
Yin’s Market ST-33
Village Chest Village SP-19
District Foot Three Li ST-36
Connecting Li H-5

Path Spirit Path DU-11
Linking Path or Maintain the Way GB-28
Pass Yang Pass (Upper Hinge) GB-3
Outer Pass (Outer Gate)
Plant, Animal and object
Plant Grain Bone-Hole ( Grain Seam) LI-19
Animal Crouching Rabbit ST-32
Object Celestial Tripod LI-17
Character Celestial Pivot ST-25
Inner Courtyard ST-44

104 Meeting Points

1. LU-01 (Zhong Fu) Central Treasury, Central Residence
Meeting Point of the Lung and Spleen Channels
Front Mu of the Lungs
2. LU-09 (Tai Yuan) Great Abyss
Yuan (Source) Point
Shu-Stream & Earth Point
Hui-Meeting Point of the Vessels
3. LI-14 (Bi Nao) Upper Arm
Meeting Point of the Large Intestine Channel with the Small Intestine and Bladder
Channels
4. LI-15 (Jian Yu) Shoulder Bone
Meeting Point of the Large Intestine Channel with the Yang Motility Vessel
5. LI-16 (Ju Gu) Great Bone
Meeting Point of the Large Intestine Channel with the Yang Motility Vessel
6. LI-20 (Ying Xiang) Welcome Fragrance
Meeting Point of the Large Intestine and Stomach Channels
7. ST-01 (Cheng Qi) Tear Container
Meeting Point of the Stomach Channel with the Yang Motility and Conception Vessels
8. ST-03 (Ju Liao) Great Bone Hole
Meeting Point of the Stomach Channel with the Yang Motility Vessel
9. ST-04 (Di Cang) Earth Granary
Meeting Point of the Stomach and Large Intestine Channels with the Yang Motility
and Conception Vessels
10. ST-07 (Xia Guan) Below the Joint
Meeting Point of the Stomach and Gallbladder Channels
11. ST-08 (Tou Wei) Head Corner

Meeting Point of the Stomach and Gallbladder Channels with the Yang Motility
Vessel
12. ST-09 (Ren Ying) Man's Prognosis
Meeting Point of the Stomach and Gallbladder Channels
Point of the Window of Heaven, Point of the Sea of Qi
13. ST-12 (Que Pen) Empty Basin
Meeting Point of the Stomach, Large Intestine, Small Intestine, Sanjiao, and
Gallbladder Channels
14. ST-30 (Qi Chong) Surging Qi
Meeting Point of the Stomach Channel with the Penetrating Vessel
Point of the Sea of Water and Grain
15. SP-06 (San Yin Jiao) Three Yin Intersection
Meeting Point of the Spleen, Liver, and Kidney Channels
16. SP-12 (Chong Men) Surging Gate
Meeting Point of the Spleen and Liver Channels with the Yin Linking Vessel
17. SP-13 (Fu She) Bowel Abode
Meeting Point of the Spleen and Liver Channels with the Yin Linking Vessel
18. SP-15 (Da Heng) Great Horizontal
Meeting Point of the Spleen Channel with the Yin Linking Vessel
19. SP-16 (Fu Ai) Abdominal Lament
Meeting Point of the Spleen Channel with the Yin Linking Vessel
20. SI-10 (Nao Shu) Upper Arm Shu
Meeting Point of the Small Intestine and Bladder Channels with the Yang Linking
and Yang Motility Vessels
21. SI-12 (Bing Feng) Grasping the Wind
Meeting Point of the Small Intestine, Large Intestine, Sanjiao and Gallbladder

Channels
22. SI-18 (Quan Liao) Cheek Bone Hole
Meeting Point of the Small Intestine and Sanjiao Channels
23. SI-19 (Ting Gong) Auditory Palace
Meeting Point of the Small Intestine, Sanjiao and Gallbladder Channels
24. BL-01 (Jing Ming) Bright Eyes
Meeting Point of the Bladder, Small Intestine, Stomach, Gallbladder, and
Sanjiao Channels with the Governing, Yin Motility and Yang Motility Vessels
25. BL-11 (Da Zhu) Great Shuttle
Hui-Meeting Point of the Bones, Point of the Sea of Blood,
Meeting Point of the Bladder, Small Intestine, Sanjiao and Gallbladder Channels
and the Governing Vessel
26. BL-12 (Feng Men) Wind Gate
Meeting Point of the Bladder Channel with the Governing Vessel
27. BL-17 (Ge Shu) Diaphragm Shu
Hui-Meeting Point of Blood
28. BL-31 (Shang Liao) Upper Bone Hole
Meeting Point of the Bladder and Gallbladder Channels
29. BL-32 (Ci Liao) Second Bone Hole
Meeting Point of the Bladder and Gallbladder Channels
30. BL-33 (Zhong Liao) Central Bone Hole
Meeting Point of the Bladder and Gallbladder Channels
31. BL-34 (Xia Liao) Lower Bone Hole
Meeting Point of the Bladder and Gallbladder Channels
32. BL-35 (Hui Yang) Meeting of Yang
Meeting of Yang

33. BL-41 (Fu Fen) Attached Branch
Meeting Point of the Bladder and Small Intestine Channels
34. BL-61 (Pu Can) Subservient Visitor
Meeting Point of the bladder Channel with the Yang Motility Vessel
35. BL-63 (Jin Men) Metal Gate
Xi (Cleft) Point
Meeting Point of the Bladder Channel with the Yang Linking Vessel
36. KI-11 (Heng Gu) Pubic Bone
Meeting Point of the Kidney Channel with the Penetrating Vessel
37. KI-12 (Da He) Great Manifestation
Meeting Point of the Kidney Channel with the Penetrating Vessel
38. KI-13 (Qi Xue) Qi Hole
Meeting Point of the Kidney Channel with the Penetrating Vessel
39. KI-14 (Si Man) Fourfold Fullness
Meeting Point of the Kidney Channel with the Penetrating Vessel
40. KI-15 (Zhong Zhu) Central Flow
Meeting Point of the Kidney Channel with the Penetrating Vessel
41. KI-16 (Huang Shu) Huang Shu
Meeting Point of the Kidney Channel with the Penetrating Vessel
42. KI-17 (Shang Qu) Shang Bend
Meeting Point of the Kidney Channel with the Penetrating Vessel
43. KI-18 (Shi Guan) Stone Pass
Meeting Point of the Kidney Channel with the Penetrating Vessel
44. KI-19 (Yin Du) Yin Metropolis
Meeting Point of the Kidney Channel with the Penetrating Vessel
45. KI-20 (Tong Gu) Open Valley

Meeting Point of the Kidney Channel with the Penetrating Vessel
46. KI-21 (You Men) Dark Gate
Meeting Point of the Kidney Channel with the Penetrating Vessel
47. P-01 (Tian Chi) Celestial Pool
Meeting Point of the Pericardium, Gallbladder, Liver and Sanjiao Channels
Point of the Window of Heaven
48. SJ-13 (Nao Hui) Upper Arm Convergence
Meeting Point of the Sanjiao Channel and the Yang Linking Vessel
49. SJ-15 (Tian Liao) Celestial Bone Hole
Meeting Point of the Sanjiao and Gallbladder Channels and the Yang Linking Vessel
50. SJ-17 (Yi Feng) Wind Screen
Meeting Point of the Sanjiao and Gallbladder Channels
51. SJ-20 (Jiao Sun) Angle Vertex
Meeting Point of the Sanjiao, Small Intestine and Gallbladder Channels
52. SJ-22 (He Liao) Harmony Bone Hole
Meeting Point of the Sanjiao, Gallbladder and Small Intestine Channels
53. GB-01 (Tong Zi Ziao) Pupil Bone Hole
Meeting Point of the Gallbladder, Small Intestine and Sanjiao Channels
54. GB-03 (Shang Guan) Upper Gate
Meeting Point of the Gallbladder, Sanjiao and Stomach Channels
55. GB-04 (Han Yan) Forehead Fullness
Meeting Point of the Gallbladder, Sanjiao and Stomach Channels
56. GB-05 (Xuan Lu) Suspended Skull
Meeting Point of the Gallbladder, Stomach, Sanjiao and Large Intestine Channels
57. GB-06 (Xuan Li) Suspended Tuft
Meeting Point of the Gallbladder, Stomach, Sanjiao and Large Intestine Channels

58. GB-07 (Qu Bin) Temporal Hairline Curve
Meeting Point of the Gallbladder and Bladder Channels
59. GB-08 (Shuai Gu) Valley Lead
Meeting Point of the Gallbladder and Bladder Channels
60. GB-09 (Tian Chong) Celestial Hub
Meeting Point of the Gallbladder and Bladder Channels
61. GB-10 (Fu Bai) Floating White
Meeting Point of the Gallbladder and Bladder Channels
62. GB-11 (Tou Qiao Yin) Head Portal Yin
Meeting Point of the Gallbladder, Bladder, Small Intestine and Sanjiao Channels
63. GB-12 (Wan Gu) Completion Bone
Meeting Point of the Gallbladder and Bladder Channels
64. GB-13 (Ben Shen) Root Spirit
Meeting Point of the Gallbladder Channel with the Yang Linking Vessel
65. GB-14 (Yang Bai) Yang White
Meeting Point of the Gallbladder with the Yang Linking Vessel and the Sanjiao,
Stomach and Large Intestine Channels
66. GB-15 (Tou Lin Qi) Head Overlooking Tears
Meeting Point of the Gallbladder and Bladder Channels with the Yang Linking Vessel
67. GB-16 (Mu Chuang) Eye Window
Meeting Point of the Gallbladder Channel with the Yang Linking Vessel
68. GB-17 (Zheng Ying) Upright Construction
Meeting Point of the Gallbladder Channel with the Yang Linking Vessel
69. GB-18 (Cheng Ling) Spirit Support
Meeting Point of the Gallbladder Channel with the Yang Linking Vessel
70. GB-19 (Nao Kong) Brain Hollow

Meeting Point of the Gallbladder Channel with the Yang Linking Vessel
71. GB-20 (Feng Chi) Wind Pool
Meeting Point of the Gallbladder and Sanjiao Channels with the Yang Motility and
Yang Linking Vessels
72. GB-21 (Jian Jing) Shoulder Well
Meeting Point of the Gallbladder, Sanjiao, and Stomach Channels with the Yang
Linking Vessel
73. GB-23 (Zhe Jin) Sinew Seat
Meeting Point of the Gallbladder and Bladder Channels
74. GB-24 (Ri Yue) Sun and Moon
Meeting Point of the Gallbladder and Spleen Channels
Front Mu of the Gallbladder
75. GB-26 (Dai Mai) Girdling Vessel
Meeting Point of the Gallbladder Channel with the Girdling Vessel
76. GB-27 (Wu Shu) Fifth Pivot
Meeting Point of the Gallbladder Channel with the Girdling Vessel
77. GB-28 (Wei Dao) Linking Path
Meeting Point of the Gallbladder Channel with the Girdling Vessel
78. GB-29 (Ju Liao) Squatting Bone Hole
Meeting Point of the Gallbladder Channel with the Yang Motility Vessel
79. GB-30 (Huan Tiao) Jumping Round
Meeting Point of the Gallbladder and Bladder Channels
Ma Dan-yang Heavenly Star Point
80. GB-34 (Yang Ling Quan) Yang Mound Spring
He-Sea & Earth Point
Hui-Meeting Point of the Sinews

Ma Dan-yang Heavenly Star Point
81. GB-39 (Xuan Zhong) Suspended Bell, Suspended Time
Hui-Meeting Point for Marrow
82. LIV-13 (Zhang Men) Camphorwood Gate
Hui-Meeting Point of the Zang, Meeting Point of the Liver and Gallbladder Channels
Front Mu of the Spleen
83. LIV-14 (Qi Men) Cycle Gate
Meeting Point of the Liver and Spleen Channels with the Yin Linking Vessel
Front Mu of the Liver
84. REN-01 (Hui Yin) Meeting of Yin
Meeting Point of the Conception, Penetrating and Governing Vessels
Sun Si-miao Ghost Point
85. REN-02 (Qu Gu) Curved Bone
Meeting Point of the Conception Vessel with the Liver Channel
86. REN-03 (Zhong Ji) Central Pole
Meeting Point of the Conception Vessel with the Spleen, Liver, and Kidney Channels
Front Mu of the Bladder
87. REN-04 (Guan Yuan) Origin Pass
Meeting Point of the Conception Vessel with the Spleen, Liver, and Kidney Channels
Front Mu of the Small Intestine
88. REN-07 (Yin Jiao) Yin Intersection
Meeting Point of the Conception and Penetrating Vessels and the Kidney Channel
89. REN-10 (Xia Wan) Lower Venter
Meeting Point of the Conception Vessel with the Spleen Channel
90. REN-12 (Zhong Wan) Central Venter
Hui-Meeting Point of the Fu, Meeting Point of the Conception Vessel with the Small

Intestine, Sanjiao and Stomach Channels
Front Mu of the Stomach
91. REN-13 (Shang Wan) Upper Venter
Meeting Point of the Conception Vessel with the Stomach and Small Intestine Channels
92. REN-17 (Shan Zhong) Chest Center
Hui-Meeting Point of the Qi, Point of the Sea of Qi, Meeting Point of the Conception
Vessel with the Spleen,
Kidney, Small Intestine and Sanjiao Channels
Front Mu of the Pericardium
93. REN-22 (Tian Tu) Celestial Chimney
Meeting Point of the Conception and Yin Linking Vessels
Point of the Window of Heaven
94. REN-23 (Lian Quan) Ridge Spring
Meeting Point of the Conception and Yin Linking Vessels
95. REN-24 (Cheng Jiang) Sauce Receptacle, Container of Fluids
Meeting Point of the Conception Vessel with the Governing Vessel and the Large
Intestine and Stomach Channels
Sun Si-miao Ghost Point
96. DU-01 (Chang Qiang) Long Strong
Luo (Connecting) Point
Meeting Point of the Governing Vessel with the Conception Vessel and the
Gallbladder and Kidney Channels
97. DU-14 (Da Zhu) Great Hammer
Point of the Sea of Qi, Meeting Point of the Governing Vessel with the Six Yang
Channels of the Hand and Foot
98. DU-15 (Ya Men) Mute's Gate

Point of the Sea of Qi, Meeting Point of the Governing and Yang Linking Vessels
99. DU-16 (Feng Fu) Wind Mansion
Point of the Sea of Marrow, Meeting Point of the Governing and Yang Linking
Vessels
Point of the Window of Heaven, Sun Si-miao Ghost Point
100. DU-17 (Nao Hu) Brain's Door
Meeting Point of the Governing Vessel with the Bladder Channel
101. DU-20 (Bai Hui) Hundred Convergences
Point of the Sea Of Marrow, Meeting Point of the Governing Vessel with the Bladder,
Gallbladder,
Sanjiao and Liver Channels
102. DU-24 (Shen Ting) Spirit Court
Meeting Point of the Governing Vessel with the Bladder and Stomach Channels
103. DU-26 (Shui Gou) Water Trough
Meeting Point of the Governing Vessel with the Large Intestine and Stomach Channels
Sun Si-miao Ghost Point
104. DU-28 (Yin Jiao) Gum Intersection
Meeting Point of the Governing Vessel with the Conception Vessel and the Stomach
Channel

Index of Acu-Points with English Meanings.
A
Abdomen-Bind SP 4 地仓
Abdomen-Lament SP 16 膺
Abdomen-Tonggu K 20 腹通谷
窗
Abdomen-Yinjiao Ren 7 阴交
Abdomen-Zhongzhu K 15 中注
All-Round Flourishing SP20 周荣
Angel Vertex TW 20 角孙
Arm Five Li LI 13 手五里
Arm Three Li LI10 鱼际
Armpit Pool (abyss) GB 22 渊腋
Assuming Fullness ST 20 承满
Attached Branch ST 41 解谿
Auditory Convergence GB 2 听会
Auditory Palace SI 9 肩贞
B
Back Revine SI 3 後溪
Bamboo Gathering UB 2 攒竹
Beam Gate ST 21 梁门
Beam Hill ST 34 梁丘
Before Vertex Du 21 前顶

Behind Vertex Du 19 后顶
Below the Joint ST 7 下关
Bend Middle UB 40 委中
Bend Yang UB 39 委阳
Bladder Huang UB 53 胞肓
Bladder Shu UB 28 膀胱俞
Blazing Valley K 2 然谷
Body Pillar Du 12 身柱
Bountiful Bulge ST 40 承满
Bowel Abode SP 13 府舍
Brain Hollow GB 19 脑空
Brain Door Du 17 脑户
Branch Ditch TW 6 支沟
Branch to correct SI 7 支正
Breast Centre ST 17 乳中
Breast Root ST 18 乳根
Breast Window ST 16 膺
Bright Eyes UB 1 睛明
窗
Bright Light GB 37 光明
Broken Sequence LU7 列缺
Bundle Bone UB 65 束骨
C
Calf's Nose ST 35 上巨止
Camphorwood Gate LIV 13 章门

Capital Gate UB 64 京骨
Celestial Bone Hole TW 15 天髎
Celestial Chimney Ren 22 天突
Celestial Connection UB 7 玉枕
Celestial Countenance SI 17 天容
Celestial Gathering SI 11 天宗
Celestial Hub GB 9 天沖 Celestial Pillar UB 10 天柱 Celestial Pivot ST 25 天枢
Celestial Pool P 1 天池
Celestial Ravine SP 18 天溪
Celestial Spring P 2 天泉
Celestial Store House LU 3 天府
Celestial Tripod LI 17 天鼎
Celestial Well TW 10 天井
Celestial Window SI 16 天窗
Celestial Window TW 16 天口
Centre Palace Ren 16 中庭
Central Back Bone UB 29 中膂俞
Central Bone Hole UB 33 中髎
Central Flow K 15 中注
Central Hub P 9 中冲
Central Islet TW 3 中渚
Central Metropolis LIV 6 中都
Central Pivot Du 7 中枢
Central Pole Ren 3 中极

Central River GB 32 膝阳关
Central Shoulder SI 15 肩中俞
Central Treasury LU 1 中府
Central Venter Ren 12 中脘
Channel Ditch LU 8 经渠
Cheek Bone Hole SI 18 颧髎
Chest Centre Ren 17 膻中
Chest Village SP 19 胸乡
Clear Cold Abyss TW 11 清冷渊
Cleft Gate P 4 郄门
Cloud Gate LU 2 云 门
Collection Hole LU 6 孔最
Completion Bone GB 12 头 完骨
Connecting Li SI 5 阳谷
Convergence and Gathering TW 7 会宗
Corridor Walk K 22 步廊
Crooked Wall SI 13 曲垣
Crouching Rabbit St-32 伏兔
Cubit Marsh LU 5 尺泽
Curved Bone Ren 2 曲骨
Cyan Spirit H 2 青灵
Cycle Gate LIV 14 期门
D
Dark Gate K 21 幽门

Declining Connection UB 8 络却
Deviation Turn UB 4 曲差
Diaphragm Pass UB 46 膈关
Diaphragm shu UB 17 膈俞
Dispersing River bed TW 12 消泺
E
Ear Gate TW 21 耳门
Earth Five Fold Convergence GB 42地五会
Earth Granary ST 4 地仓
Earth's Crux SP 8 地机
Elbow Bone LI 12 肘髎
Empty Basin ST 12 缺盆
Extending Vessel UB 62 申脉
Extremity of Yang Du 9 至阳
Extremity of Mouth Du 27 兑端
Eye Window GB 16 目窗
Eyebrow Ascension GB 3 上关
F
Fifth Pivot GB 27 五枢
Fifth Place UB 5 五处
Fish Border LU 10 鱼际
Floating White GB 10 浮白
Florid Canopy Ren 20 华蓋

Fontanel Meeting Du 22 囟会
Food Hole SP 17 食窦
Foot Five Li LIV 10 足五里
Foot over looking Tears GB 41 足临泣
Foot Portal Yin GB 44 足窍阴
Forehead Fullness GB 4 颔厌
Four Rivers TW 9 四渎
Four Whites ST 2 四白
Front Valley SI 2 前谷
G
Gallbladder Shu UB 19 胆俞
Gau Huang Shu UB 43 膏肓俞
Gate of Abundance UB 37 殷门
Girdling Vessel GB 26 带脉
Governing Shu UB 16 督俞
Grain Bone Hole LI 19 口禾
Grasping the Wind SI 12 秉
髎
风
Great Abyss LU 9 太渊
Great Bone LI 16 巨骨
Great Bone Hole ST 3 巨髎
Great Embracement SP 21 大包
Great Gigantic ST 27 大巨
Great Hammer Du 14 大椎
Great Horizontal SP 15 大横
Great Manifestation K 12 大赫
Great Metropolis SP 2 大都

Great Mound P 7 大陵
Great Ravine K 3 太溪
Great Reception ST 5 大
Great Shuttle UB 11 大杼
迎
Great Tower Gate Ren 14 巨阙
Guarding White LU 5 尺泽
Guest House K 9 築賓
Gum Intersection Du 28 齦交
Gushing Spring K 1 涌泉
H
Harmony Bone Hole TW 22 耳和髎
Head Corner ST 8 头维
Head Overlooking Tears GB 15 头临泣
Head Portal Yin GB 11 头窍 阴 Heart Shu UB 15 心俞
Hidden White SP 1 隐白
Highest spring H 1 极泉
Hill Ruins GB 40 丘止
Huang Gate UB 51 肓门
Huang Shu K 16 肓俞
Humor Gate TW 2 液门
Hun Gate UB 47 魂门
Hundred Convergences DU 20 腰俞
I

Inner Court ST 44 内庭
Inner Pass P 6 內关
Instep Yang UB 59 跗阳
Interior Strengthening Ren 2 曲骨
Intermediatery Courier P 5 间使
Intersection Reach K 5 水泉
J
Jade Hall Ren 18 玉堂
Jade Pillow UB 9 玉枕
Jade Pivot Ren 21 璇 机
Jaw Bone ST 6 颊车
Jue Yin Shu UB 14 厥阴俞
Jumping Round GB 30 环 跳 K
Kidney Shu UB 23 肾俞
Kiln Path Du 13 陶道
Knee Joint LIV 7 膝关
Knee Yang Joint GB 33 膝阳关
Kunlun Mountain UB 60 昆仑
L
Large Goblet K 4 大钟 Large Intestine Shu UB 25 大腸俞
Large Pile LIV 1 大敦

Leaking Valley SP 7 漏谷
Leg Three Li ST 36 足三里
Lesser Mansion H 8 少府
Lesser Marsh SI 1 少泽
Lesser Sea H 3 少海
Lesser Shang LU-11 少 商
Lesser Surge H9 少沖
Life Gate Du 4 命门
Light Guard UB 6 承光
Linking Path GB 28 维道
Lively Centre K 26 彧中
Liver Shu UB 18 肝俞
Long Strong Du 1 长强
Lower Bone Hole UB 34 下髎
Lower Great Hollow ST 39 下巨止
Lower Ridge LI 8 下廉
Lower Venter Ren 10 下脘
Lumber Shu Du 2 腰俞
Lumber Yang Du 3 腰阳关
Lung Shu UB 13 肺俞
M
Man's Wellcome ST 9 人迎
Marsh at Bend P 3 曲泽
Meeting of Yang UB 35 会阳
Meeting of Yin Ren 1 会阴

Metal Gate UB 63 金门
Mound centre LIV 4 中封
Mountain Support UB 57 承山
Moving between LIV 2 行间
Mute's Gate Du 15 哑门
N
Not Contained ST 19 不容
Nourishing the Aged SI 6 养老
O
Open Valley K 20 腹通谷
Origin Pass Ren 4 关 元
Origin Pass Shu UB 26 关元俞
Outer Hill GB 36 外丘
Outer Mound ST 26 外陵
Outer Pass TW 5 外关 Outer shoulder Shu SI 14 肩外俞
P
Palace of Toil P 8 劳宮 Pass Gate ST 22 关门
Passage Hub TW 1 关冲
Pinched Ravine GB 43 俠溪
Po Door UB 42 魄戶
Pool at the Bend LI 11 曲池
Protuberance Assistant LI 18 扶突
Pubic Bone K 11 横谷
Pupil Bone Hole GB 1 瞳子髎

Purple Palace Ren 19 胸
紫宮
Q
Qi Abode ST 21 梁门
Qi Door ST 13 气戶
Qi Point K 13 气 穴
R
Ravine divides ST 41 解谿
Reaching Yin UB 67 至阴
Recover Flow K 7 復溜
Reflection Abode UB 49 意舍
Return ST 15 屋翳
Ribbon Opening ST 38 条口
Ridge Spring Ren 23 廉泉
Roof ST 15 屋翳
Root Spirit GB 13 本神
S
Sauce Receptacle Ren 24 承漿
Sea of Blood SP10 血海
Sea of Qi Ren 6 气海
Sea of Qi Shu UB 24 气海俞
Second Bone Hole UB 32 次髎 Second Space LI 2 二间
Sequential Limit UB 54 秩边
Severe Mouth ST 45 厉兑

Shang Bend K 17 商曲
Shang Hill SP 5 商丘 Shang Yang LI 1 商阳
Shining Sea 照海
Shoulder Bone LI 15 肩髃
Shoulder Opening TW 14 肩髎
Shoulder Well GB 21 肩井
Shu Mansion K 27 俞府
Silk Bamboo Hole TW 23 丝竹空
Sinew Contraction Du 8 筋缩
Sinew Seat GB 23 輒筋
Sinew Support UB 56 承筋
Skull Rest TW 19 颅息
Slippery Flesh Gate ST 24 滑肉门
Small Intestine Shu UB 27 小腸俞
Small Sea SI 8 小海
Spasm Vessel TW 18 契脈
Spinal Centre Du 6 脊中
Spirit Court Du 24 神庭
Spirit Gate H 7 神门
Spirit Gate Ren 8 神阙 Spirit Hall UB 44 神堂
Spirit Path Du 11 神道
Spirit Pathway H4 灵道
Spirit Ruins K 24 灵止
Spirit Seal K 23 神封

Spirit Storehouse K 25 水泉
Spirit Support GB 18 承灵
Spirit Tower Du 10 棂台
Spleen Shu UB 20 脾俞
Spring at the Bend LIV 8 曲泉
Squatting Bone Hole GB 29 居髎
Stomach Granary UB 50 胃仓
Stomach Shu UB 21 胃俞
Stone Gate Ren 5 石门
Stone Pass K 20 腹通谷
Store Room ST 14 库房
Subservient Visitor UB 61 仆参
Sun and Moon GB 24 日月
Sunken Valley ST 43 陷谷
Superficial Cleft UB 38 浮郄
Support the Torso UB 36 承扶
Supreme Surge LIV 3 太沖
Supreme Unity ST 23 太乙
Supreme White SP 3 太白
Surging Gate SP 12 沖门
Surging Qi ST 30 气沖
Surging Yang ST 32 伏兔
Suspended Bell GB 39 悬钟
Suspended Pivot Du 5 悬枢
Suspended Skull GB 5 悬颅
Suspended Tuft GB 6 悬厘

T
Taking Flight UB 58 飞阳
Tear Container ST 1 承泣
Temporal Hairline GB 7 曲鬓
Thigh Joint ST 31 髀关
Third Space LI 3 三间
Three Yang Connections TW 8 三 阳 絡
Three Yin Junctions SP 6 三阴交
Tripple Burner Shu UB 22 三焦俞
True Shoulder SI 9 肩贞
Turtledove Tail Ren 15 鸠尾
U
Union valor LI 4 合谷
Unyielding Space Du 18 强间
Upper Arm LI 14 臂臑
Upper Arm Convergence TW 13 臑会
Upper Arm Shu SI 10 臑俞
Upper Bone Shu UB 31 上髎
Upper Gate UB 3 眉冲
Upper Great Hollow ST 37 上巨止
Upper Ridge LI 9 上廉
Upper Star Du 23 上星
Upper Venter Ren 13 上脘
Upright Construction GB 17 正营
Urgent Pulse LIV 12 急脉

ACUPUNCTURE POINTS ON SPECIFIC AREA USE AS LOCAL POINTS FOR THAT AREA
1. SCALP - DU-20, GB-8,16,17,18, UB-5,6,7,8,ST-8, EX-6.
2. EYE - EX-1,2,3,4, ST-1,UB-1,2, GB-1,TW-23.
3. FACE - LI-19,20, SI-18,19, GB-2,3, TW-22, DU-25, 26,27,28,
REN-24, EX-5,10, ST-2,3,4,5,6,7.
4. FRONT OF NECK - LI-15,16,17, SI-16,17, EX-11,12, REN-22,23.
5. NAPE OF NECK - SI-15, TW-16, GB-19,20, UB-10, DU-14,15.
6. CHEST - P-1, LU-1,2, LIV-14, SP-17,18,19,20, K-22 TO K-27, ST-12 TO 18, REN-13 TO 21.

7. BACK - UB-11 TO UB-35,41 TO 54, EX-21, SI-9,10,11,12,13.
8. ABDOMEN - ST-20 TO 30, SP-15,16,17, K-12 TO 21, REN-2 TO 12
9. ARM - LU-3,4,P 2, H-2, TW-11,12,13,14,15, LI-12,13,14.
10. FOREARM - LI-5 TO 10, H-4,5,6, LU-7,8, P-4,5,6, SI-6,7,8, TW-6,7,8.
11. ELBOW - LU-5, P-3, H-3, SI-8, TW-10, LI-11.
12. WRIST - P-7, H-7, LU-9, SI-4, TW-4, LU-9.
13. HAND - H-8,9, P-8,9, LU-10,11, TW-1,2,3, SI-1,2,3,4, LI-1,2,3,4, EX-28,29,30.
14. BUTTOCK - GB-30,31, ST-32,33, UB-36, 37, SP-11,12, LIV-10,11
15. KNEE - ST-34,35, GB-33,34, UB-38,39, 40, SP-10, K-10, LIV-8, EX-31,32.
16. LEGS - UB-55,56,57,58,59, GB-35,36,37,38, ST-36,37,38,39,40, SP-6,7,8,9, LIV-5,6,7, K-7,8,9.
17. ANKLE - ST-41, GB-41, UB-60,61,62, SP-5, LIV-4, K-3,4,5,6.
18. FOOT - ST-42,43,44,45, GB-42,43,45, UB-62,63,64,65,66,67,
K-1,2,3, LIV-1,2,3,4, SP-1,2,3,4,5.
Index of Acu-Points with Chinese alphabet

A
Abdomen-Tonggu K 20 腹通谷
Abdomen-Yinjiao Ren 7 阴交
Abdomen-Zhongzhu K 15 中注 Abdomen-Zigong Ex 16 子宫 Anmian I Ex 8 安眠1 Anmian II Ex 9
安眠2
B
Bafeng Ex 36 八风
Baihuanshu UB 30 白环 俞
Baihui Du 20 百会
Baohuang UB 53 胞肓
Baxie Ex 28 八邪
Benshen GB 13 本神
Biguan ST 31 髀关
Binao LI 14 臂臑
Bingfeng SI 12 秉风
Bizhong Ex 23 臂中
Bulang K 22 步廊
Burong ST 19 不容
C
Changqiang Du 1 长强
Chengfu UB 36 承扶
Chengguang UB 6 承光
Chengjiang Ren 24 承漿

Chengjin UB 56 承筋
Chengling GB 18 承灵
Chengman ST 20 承满
Chengqi ST 1 承泣
Chengshan UB 57 承山
Chest-Zigong Ren 19 胸
Chize LU 5
紫宮
尺泽
Chongmen SP 12 沖门
Chongyang ST 42 沖阳
Ciliao UB 32 次髎
D
Dabao SP 21 大包
Dachangshu B 25 大腸俞
Dadu SP 2 大都
Dadun LIV 1 大敦
Dahe K 12 大赫
Daheng SP 15 大横
Daimai GB 26 带脉 Daju ST 27 大巨
Daling P 7 大陵
Dannang Ex 35 胆囊
Danshu UB 19 胆俞
Dazu UB 11 大杼
Daying ST 5 大迎
Dazhong K 4 大
钟

Dazhui Du 14 大椎
Dicang ST 4 地仓
Diji SP 8 地机
Dingchuan Ex 17 定喘
Diwuhui GB 42 地五会
Dubi ST 35
Duiduan Du 27
犊鼻
兑端
Dushu UB 16 督俞
E
Ear-Heliao TW 22 耳和髎
Erbai Ex 24 二白
Erjian LI 2 二间 Ermen TW 21 耳门
F
Feishu UB 13 肺俞
Feiyang UB 58 飞阳
Femur-Futu ST 32 伏兔
Femur-Juliao GB 29 居髎
Femur-Wuli LIV 10 足五里
Femur-Zhongdu GB 32 股中渎
Fengchi GB 20 风池
Fengfu Du 16 风府
Fenglong ST 40 丰隆
Fengmen UB 12 风门

Fengshi GB 31 风市
Foot-Linqi GB 41 足临泣
Foot-Qiaoyin GB 44 足窍阴
Fuai SP 16 腹哀
Fubai GB 10 浮白
Fufen UB 41 附分
Fujie SP 14 腹结
Fuliu K 7 復溜
Fushe SP 13 府舍
Fuyang UB 59 跗阳
Fuxi UB 38 浮郄
G
Ganshu UB 18 肝俞
Gaohuang UB 43 膏肓俞
Geguan UB 46 膈关
Geshu UB 17 膈俞
Gongsun SP 4 公孫
Guanchong TW 1 关冲
Guangming GB 37 光明
Guanmen ST 22 关门
Guanyuan Ren 4 关 元
Guanyuanshu UB 26 关元俞
Guilai ST 29 归来
H
Hand-Wangu SI 4 腕骨

Hanyan GB 4 颔厌
Head-Linqi GB 15 头临泣
Head-Qiaoyin GB 11 头窍 阴 Head-Wangu GB 12 头 完骨
Heding Ex 31 鹤顶
Hegu LI 4 合谷
Henggu K 11 横谷
Heyang UB 55 合阳
Houding Du 19 后顶 Houxi SI 3 後溪
Huagai Ren 20 华蓋
Huangmen UB 51 肓门
Huangshu K 16 肓俞 Huantiao GB 30 环 跳
Huaroumen ST 24 滑肉门
Huatuojiaji Ex 21 华佗脊夹
Huiyang UB 35 会阳
Huiyin Ren 1 会阴
Huizong TW 7 会宗
Hunmen UB 47 魂门
J
Jiache ST 6 颊车
Jiachenjiang Ex 5 铗承浆
Jianjing GB 21 肩井
Jianli Ren 11 建里

Jianliao TW 14 肩髎
Jianshi P 5 间使
Jianwaishu SI 14 肩外俞
Jianyu LI 15 肩髃
Jianzhen SI 9 肩贞
Jianzhong Ex 22 肩中
Jianzhongshu SI 15 肩中俞
Jiaosun TW 20 角孙
Jiaoxin K 8 交信
Jiexi ST 41 解谿
Jimai LIV 12 急脉
Jimen SP 11 箕门
Jingbi Ex 13 颈臂
Jinggu UB 64 京骨
Jingmen GB 25 京门
Jingming UB 1 睛明
Jingqu LU 8 经渠
Jinjin Yuye Ex 10 金津 Jinjin
Jinmen LIV 12 急
玉液 Yuye
脉
Jinsuo Du 8 筋缩
Jiquan H 1 极泉
Jiuwei Ren 15 鸠尾
Jizhong Du 16 风府
Jueyinshu UB 14 厥阴俞
Jugu LI 16 巨骨
Jujue Ren 14 巨阙

Juliao ST 3 巨髎
K
Kongzui LU 6 孔最
Kufang ST 14 库房
Kunlun UB 60 昆仑
L
Lanwei Ex 33 阑尾
Laogong P 8 劳宮
Liangmen ST 21 梁门
Liangqiu ST 34 梁丘
Lianquan Ren 23 廉泉
Lidui ST 45 厉兑
Lieque LU7 列缺
Ligou LIV 5 蠡 沟
Lingdao H4 灵道
Linghou Ex 34 陵后
Lingtai Du 10 棂台
Lingxu K 24 灵止
Lougu SP 7 漏谷
Luoque UB 8 络却
Luozhen Ex 26 络视
Luxi TW 19 颅息

M
Meichong UB 3 眉冲
Mingmen Du 4 命门
Muchuang GB 16 目窗
N
Naohu Du 17 脑户
Naohui TW 13 臑会
Naokong GB 19 脑空
Naoshu SI 10 臑俞
Neck-Futu LI 18 扶突
Neiguan P 6 內关
Neiting ST 44 内庭
Nose-Heliao LI 19 禾
髎
P
Pangguangsh UB 28 膀胱俞
Pelvis -Zigong Ex 16 子宫
Pianli LI 6 谝历
Pishu UB 20 脾俞
Pohu UB 42 魄戶
Pushen UB 61 仆参
Q
Qianding Du 21 前顶
Qiangjian Du 18 强间

Qiangu SI 2 前谷
Qichong ST 30 气沖
Qihai Ren 6 气海
Qihaishu UB 24 气海俞
Qihu ST 13 气戶
Qimai TW 18 契脈
Qimen LIV 14 期门 Qinglengyuan TW 11 清冷渊
Qingling H 2 青灵
Qishe ST 11 气舍
Qiuhou Ex 4 球后
Qiuxu GB 40 丘止
Qixui K 13 气 穴
Quanliao SI 18 颧髎
Qubin GB 7 曲鬓
Quhai UB 4 曲差
Quchi LI 11 曲池
Quepen ST12 缺盆
Qugu Ren 2 曲骨
Ququan LIV 8 曲泉
Quyuan SI 13 曲垣
Quze P 3 曲泽
R
Rangu K 2 然谷
Renying ST 9 人迎

Renzhong Du 26 人中
Riyue GB 24 日月
Rugen ST 18 乳根
Ruzhong ST 17 乳中
S
Sanjian LI 3 三间
Sanjiaoshu UB 22 三焦俞
Sanyanglu TW 8 三 阳 絡
Sanyinjiao SP 6 三阴交
Shangguan GB 3 上关
Shangjuxu ST 37 上巨止
Shanglian LI 9 上廉
Shanglianquan Ex 12 上廉泉
Shangliao UB 31 上髎
Shangqiu SP 5 商丘
Shangqu K 17 商曲
Shangwan Ren 13 上脘
Shangyang LI 1 商阳
Shangxing Du 23 上星
Shangzhong Ren 17 膻中
Shaochong H9 少沖
Shaofu H 8 少府
Shaohai H 3 少海
Shaoshang LU 11 少 商
Shaoze SI 1 少泽

Shencang K 25 神藏
Shendao Du 11 神道
Shenfeng K 23 神封
Shenjue Ren 8 神阙
Shenmai UB 62 申脉
Shenmen H 7 神门 Shenshu UB 23 肾俞
Shentang UB 44 神堂
Shenting Du 24 神庭
Shenzhu Du 12 身柱
Shidou SP 17 食窦 Shiguan K 18 石关 Shimen Ren 5 石门
Shiqizhui Ex 19 十七锥
Shixuan Ex 30 十宣
Shousanli LI10 手三里
Shuaigu GB 8 率 谷
Shufu K 27 俞府
Shugu UB 65 束骨
Shuidao ST 28 水道
Shuifen Ren 9 水分
Shuiquan K 5 水泉
Shuitu ST 10 水突
Sibai ST 2 四白
Sidu TW 9 四渎
Sifeng Ex 29 四缝
Siman K 14 四满

Sishencong Ex 6 四神聪
Sizhukong TW 23 丝竹空
Sulio Du 25 素髎
T
Taibai SP 3 太白
Taichong LIV 3 太沖 Taixi K 3 太溪
Taiyang Ex 2 太阳
Taiyi ST 23 太乙
Taiyuan LU 9 太渊
Taodao Du 13 陶道
Tianchi P 1 天池
Tianchong GB 9 天沖
Tianchuang SI 16 天窗
Tianding LI 17 天鼎
Tianfu LU 3 天府
Tianjing TW 10 天井
Tianliao TW 15 天髎
Tianquan P 2 天泉
Tianrong SI 17 天容
Tianshu ST 25 天枢
Tiantu Ren 12 中脘
Tianxi SP 18 天溪
Tianyou TW 16 天口
Tianzhu UB 10 天柱

Tianzong SI 11 天宗
Tiaoko ST 38 条口
Tinggong SI 19 听宮
Tinghui GB 2 听会
Tonggu UB 66 足通谷
Tongli H 5 通里
Tongtian UB 7 通天
Tongziliao GB 1 瞳子髎
Touwei ST 8 头维
W
Waiguan TW 5 外关 Wailing ST 26 外陵
Waiqiu GB 36 外丘
Weibao Ex 15 维胞
Weicang UB 50 胃仓
Weidao GB 28 维道
Weishang Ex 14 胃上
Weishu UB 21 胃俞
Weiyang UB 39 委阳
Weizhong UB 40 委中
Wenliu LI 7 溫溜
Wuchu UB 5 五处
Wuli LI 13 手五里
Wuming Ex 18 无名
Wushu GB 27 五枢
Wuyi ST 15 屋翳

X
Xiabai LU 4 俠白
Xiaguan ST 7 下关
Xiajuxu ST 39 下巨止
Xianlian LI 8 下廉
Xianliao UB 34 下髎
Xiangu ST 43 陷谷
Xiaochangshu UB 27 小腸俞
Xiohai SI 8 小海
Xiaoluo TW 12 消泺
Xiawan Ren 10 下脘
Xiaxi GB 43 俠溪
Xiguan LIV 7 膝关
Ximen P 4 郄门
Xingjian LIV 2 行间
Xinhui Du 22 囟会
Xinshu UB 15 心俞
Xiongxian SP 19 胸乡
Xiyan Ex 32 膝眼
Xiyangguan GB 33 膝阳关
Xuanji Ren 21 璇 机
Xuanli GB 5 悬颅
Xuanshu Du 5 悬枢
Xuehai SP10 血海

Y
Yamen Du 15 哑门
Yangbai GB 14 阳白
Yangchi TW 4 阳池
Yangfu GB 38 阳辅
Yanggang UB 48 阳纲
Yanggu SI 5 阳谷
Yangjiao GB 35 阳 交
Yanglao SI 6 养老
Yanglingquan GB 34 阳陵泉
Yangxi LI 5 阳 溪
Yaoqi Ex 20 喓奇
Yaoshi Du 2 腰俞
Yaoyangguan Du 3 腰阳关
Yatong Ex 27 牙痛
Yemen TW 2 液门
Yifeng TW 17 医风
Yiming Ex 7 医明
Yinbai SP 1 隐白
Yinbao LIV 9 阴 包
Yindu K 19 阴 都
Yingchuang ST 16 膺
Yingu K 10
窗
阴谷
Yingxiang LI 20 迎香
Yinjiao Du 28 齦交
Yinlian LIV 11 阴廉

Yinlingquan SP 9 阴陵泉
Yinmen UB 37 殷门
Yinshi ST 33 阴市
Yintang Ex 1 印堂
Yinxi H6 阴郄
Yishe UB 49 意舍
Yixi UB 45 亿 譆
Yongquan K 1 涌泉
Youmen K 21 幽门
Yuanye GB 22 渊腋 Yuji LU 10 鱼际
Yunmen LU 2 云 门
Yutang Ren 18 玉堂
Yuyao Ex 3 鱼Yuzhen UB 9 玉枕
腰
Yuzhong K 26 彧中
Z
Zanzhu UB 2 攒竹
Zengyin Ex 11 增音
Zhangmen LIV 13 章门
Zhaohai K 6 照海
Zhejin GB 23 輒筋
Zhengying GB 17 正营
Zhibian UB 54 秩边
Zhiggou TW 6 支沟
Zhishi UB 52 志室
Zhiyang Du 9 至阳

Zhiyin UB 67 至阴
Zhizheng SI 7 支正
Zhongchong P 9 中冲 Zhongdu LIV 6 中都
Zhongfeng LIV 4 中封
Zhongfu LU 1 中府
Zhongji Ren 3 中极
Zhongquan Ex 25 中泉
Zhongliao UB 33 中髎
Zhonglushu UB 29 中膂俞
Zhongshu Du 7 中枢
Zhongting Ren 16 中庭
Zhongwan Ren 12 中脘
Zhongzhu TW 3 中渚
Zhouliao LI 12 肘髎
Zhourong SP 20 周荣 Zhubin K 9 築賓
Zhusanl ST 36 足三里
Index Of Disease And Prescription : 1.ABDOMINAL PAIN,CV 4 5 6 8, P 6, GB 27, GV 20 26, KI 15 16 17 18 19 20 , LI 4 8 9

SP 1 2 4 5 6 9 15 16 21, ST 24 25 26 27 36 37 38 39 40 43 44 BL 16 25 43 48 57
2.ACNE ,P 6 , LI 4 11 , LU 11 , LV 11 14 , SP 6 10 , ST 36
3.ALCOHOLISM, GB 8, LI 4, SP 6, ST 36 4.ALLERGIES, LI 4 11, BL 12 38 5.ALOPECIA GB 20 11, LI 4 11, BL 16 23 38 54 6.ALZHEMER'S DISEASE, P 8, KI 9, LI 5, ST 23 45, TW 2 10 7.AMENORRHEA CV 2 3 4 5 6 , GV 1 4, KI 5 12 14, LI 4, LV 8, SP 6 8 10 ST 29 36, BL 18 20 23 25 37 38 60
8.AMYOTROPHIC LATERAL SCLEROSIS (Mascular Atrophy) CV 17, GV 14 20, LI 4 11, LV 3, ST 36, BL 10 15 60
9.ANEMIA GB 43, GV 4 20, KI 1, LI 4 11, LV 8 14, SP 6 10, ST 44, BL 11 12 15 17 18 20 21
10.ANGINA PECTORIS CV 14 15, P 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 , GB 20, GV 8 11 12, HT 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 KI 1 4 5 23 24, LI 4, LU 5 9 ,,LV 3 , SI 1, ST 19 36, TW 6 7
11.ANKLE PAIN,GB 39 40 42, LV 6, ST 41, BL 58 63 12.ANOREXIA CV 5 6 9 10 11 12 13 14, P 2 6, GB 6 28, GV 9, HT 3 7, KI 3 17 22 23 24 25 26 27, LI 4 11, LV 4 13,
SP 1 2 4 8 9 19 20ST 19 20 21 22 23 36 39 42 44 45, TW 1 BL 13 17 18 19 20 22 40 41 42 44 46 57 64
13.ANOSMIA (loss of Smell) GB 20, GV 16 23, LI 4 19 20, SP 4, ST 6 8, BL 1 2 17 21

14.ANXIETY CV 14 17, P 7, GV 15 24, HT 4 5 6 7 8 9 , KI 1 4 9 , LU 4 10, LV 2 5 SI 3 4 7 , ST 36 40, BL 14 20
15.ARM PAIN P 5 6 , GB 21, HT 2 5 3, LI 1 4 10 11 12 15 16 , LU 5 6 SI 2 6 7 8 9 10 11 12, ST 36, TW 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
16.ARTERIES, CV 3, SP 10, ST 36, BL 17 17.ARTHRITIS P 6, , GB 34, GV 14, LI 4 11 15, LV 2, SI 9, SP 5, ST 36, TW 5 BL 8 10 11 58 60
18.ASTHMA, CV 6 12 16 17 18 20 21 22 23 , GB 19 20 23 25 35, GV 10 12 14 KI 1 2 3 4 5 6 , LI 4 8, LU 1 2 3 5 6 7 8 9 10 11, LV 8 14 SI 4 14 15, SP 21, ST 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 18 36 , TW 3 5 BL 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 20 21 22 23 25 36 37 38 40 51
19.BACK ACHE GV 4 14 , SI 6 14, TW 3 6, BL 9 10 11 23 24 25 29 50 51 54 55 60 62 63 65
20.BACK PAIN,GB 25 26, GV 5 6 7 10 12 14, KI 7 15, SP 2 3 5 , TW 3, BL 33 40 54 60
21.BELCHING, CV 12 13, P 6, KI 21, ST 36
22.BLURRED VISION, P 1, GB 4 13 14 15 16 17 41 43, GV 16 18 20 21 22, HT 5, KI 1 4, LI 2, SI 6, ST 8, BL 1 2 4 5 6 18 23
23.BREAST PAIN,P 1 3, GB 41 42, SI 1, SP 5, ST 18 24.BRONCHITIS, CV 13 14 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 , P 6 9, GB 10 11 18 20 21, GV 10 12 14 HT 3, KI 3 21 22 23 26 27 , LI 4 8 10 11, LU 1 3 5 6 8 9 , LV 1 14 SI 14 15, SP 18, ST 10 14 15 36, TW 3 10 BL 8 10 11 12 13 14 17 18 36 37 38 39 41 42 43

25.CALF CRAMP, GB 30 34, SP 6, ST 31, BL 50 54 55 56 57 61 63 26.CATARACT P 6, GB 1 2 3 14 20 41, GV 14 20 28, LI 4 11, LU 9, LV 3, ST 1 2 6 14 TW 1 5 23, BL 1 2 8 10 11 18 64 67
27.CERVICAL PAIN GB 21, GV 14, LI 4, SI 10 11 12 13 14 15 , TW 3 5 15, BL 11 13 60
28.CHEST PAIN P 5 6 GB 34, HT 6 8 9, KI 21 24 24 26 27 LU 1 2 4 7 8 9, LV 14, SI 1 11 SP 18 19 21, ST 13 14 18 19, TW 5 6, BL 14 15 17 19 24 25 42
29.CHRONIC FATIGUE SYNDROME CV 4 6, P 6 8, GB 20, GV 4, LI 4 11, LV 8, SP 6, ST 36, BL 17 18 20 38
30.COMMON COLD CV 12, GB 18 19 20, GV 14 16, LI 4 11, SP 6, ST 36, TW 4 5, BL 11 12 13
31.CONJUNCTIVITIS, P 7, GB 1 4 14 20 37 42, GV 12 14, LI 4 5 20, LU 9, LV 2, ST 1 2 36 44 , TW 23, BL 1 2 10 18 20 32.COLITIS, CV 6, GB 28, KI 2 7 15, LI 4, LU 8, LV 2 8 11, SP 1 9 14 33.CONSTIPATION CV 1 4 6 12, P 6, GB 24 27 28 34, HT 5, KI 6 8 15 16 17 18, LI 2 3 4 6 11 13 LV 1 2 3 8 12, SP 3 5 6 13 15 16, ST 22 23 25 26 27 28 36, TW 6 BL 23 24 25 27 28 30 31 32 33 34 38 45 46 48 50 52 56 57 58
34.COUGH
CV 6 12 16 17 20 21 22 23, P 2 4, GB 8 10 11 20 21 44, GV 9 10 11 12 14 23 KI 1 3 19 22 24 27, LI 4 11 13 15 18, LU 1 2 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11, LV 14 SI 1 2 15, SP 5 14 18 20, ST 9 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 25 36 38 40 41 TW 5 10, BL 11 12 13 14 15 17 20 21 37 38 42 43 44 45
35.DEAFNESS, CV 2 5 23, P 2 3 4 5 7 9 , GB 1 2 3 4 10 11 15 17 20 23 25 41 43 44 GV 15 16 20, HT 5 6 , LI 1 2 3 4 5 6 11 17 19, LV 3 5 6 8

SI 1 3 5 8 9 16 17 19 , ST 1 4 7 36 38, TW 2 3 5 7 8 9 10 16 17 18 19 21 23 BL 1 18 23 65
36.DEPRESSION CV 3 6 12 , P 4 6 , GV 4 13 14 20 , HT 3 7 , LI 4, LV 3 , LU 4, SP 6, BL 13 15 38
37.DIABETES, CV 4 12, P 6, GV 26, HT 6,,KI 2 5 7, LV 2, SP 6,,ST 33 36 BL 13 15 17 20 22 23 26 28 29 31 32 34 50
38.DIARRHEA, CV 4 5 6 8 9 12 13, P 6, GB 25 26 39, GV 3 4 5 6 ,,KI 8 13 14 LI 10 11, LV 6 8 13, SP 3 4 6 14 15, ST 16 22 25 34 36 37 39 TW 6 18, BL 10 21 22 23 24 25 28 35 43
39.DIVERTICULITIS, CV 6, SP 6, ST 25, BL 25(Inflammation of intestine) 40.DIZZINESS, GB 4 8 20 41 43, GV 14 17 19 20 24, KI 1, LU 3, ST 8 36 BL 3 5 9 10 12 40 62 64 65 67
41.DRY MOUTH, GB 44, LI 3, LU 11, ST 19,,TW 4 42.DYSPEPSIA, CV 5 6 10 11 12 13 , P 6, GB 25, GV 5, KI 1 19 20 , LI 4 13 LV 3 8 13 14, SP 3 4 5 6 7 , ST 21 22 23 25 36 44 45 BL 17 20 21 25 42
43.EAR ACHE, GB 11, ST 7, TW 19 44.EDEMA,, CV 5 6 8 9 11, GB 28, GV 28, KI 7, LI 6, LV 13, SP 8 9 ST 22 25 28 43, BL 20 22 23 27 47 52
45.ELBOW PAIN, P 3, HT 1 3 5 9 , LI 10 11 12 13 15, LU 5, SI 7, TW 10 46.EMPHYSEMA, , CV 12 13 15 16 17 20 21, GV 4 10 12 14, HT 3 6 (Inflamation of air sac in lung) KI 1 3 4 9 20, LI 1, LU 5 7 8 9 11, LV 1, SI 14, SP 21 ST 13 14 16 36 40, BL 11 12 13 17 18 22 23 36 37 38
47.ENDOMETRIOSIS, GB 26 28 29, GV 2 4 , KI 2 8, LV 5, SP 9 12 ST 29, BL 23 30

48.ENURESIS, CV 4 6, GV 1, KI 3 11, LV 1 9, SP 6, ST 23 25 36 BL 22 27 28 32 33
49.EYE PAIN, GB 1 11 16 44, GV 23, LI 3 4 5 11, ST 8, TW 23, BL 1 2 6 18 58 50.EYE REDNESS, LI 4, LV 3, TW 1 2 3 , BL 18 51.EYE (STYE), GB 14, LI 4, LV 3, SP 1 9, ST 2 36 52.FEAR, HT 4 5 8, KI 1 4 , LI 13, ST 36, TW 18, BL 23 38 47 66 53.FEVER, P 3 9, GV 4 13 14 16, HT 9, LI 1 2 4 5 11, LU 10 11 SI 5, SP 2, ST 43, TW 1 3 5 6 15, BL 5 11 12 13 19 39
54.FINGER PAIN , SI 4 7 8 55.FLANK PAIN, P 1 2 8, GB 34 39 40 41, GV 5, LV 13, SP 17 19 20 21 56.FOOT PAIN, GB 39 41, KI 2 3, LV 3, ST 34 41 44, TW 3 4,,BL 55 56 61 62 57.GALLSTONES, CV 10 12 13 , GB 34 , LV 13 14 , ST 36 , TW 6 , BL 18 19 58.GASTRITIS , CV 10 12 13 14 15 , P 5 6 7 8 , KI 20 , LI 4 11 , LU 5 LV 13 SP 4 5 , ST 19 21 22 23 24 28 36 37 , TW 6 8 BL 13 17 18 19 20 21 22 26 66
59.GENITAL PAIN , CV 1 , GB 30 , GV 1 , KI 10 11 12 , LV 4 8 12 , BL 47 49 50 60.GINGIVITIS , GB 4 12 , GV 27 , LI 4 , SI 8 16 17 18 , ST 4 5 42 44 45 , TW 2 20 61.GOUT, LV 2 3 4 , SP 4 5 6 , ST 44 , BL 39 62.HEADACHE (HANGOVER), CV 5 , GB 4 8 20 , KI 1 , SI 1 , ST 2 8 44 , TW 12 , BL 60 63.HEADACHE (FRONTAL), GB 14 20 , GV 14 20 23 24 , LI 4 , SI 1 , ST 8 , BL 2 63 64.HEADACHE (MIGRAINE) , CV 4 12 , GB 1 4 5 6 8 9 11 12 14 15 17 18 19 20 38 44 GV 19 , KI 10 11 LI 4 10 11 , LU 6 , SP 6 , ST 8 36 44, TW 3 5 10 22 23 BL 2 7 10 62 67

65.HEART PALPATAIONS , CV 4 12 14 , P 6 7 , GB 35 , HT 5 7 , KI 25 , ST 36 , BL 12 15 66.HEEL PAIN , KI 3 4 ,, SP 5 , BL 57 60 61 67.HEPATITIS, GB 24 34 , GV 14 , LV 4 13 14 , ST 36 , BL 18 19 20 21 68.HERNIA , CV 2 3 4 5 6 7 , GB 26 27 , KI 6 , LV 1 2 3 4 5 6 12 , SP 5 6 12 13 14 ST 23 26 27 28 29 43 , BL 29 30 32 55
69.HICCUPS , CV 6 12 13 15 17 22 , P 6 8 , GB 20 24, GV 16 26 , KI 3 17 18 , LI 5 9 LU 6 , LV 2 8 13 14 , SP 3 , ST 11 13 18 25 36 ,,BL 14 17 18 19 21 38 40 41
70.HYPERTENSION , CV 12, P 8 9 , GB 20 25 34 , HT 7 , KI 1 3 , LI 11, LV 2 3 13 SP 6 , ST 36 40 , BL 15 19 54
71.HYPERTHYROID, CV 22 23, P 6, GB 1 20 21 26, GV 12 14, KI 15, LI 4 ST 2 9 10 26, BL 10 11
72.HYPOTENSION , GV 20 25 26 , HT 1 5 6 , KI 1 , LV 3 , SP 6 , ST 9 36 , BL 15 17 18 22 23 38 73.IMMUNE SYSTEM , LI 4 11 , SP 10 , GV 14 20 , ST 36 74.INCONTINENCE, CV 1 2 3 4 6 , GB 34 , GV 4 20 , HT 8 , ST 22 36 , BL 22 23 24 25 75.INFLUENZA , P 6 , GB 20 , GV 13 14 16 , LI 4 , LU 7 9 10 , SP 15 , ST 36 , TW 5 ,BL 11 12 38 76.INSOMNIA , CV 4 6 12 , P 6 7 , GB 17 20 41 44 , GV 4 18 19 20 24 , GV 4 18 19 20 24 HT 6 7 , KI 1 6 24 , LI 1 4 , LU 9 10 , LV 2 10 , SI 3 , SP 1 2 6 9 , ST 12 27 36 40 45 TW 16 , BL 13 15 18 20 21 23 26 30 39 42 62

78.JAW (LOCK JAW) , CV 24, GB 7, GV 20, LI 4 19, ST 5 6 7 44, TW 6 17 22 79.KIDNEY STONES, GB 26 34, KI 3, SP 6, ST 36, BL 22 23 24 25 26 27 46 47 80.KNEE INFLAMMATION, GB 31 33 34 39, GV 3, KI 10, P 9, BL 54 56 81.KNEE PAIN, GB 30 33 34 39, GV 12 14, KI 1 10, LV 4 7 8, SI 2, SP 9 10 ST 33 34 35 36, BL 53 54
82.LEG PAIN, GB 28 29 30 31 34 37 39 40 41, KI 2 8 10, LV 9 11, SP 6 9 10 ST 31 32 38, BL 49 54 56 57 58 62 63 64 65
83.LIVER CIRRHOSIS, LV 3 9 14, SP 10, ST 36, BL 18 19 20 23 24 25 84.LOW BACK PAIN, GB 25 26 27 28 29 30 34, GV 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9, KI 3 7 LV 2 3 4 9 11 13, SI 3, SP 2 3 8, ST 31 36 37 BL 13 18 22 23 25 26 30 31 32 33 34 35 49 51 54 55 60 62 63 64 65
85.LOW BACK SPRAIN, GB 34, KI 9, LV 6, SP 8 9, BL 23 24 25 50 51 55 86.MENSTRATION (IRREGULAR CYCLE),CV 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 , GB 26 34 41, GV 2 KI 2 3 5 6 8 13 14 15, LV 1 2 5 9 11, SP 1 6 9 10, ST 25 30 36, BL 18 23 31 32 33 34
87.MENORRHAGIA, CV 3 4 5 6 , HT 1 8, KI 2 10, LV 1 2 3 6, SP 1 2 6 8, ST 10 12 36 TW 3, BL 23 54
88.MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS, GB 41, GV 12, HT 1, LV 3 5, SP 10,,ST 43 89.MUSCULAR DYSTOPHY, CV 4 6 12, P 6, GB 34 35, GV 4, KI 27, LV 8 13 14 SI 3, SP 6, ST 25 36, BL 20 21 22 25 54 57 60
90.NAUSEA, CV 12, P 4 6, GB 14, HT 4, LU 4 9 5, LV 3 13, SP 1, ST 18 24 36 TW 5 7, BL 19 21

91.NECK PAIN, GB 4 20 21 36 39 40, GV 13 14 16, LI 4 11, LU 7, SI 3 6 13 14 15 ST 5, TW 5 10 15 17
92.NECK SPRAIN, GB 20, SI 3 14, TW 10 16, BL 12 64 93.NECK STIFFNESS, GB 7 13 19 20 21 36 39, GV 10 14 15 16 18 19, HT 3, LI 1 11 LU 7, SI 3 4 5 7 14 15 16 19, ST 6 11, TW 5 10 12 15 16, BL 1 2 4 10 11 12 64 65 66
94.OBESITY, GB 34, LI 4, LV 3, SP 6, ST 36 95.OTITIS EXTERNA, GB 2, LI 1 4 11, SI 19, ST 7, TW 3 22 96.OTITIS MEDIA, GB 2 3 12 20 21 41, LI 4 11, SI 14 15 17 19, ST 6 7 36 TW 5 17 19 21 97.PARKINSON'S DISEASE, CV 4, GB 20, GV 4 12 20, SI 3 98.PNEUMONIA, CV 12 17 22, GV 12 14, KI 24 25 26 27, LI 4 10 11 13, LU 1 5 6 7 9 LV 14, SI 14, ST 13 14 15 16 36, TW 5 6 , BL 11 12 13 14 15 20 23 36 37 38
99.PROSTATITIS, CV 3 4 , GV 4, SP 6 9, ST 36, BL 23 28 47 100.PSORIASIS, P 6, LI 4 11 15, LV 3, SP 6 10, ST 25, BL 25 101.RECTAL PROLAPSE, CV 2 3 4 8, P 6, GB 20, GV 1 2 4 20, KI 1 5 15 SP 4 6 9 12, ST 15 25 26 36, TW 1 3 7, BL 22 23 24 25 31 32 33 34 57 58
102.SCAPULA PAIN, SI 8 9 10 11 13 14, TW 15 103.SCIATICA, GB 25 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40, GV 3 4 , KI 4, LV 4 SP 2 4 6 9 , ST 31 36 BL 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 48 49 50 51 53 54 57 58 60 64
104.SHOULDER PAIN, GB 4 20 21 29 30, HT 2, LI 11 14 15 16, LU 2 SI 3 6 8 9 10 11 12 13 14, ST 32 38, TW 3 6 10 13 14 15 16, BL 10 21 37

105.STOMACH ACHE, CV 9, P 5, GV 8, KI 18, LU 1, SP 2 3 4 5, ST 19 20 21 36 106.STROKE, CV 12 24, P 5 6 9, GB 12 15 20 21 30 34 39, GV 12 15 16 20 26 HT 9, LI 1 4 9 10 11, LU 10 11, LV 2, ST 36, TW 10, BL 10 18 25 54 62
107.SYNCOPE, CV 8, GB 43, GV 20 26, HT 3 9, LU 11, LV 1, SI 3 5, ST 36 45 BL 3 38 58 (Shock)
108.TACHYCARDIA, GB 20, HT 3 7, KI 25, SI 14, SP 19, ST 36, BL 10 11 12 38 (Abnormal Heart Action) 109.THIGH PAIN, GB 30, LV 11, SP 5, ST 32,,BL 51 110.THROAT SORENESS, CV 22, KI 1 2 3 6 , LI 1 2 3 4 11 17 18, LU 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 LV 3, SI 17 19, ST 9 10 11 12, TW 1 2 3 6 , BL 11 15 54
111.TINNITUS, GB 2 4 10 11 12 20 21 42, GV 4 20, LI 4 5 6, SI 2 3 4 5 9 16 17 ST 36 44, TW 1 2 3 5 17 18 19 21 22, BL 8
112.TOOTH ACHE, CV 24, GB 2 4 5 6 10 12 17,,GV 16 26, KI 6LI 1 4 6 10 11 LV 2 3, ST 6 36 42 44, TW 5 17, LI 4 specific for lower jaw, ST 44 specific for upper jaw
113.TRIGEMINAL NEURALGIA, CV 24, GB 1 11 14 20 41, , LI 4 11 20 LU 7, LV 3, SI 4 8 18, ST 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 36 40 44, BL 2
114.TRISMUS (LOCKJAW), CV 24, GB 7, GV 20, LI 4 19, ST 5 6 7 44,TW 6 17 22 115.ULCER (GASTRIC), CV 10 12 13 14, P 6 8, HT 5 7, LI 4 13, LU 5, SP 1 ST 36 38, TW 6, BL 17 18 19 20 22 23 25 38 44 45

116.UTERUS PROLAPSE, CV 1 6, GV 20, KI 1 2 3 11, LV 8 12, SP 6, ST 36, BL 31 32 117.VENERIAL DZ (GONORRHEA), CV 1 2 3 4, KI 4 7 8 9 10 12 18, LV 1 4, SP 6 11 12 15, ST 25 31, BL 22 24 26 27 28 31 32 33 34 35 48 57 61 118.VERTIGO, CV 4 6 12, P 1 6 7, GB 3 4 8 13 15 16 17 20 21 34 41 43 GV 16 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 26, HT 3 5 6 7 , KI 1 3, LI 1 2 4, LU 3 10 LV 2 3 , SI 3 7 15, SP 6, ST 2 7 36 40 41, TW 2 3 12 23 BL 1 2 5 6 8 9 10 11 15 16 17 18 20 23 40 58 60 62 65 66 67
119.VOMITING DUE TO PREGNANCY, CV 22, P 6, KI 21, ST 36, BL 17 120.WRITERS' CRAMP, P 5 8, H 3, LI 3 4 5 11, LU 6 7 9 10 11, SI 4 6, TW 4 6

GALL BLADDER
11 pm-1 am
TRIPPLE WARMER
9-11 pm
PERICARDIUM
7-9 pm
URINARY BLADDER
3-5 pm
SMALL INTESTINE
1-3 pm
LARGE INTESTINE
5-7 am
LIVER
1-3 am
KIDNEY
5-7 pm
HEART
11am-1pm
STOMACH
7-9 am
SPLEEN
9-11 am
LUNG
3-5 am


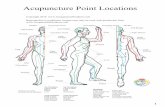

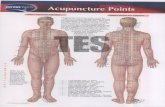















![The Immediate Analgesic Effect of Acupuncture for …downloads.hindawi.com/journals/ecam/2017/3837194.pdfon the traditional Chinese medicine theory of meridians andcollaterals,4[31,32,35,37]usedtenderpointsnear](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/5ea009550d586460bd25b90c/the-immediate-analgesic-effect-of-acupuncture-for-on-the-traditional-chinese-medicine.jpg)