Wellbeing for Leaders Social and Emotional Learning (SEL)
-
Upload
joella-sharp -
Category
Documents
-
view
220 -
download
0
Transcript of Wellbeing for Leaders Social and Emotional Learning (SEL)
- Slide 1
- Wellbeing for Leaders Social and Emotional Learning (SEL)
- Slide 2
- Acknowledgement of Country I would like to acknowledge the traditional custodians of this land and pay my respects to Elders past, present and future, for they hold the memories, the traditions, the culture and hopes of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Australians.
- Slide 3
- Learning intentions What is SEL? Whole school approach to SEL SEL in the classroom SEL & Early Intervention SEL outside the classroom Parent engagement & SEL Bringing it all together- Where to from here?
- Slide 4
- video
- Slide 5
- What will schools look like in 2030? Global survey of 645 education experts by the World Innovation Summit for Education (W.I.S.E) predict major changes to schools by 2030: DBB Avalon
- Slide 6
- Survey of 645 education experts found: 93% favour schools using innovative methods; only 7% favour a return to fundamentals. Personal skills (75%) and know-how (59%) will play a bigger role than academic grades (42%) 73% said the teachers role will morph into a guide. Company qualifications for things like professional skills, collaboration or creativity (37%) will rank almost equally with school diplomas (39%) as indicators of student ability 90% believe education will be life-long
- Slide 7
- Guide to Coordinated Whole School Approach to SEL 1.School infrastructure that supports SEL -Wellbeing team, Positive school community (C1) 2. Articulate shared values & school mission 3. Assess current programs & initiatives 4. Assess school culture and climate- surveys, focus groups 5. Unified approach across the school 6. Improve staff readiness to teach SEL
- Slide 8
- Activity: Values & school mission 1.What skills do we want our children to leave primary school with? 2.Does the mission and ethos of your school support SEL? 3.Is SEL seen as a priority at your school? Why/Why not?
- Slide 9
- SEL - How does it all fit together? 2. Student Skills for Resilience/SEL P2 Supportive and connected school culture P6 Safe school learning and teaching P7 Student wellbeing and student ownership P9 Early intervention and targeted student support P10 Partnerships with families, parish and community
- Slide 10
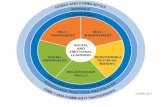
- What is SEL? (Personal & Social Capability) SocialEmotionalLearning Understanding other people Knowing our self SEL can be taught & learnt
- Slide 11
- Benefits of SEL Boost Academic performance Increase Student Interest in Learning Prevents & reduces bullying Improves school climate Improves student behaviour Reduced emotional distress Positive influence on teachers- teaching techniques, social behaviour, general wellbeing. https://static.squarespace.com/static/513f79f9e4b05ce7b70e9673/t/526a2589e4b01768fee91a6a/1 382688137983/the-missing-piece.pdf
- Slide 12
- The Melbourne Declaration on the Educational Goals for Young Australians (MCEETYA 2008) Recognises that personal and social capability (SEL): assists students to become successful learners, improve academic learning and enhancing their motivation. Needs to be addressed in all learning areas and at every stage of a students schooling.
- Slide 13
- Key ingredients - SEL Systematic approach Parent & family engagement Taught in and out of the classroom Proactive approach Embed into the curriculum Importance of the learning environment, relationships and hands on learning
- Slide 14
- Key ingredients - SEL Explicit teaching Practise and transfer Early intervention skills beget skills Application in real world & beyond the classroom Data collection Taught by school staff
- Slide 15
- Findings from OECD Report, 2015 Link between SEL & positive outcomes Parents & families engagement crucial Importance of the learning environment, relationships and hands on learning Early intervention programmes skills beget skills Importance of embedding into the curriculum
- Slide 16
- Skills beget skills Early intervention Primary school High school SEL Parent engagement
- Slide 17
- https://primary.portal.kidsmatter.edu.au/
- Slide 18
- Activity: Assess school culture & climate SEL checklist SEL surveys Friendship survey KidsMatter surveys- student K-6 now available Self assessment Behaviour Incident data 1. What data are you using to assess school culture & climate? 2. What does it tell you about SEL?
- Slide 19
- Unified approach across the school EARLY STAGE 1 (Kindergarten)STAGE 1 (Year 1 & 2)STAGE 2 (Year 3 & 4)STAGE 3 (Year 5 & 6) 1a Typically by the end of preschool Students will: 1b Typically by the end of Kindergarten Students will: Typically by the end of year 2 Students will: Typically by the end of year 4 Students will: Typically by the end of year 6 Students will: Core competency area: Self- Awareness Recognises Emotions Recognise and identify their own emotions.Identify a range of emotions and describe situations that may evoke these emotions.Compare their emotional responses with those of their peers.Describe the influence that people, situations and events have on their emotionsExplain how the appropriateness of emotional responses influences behaviour. Examples Recognising when they are feeling happy, sad, afraid or angry and naming the emotion or selecting a photograph of a face that matches their current emotional state. Describing responses such as being excited at a birthday party or feeling disappointed when not selected for an award. Considering how others respond to difficult situations in historical contexts or when listening to fictional stories.Discussing their emotional responses to events, such as celebrations, sporting events or news stories. Explaining the likely consequences of inappropriate emotional responses in a range of social situations. Recognise personal qualities and achievement s Express a personal preference. Identify their likes and dislikes, needs and wants, and explore what influences these. Identify and describe personal interests, skills and achievements and explain how these contribute to family and school life. Describe personal strengths and challenges and identify skills they wish to develop.Describe the influence that personal qualities and strengths have on their learning outcomes. Examples Choosing to engage in an activity. Describing activities they enjoy at school, noting their strengths. Identifying a personal quality or skill, such as being good at soccer or spelling, and describing how this might be useful to others. Listing a range of strengths supported by examples from home, school and community experiences. Keeping a journal or blog of how their personal qualities have helped achieve a positive learning outcome. Understand themselves as learners Express a personal preference.Identify their likes and dislikes, needs and wants, and explore what influences these. Identify and describe personal interests, skills and achievements and explain how these contribute to family and school life. Describe personal strengths and challenges and identify skills they wish to develop.Describe the influence that personal qualities and strengths have on their learning outcomes. Examples Choosing to engage in an activity Describing activities they enjoy at school, noting their strengths. Identifying a personal quality or skill, such as being good at soccer or spelling, and describing how this might be useful to others. Listing a range of strengths supported by examples from home, school and community experiences. Keeping a journal or blog of how their personal qualities have helped achieve a positive learning outcome. Develop reflective practice Recognise and identify participation in or completion of a task. Reflect on their feelings as learners and how their efforts affect skills and achievements.Reflect on what they have learnt about themselves from a range of experiences at home and school.Reflect on personal strengths and achievements, based on self-assessment strategies and teacher feedback. Monitor their progress, seeking and responding to feedback from teachers to assist them in consolidating strengths, addressing weaknesses and fulfilling their potential. Examples Communicating I have finished or I am working hard. responding to open-ended statements such as Im proud of this because or using visual aids to illustrate their response. Responding to prompts which help them acknowledge their successes and identify what they could do to make improvements. With support, identifying strategies that help them complete tasks when they are uncertain and reflecting on their contributions to group activities. Building on their strengths in various roles in small and large groups, setting personal challenges to develop new skills and strategies. Core competency area: Self Management Express emotions appropriately Recognise and identify how their emotions influence the way they feel and act.Express their emotions constructively in interactions with others.Describe ways to express emotions to show awareness of the feelings and needs of others. Identify and describe strategies to manage and moderate emotions in increasingly unfamiliar situations. Explain the influence of emotions on behaviour, learning and relationships. Examples Communicating the physical changes they experience when excited, angry or stressed such as when they are excited they feel happy; or when they are angry their body goes tense. Communicating when they feel left out, lonely, excited, disappointed or unsafe during class and physical activities. Using different tone and voice level in and outside the classroom, and when interacting with adults and peers. Learning when, how and with whom it is appropriate to share anger, frustration and excitement. Noticing how emotions such as anger and excitement affect learning and impact on achievements and successes. Develop self-discipline and set goals Make a choice to participate in a class activity.Follow class routines to assist learning.Set goals in learning and personal organisation by completing tasks within a given time.Explain the value of self-discipline and goal-setting in helping them to learn. Analyse factors that influence ability to self-regulate; devise and apply strategies to monitor own behaviour and set realistic learning goals. Examples Choosing to complete a task for positive reinforcement. Using class routines such as turn-taking, sitting when listening to stories, following instructions, managing transitions between activities. Organising their time using calendars and clocks. Identifying how distractions and priorities influence learning. Identifying desired goals and making plans to achieve these results. Works Independently and shows initiative Attempt tasks with support or prompting.Attempt tasks independently and identify when and from whom help can be sought. Work independently on routine tasks and experiment with strategies to complete other tasks where appropriate. Consider, select and adopt a range of strategies for working independently and taking initiative.Assess the value of working independently, and taking initiative to do so where appropriate. Examples Completing a selected task. Identifying situations where help is needed and the people who can help them, and when it is appropriate to 'give tasks a go. Describing their daily school routine, identifying areas where it is appropriate and helpful for them to show initiative. Recognising when strategies previously used are not as effective as new strategies. Identifying situations where it is preferable to work independently or with others. Become confident, resilient and adaptable and Identify people and situations with which they feel a sense of familiarity or belonging.Identify situations that feel safe or unsafe, approaching new situations with confidence.Undertake and persist with short tasks, within the limits of personal safety. Persist with tasks when faced with challenges and adapt their approach where first attempts are not successful. Devise strategies and formulate plans to assist in the completion of challenging tasks and the maintenance of personal safety. Examples Identifying family, friends, familiar people in the community. Choosing strategies to manage unsafe situations such as No Go Tell Continuing to practise a physical activity despite individual limitations. Persisting to inform a trusted adult about an unsafe encounter, event or situation. Developing coping strategies for managing set backs. Core competency area: Social Awareness Appreciates Diverse Perspectives Show an awareness for the feelings, needs and interests of others.Acknowledge that people hold many points of view.Describe similarities and differences in points of view between themselves and people in their communities.Discuss the value of diverse perspectives and describe a point of view that is different from their own. Explain how means of communication differ within and between communities and identify the role these play in helping or hindering understanding of others. Examples Showing interest in a peers ideas or opinions. Identifying the range of likes and dislikes within their class. Comparing changes in attitudes about behaviours in different places or over time. Exchanging views with a classmate on a topical issue and reporting their perspective to the class. Describing ways that language or gestures are used in a range of social settings. Contribute to Civil Society Show an awareness for the feelings, needs and interests of others.Describe ways they can help at home and school. Describe how they contribute to their homes, classrooms and local communities, and how others care for and assist them. Identify the various communities to which they belong and what they can do to make a difference. Identify a community need or problem and consider ways to take action to address it. Examples Showing interest in a peers ideas or opinions. Describing their role in completing class activities and family chores. Describing contributions made by significant individuals to their communities. Identifying ways they can advocate for specific groups in their communities. Considering current methods of waste management in their local environment and ways they might contribute to improving these. Understands Relationships Show an awareness for the feelings, needs and interests of others. Explore relationships through play and group experiences.Identify ways to care for others, including ways of making and keeping friends. Describe factors that contribute to positive relationships, including with people at school and in their community. Identify the differences between positive and negative relationships and ways of managing these. Examples Showing interest in a peers ideas or opinions. Discussing different ways of working together. Discussing how words and actions can help or hurt others, and the effects of modifying their behaviour. Identifying the importance of including others in activities, groups and games. Identifying behaviours that display the positive use of power in relationships. Core competency area: Relationship Skills (part of Social Management in ACARA personal and social capability) Communicates Effectively Respond to the feelings, needs and interests of others.Identify positive ways to initiate, join and interrupt conversations with adults and peers.Discuss the use of verbal and nonverbal communication skills to respond appropriately to adults and peers. Identify communication skills that enhance relationships for particular groups and purposes.Identify and explain factors that influence effective communication in a variety of situations. Examples Giving appropriate response to a peers achievements such as by clapping, smiling or cheering. Practising encouraging others, listening to others ideas, greeting others by name, excusing themselves when interrupting. Using spoken language and body language to share observations and ideas. Actively listening and responding to opinions that differ from their own. Making and responding to introductions, building on the ideas of others in discussions, offering and accepting constructive criticism. Works Collaboratively (The description above also applies to this sub-element) Respond to the feelings, needs and interests of others. Share experiences of cooperation in play and group activities.Identify cooperative behaviours in a range of group activities.Describe characteristics of cooperative behaviour and identify evidence of these in group activities. Contribute to groups and teams, suggesting improvements in methods used for group investigations and projects. Examples Giving appropriate response to a peers achievements such as clapping, smiling or cheering. Taking turns, sharing resources and following class routines. Participating in guided group investigations. Including others in the group and respecting their opinions, working for a common goal. Encouraging others, negotiating roles and relationships and managing time and tasks. Core competency area: Responsible Decision Making (part of Social Management in ACARA Personal and Social Capability) Make Decisions (The description above also applies to this sub-element) Responds to the feelings, needs and interests of others). Identify options when making decisions to meet their needs and the needs of others. Practise individual and group decision making in situations such as class meetings and when working in pairs and small groups. Contribute to and predict the consequences of group decisions in a range of situations. Identify factors that influence decision making and consider the usefulness of these in making their own decisions. Examples Giving appropriate response to a peers achievements by clapping, smiling or cheering. Making choices about resources for play and learning tasks. Naming roles and responsibilities in class meetings and identifying fair methods for choosing people for these roles. Deciding how to share resources for a learning task and forecasting the outcomes of options. Identifying the people, events and situations that influence how decisions are made. Negotiate and resolve conflict Respond to the feelings, needs and interests of others. Identify a problem and seeks advice. Listens to others ideas, and recognise that others may see things differently from them. Identify a problem and draws on experience to solve it.. Practise solving simple interpersonal problems, recognising there are many ways to solve conflict. Uses a range of problem solving strategies. Identify a range of conflict resolution strategies to negotiate positive outcomes in problems. Suggest, considers and selects appropriate alternatives when resolving problems. Examples Giving appropriate response to a peers achievements by clapping, smiling or cheering. Names one way of solving a simple problem and starts to understand consequences. Identifying characters in stories who feel differently about the same situation, and how they might respond in the same situation. Names more than one way to solve a problem, verbalises what a consequence is and talks about what is right and wrong within personal and school context. Using strategies such as showing courtesy to others when voicing disagreements or an alternative point of view. Decide on the best way to solve a problem and verbalises reasons for this within personal, school and community context. Identifying issues that cause conflict and exploring how conflict has been resolved in a range of contexts. Considers ethical, safety and societal factors in solving problems. Demonstrating steps of a conflict resolution process such as listen, express feelings, discuss solutions, make amends. Develop leadership skills Respond to the feelings, needs and interests of others.Identify ways to take responsibility for familiar tasks at home and school.Discuss ways in which they can take responsibility for their own actions.Discuss the concepts of leadership and identify situations where it is appropriate to adopt this role.Initiate or help to organise group activities that address a common need. Examples Giving appropriate response to a peers achievements by clapping, smiling or cheering.Identifying ways to help at school, such as closing windows, tidying workspace, distributing resources.Discussing ways in which they participate in games and playground.Choosing a range of roles in group activities.Volunteering to lead a peer coaching activity.
- Slide 20
- (SEL) Skills Continuum Benefits Continuum of learning in SEL Tool to map SEL across a school Tracking student progress- point of need of child, strengths, weaknesses Examine whether structures are in place to support all students
- Slide 21
- Activity: Using SEL tools 1.Choose a student at your school/in your class 2.Complete the SEL checklist for this student (choose appropriate stage checklist) 3.Consider : -Students strengths -Student challenges -Moving forward 3. Discuss at your table how useful a teacher would find this tool?
- Slide 22
- SEL in the classroom CSO Broken Bay resources Component 2 St John the Baptist, Freshwater
- Slide 23
- Classroom approaches to teaching SEL Explicit SEL skills- explicit lesson plans designed specifically to promote SEL. E.g. PDHPE, Pastoral Care, Bounce Back, PBL Integration with core academic subjects- Embed into core subjects e.g. literacy, numeracy Teacher instructional practices- focus on instructional processes, pedagogies, and management approaches to promote a positive classroom climate. Which approach do you use at your school?
- Slide 24
- Effective strategies Collaborative learning strategies- student to student interaction, role play, small group problem solving, critical thinking Games & Stories Play especially in younger children Circle Time Assist students to relate to real life situations Teach self-calming strategies Building resilience in children & young people. A Literature Review for the Department of Education and Early Childhood Development (DEECD). P.37 Its the way you teach.
- Slide 25
- Positive Behaviour & SEL Teach Practice Apply Acknowledge
- Slide 26
- Academic Support(s) Check In/ Check Out Social Skill Targeted Environmental Interventions Avoid Tasks ? Skill Deficit? Step 1: Teacher and Team collect data. Data Decision Rules Universal Screening and data collection Classroom System Nonclassroom System Schoolwide System Classroom System Nonclassroom System Schoolwide System Tier 1 implemented with fidelity? Obtain Attention? Lagging Skills
- Slide 27
- SEL & PDHPE PDHPE curriculum - explicit teaching of SEL PDHPE Units on Website SEL has been mapped to Early Stage 1, Stage 1, Stage 2 & Stage 3. KidsMatter(PDHPE & SEL) KidsMatter(PDHPE & SEL)
- Slide 28
- Integration across the KLAs
- Slide 29
- Activity: Reflection Integration with core academic subjects 1.Think about a lesson you taught yesterday (or recently!) e.g. numeracy or literacy. 2.Reflect on the 5 SEL competencies. 3.How much SEL teaching was happening in this lesson?
- Slide 30
- Integration with core academic subjects 1. Are there opportunities to Practice & transfer SEL in your classroom? (e.g. literacy, numeracy, project based learning) 2. How realistic is it for teachers to embed SEL into all curriculum areas? Be explicit, name it Practise and feedback Application
- Slide 31
- Case Study: St Philip Neri, Northbridge Karen Townsend
- Slide 32
- Sals 60 second story
- Slide 33
- Resources to support SEL CSO Broken Bay resources Component 2 St Cecilias Wyong page PBL lessons Victorian Education SEL resource Friendly Schools Bounce Back Circle Solutions for Student Wellbeing Mpower girls Tribes KidsMatter programs guide Helpful management ideas for the classroom
- Slide 34
- Slide 35
- 2. Assess current programs & initiatives Brainstorm all the SEL program/strategies/ structures that are happening at your school PATCH club Meditation for anxious children PDHPE/RE Bounce Back Peer Support PBL Parent engagement Program for year 5 girls- friendship Tertiary prevention High risk Secondary Prevention At risk Primary Prevention School wide systems
- Slide 36
- Case Studies Vicki McCudden, St Cecilias Wyong Louise Kissane, St Marys Manly
- Slide 37
- Slide 38
- SEL activity 1.Choose a card that represents how you currently feel about SEL in your school. Share with your table. 2.What SEL skills does this picture activity develop?
- Slide 39
- Parent engagement & SEL Carmel Hewitt & Jo Spek (CSO)
- Slide 40
- Using resources 1.Use your Learning continuum. Choose a stage & competency E.g. Stage 2, Self awareness. 2.Use Victoria education SEL pages, Bounce Back or Friendly Schools Plus booksVictoria education SEL pages 3.Choose an activity that you could run in your class to improve this competency. 4.Complete the lesson proforma 5.Share this activity with your table group.
- Slide 41
- What do teachers require? Teacher self efficacy linked to higher program fidelity. PL for staff: involve teachers working through curriculum & teaching each other in small groups. Involve teachers as learners so they appreciate perspective of students Teachers need to understand educational rationale of approach. Other key factors: Student engagement, confidence in class control, positive relationships with students, time to prepare class.
- Slide 42
- Activity: Where to from here? New strategies/initiatives/structures to move forward. -Whole School -Individual classroom
- Slide 43
- Resources to support SEL CSO Broken Bay resources Component 2 St Cecilias Wyong page PBL lessons Victorian Education SEL resource Friendly Schools Bounce Back Circle Solutions for Student Wellbeing Mpower girls Tribes KidsMatter programs guide Helpful management ideas for the classroom
- Slide 44
- Upcoming workshops Next Wellbeing PLC 12.30-3.30 NS/PEN- 17/07/2015 Forestville Central Coast- 22/07/2015 Terrigal Register on PHRIS NVCI 8:30am 3:30pm Thursday 5 th June CSO Register on PHRIS
- Slide 45
- Expression of interest Develop a 6 lesson unit of work for boys in Year 4 & Year 5. Time will be allocated to work on these units of work. 2 people