What is a database? Example of database application: –Banks, –Hospital, –etc Extensions:...
-
Upload
elizabeth-snow -
Category
Documents
-
view
220 -
download
0
Transcript of What is a database? Example of database application: –Banks, –Hospital, –etc Extensions:...

What is a database?
• Example of database application:– Banks,– Hospital,– etc
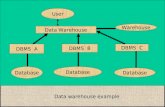
• Extensions:– Multimedia databases– Geographic Information Systems– Data warehouse– On-line analytical processing (OLAP)– Active & real-time databases– etc

What is a database?
Basic definition:• Database: A collection of related data.• Data: Known facts that can be recorded and have
an implicit meaning.• Mini-world: Some part of the real world about which
data is stored in a database. For example, student grades and transcripts at a university.

More about database definition
What is a database? Quite simply, it’s an organized collection of data. A
database management system (DBMS) such as Access, FileMaker, Lotus Notes, Oracle or SQL Server which provides you with the software tools you need to organize that data in a flexible manner. It includes tools to add, modify or delete data from the database, ask questions (or queries) about the data stored in the database and produce reports summarizing selected contents.

Data vs. information:What is the difference?
• What is data?– Data can be defined in
many ways. Information science defines data as unprocessed information.
• What is information?– Information is data that have
been organized and communicated in a coherent and meaningful manner.
– Data is converted into information, and information is converted into knowledge.
– Knowledge; information evaluated and organized so that it can be used purposefully.

Andi
Name
19
AgeSexID
Ina002 P
003
18
001 L
Udin L 20
Character
Field
Record
Database
File/Table
Student
File File
File
Item DataRecord
Record
Data Squence

Problems with file systems
• Data are Still Highly Redundant– Sharing Limited and at the File Level
• Data is Unstructured– “Flat” Files
• High Maintenance Costs– Data Dependence– Ensuring Data Consistency and Controlling Access to Data (Concurrent
Access Problematic)– Difficult to Understand by New Developers
• Difficulties in Developing New Applications• Almost Impossible to Evolve with New Capabilities• Risk of Inefficient Applications

Database vs. File Systems
Coordinates Both Physical and Logical Access to the Data
Data are Shared by All Programs Authorized to Have Access to It
Flexible Access to Data (i.e., Queries)
Multiple Users Accessing the Same Data at Same Time
Coordinates Only the Physical Access to the Data
Data Written by One Program May Not Be Readable by Another Program
Pre-determined Access to Data (I.E., Compiled Programs)
No Two Programs Can Concurrently Access the Same File