file · Web viewThe basement membrane is a layer that connects the epithelium to...
Transcript of file · Web viewThe basement membrane is a layer that connects the epithelium to...

Biology 12
Human Organization (Chapter 11)
Different levels of organization in the human body
Cells Basic unit of structure and function of organisms
Tissues
Cells of same shape and function join together to form ______ Examples: nervous tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, etc. Tissues categorized into 4 major types: __________, ________,
______________, ___________ tissue
a. Epithelial Tissue
Protects body from injury, desiccation, infection Can be specialized to perform other functions as well such as
absorption, secretion, excretion and filtration
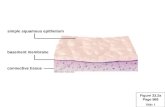
Can be organized as __________: single layer of cells
1

Can be __________: layers of cells piled on top of each other
Can be ____________: single layer of columnar epithelium that looks as though it is stratified but only one cell layer
Usually ciliated
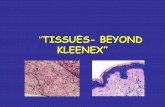
The basement membrane is a layer that connects the epithelium to connective tissue underneath
Different Kinds of Epithelial Tissues2

1. Squamous epithelium
2. Columnar epithelium Have nuclei located at bottom of cells near b.m.
3. Cuboidal epithelium
4. Glandular epithelial cells
3

Glandular epithelial cells can be a single or many If product secreted into ducts are called ___________ glands If product secreted into blood then called __________ gland
Cell Junctions
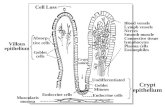
1. Tight junctions Involves joining of proteins in cell membranes of cells
e.g. found in epithelial cells of intestine to prevent escape of intestinal contents into abdomen See following diagram
4

2. Gap junction Are communication junctions Commonly found in cardiac muscle cells and smooth muscle—
to coordinate activity
5

3. Desmosomes (adhesion junctions)
Plasma membranes held together by proteins or intercellular
filaments Serve to allow cell flexibility (i.e. permit stretching of cells
without cells coming apart
b. Connective Tissue
Functions in binding organs together, support & protection,
insulation, stores fat, produces blood cells Typically cells of connective tissues are spaced widely apart and
the space in between the cells is filled with a non-cellular material called the ________ that can vary in consistency between liquid to gel
6

Classification of Connective Tissue:
Types of Connective Tissue
Loose Connective Tissue Fibrous connective tissue
(tendons and ligaments) Cartilage Bone Adipose tissue Blood tissue
1. Loose Connective Tissue Function: to hold organs in place and to bind epithelial tissue
to underlying tissue; also surrounds blood vessels and nerves
Fibres can be elastic (for flexibility) or collagen (for strength
and flexibility) C.T. helps attach epithelial tissue to other underlying tissues
(e.g. muscle)
7

Light Micrograph of Loose C.T.
2. Fibrous Connective Tissue Function: main component of tendons and ligaments __________ (bind muscle to bone), ___________ (connect
bone to bone)
8

Figure: fibrous connective tissue
3. Cartilage
C.T. made exclusively of cells called ___________ which produce matrix and collagen fibres
Is found in ears and nose as well as ends of bones in joints
functioning as a cushion and to reduce friction on the articulating surfaces of these bones
4. Bone
Mineralized internal matrix by inorganic calcium salts such as
[Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2] or ________________
5. Blood
Functions of Blood: (i) (ii) Carries carbon dioxide and waste materials away from
cells(iii)
(iv) Contains regulatory agents such as hormones that influence many activities within the body
(v)
9

(vi) Plays important role in pH, fluid and ionic balance between blood and tissues
(vii) Has ability to clot to prevent excessive blood loss in injuries
Components of Blood Whole blood can be divided into 2 components: plasma and
formed elements Made of ______ (55%) and ________________ (or cells) (45%) Plasma made of water, inorganic, organic substances Cellular component made of ________ (rbc’s), ___________
(wbc’s) and _______________ (platelets) which are made in the bone marrow of long bones, skull, ribs and vertebrae.
A.Plasma Components Proteins (7-8%) Nutrients, gases (CO2), hormones, enzymes
B.Formed Elements
10

a) Erythrocytes (Red Blood Cells) 4-5 million per mm3
No nuclei Contain haemoglobin (red pigment) Hgb binds oxygen
b) Leukocytes (white blood cells) 6000-9000 cells per mm3
Translucent cells Fight infections by producing antibodies or by phagocytosing
foreign bodies
C) Thrombocytes (Platelets)
11

Are fragments of cells called __________________ or giant cells in bone marrow
Release chemicals that aid in clotting process
Figure: rbc, platelet and wbc
6. Muscle Tissue
12

Made of cells specialized for contraction called _____ Muscle fibers are composed of 2 contractile filaents—_________
and _______ filaments 3 types of muscle:
(a)Striated or Skeletal Muscle Attached to bones of skeleton via __________ (e.g. legs,
arms, head, etc.) Muscle cells called _______ and are cylindrical and long
Fibers have alternating dark and light bands giving them striated appearance resulting from arrangement of actin and myosin filaments inside cells making up fibrils
13

Figure: striated muscle structure
(b) Smooth Muscle Non-striated Involuntary Found in organs such as g.i. system and blood vessels Slower but longer contraction than skeletal muscle
smooth muscle
14

(c) Cardiac Muscle Cells Branched/connected cells by desmosomes and gap junctions
at areas called ___________ ______ Involuntary Only found in heart
7. Nervous Tissue
Includes two types of cells: ________ and __________ cells
Neurons
Neurons contain following 3 main parts:
15

(a) ____________: conduct impulses to the cell body(b) ____________________: contains nucleus(c) ______: conducts nerve impulses away from the cell body;
often covered with a fatty like insulating layer called myelin to help speed up nerve impulses.
Many nerve cells bound together form a nerve
Organs
covered in epithelial tissue
16

Organ Systems
Often organ systems work with each other (e.g. circulatory and
respiratory or circulatory and endocrine) Different organ systems we will be looking at are:
a. Nervous system—made of brain, spinal cord, eye, ear and nerves
b. Circulatory system—made of heart, blood, and blood vessels
c. Digestive system—made of esophagus, stomach and intestines
d. Endocrine system—hormone producing organs and tissues such as the pancreas, hypothalamus, suprarenal glands, etc.
e. Musculoskeletal system —consists of skeletal muscles and bones
f. Excretory system—consists of kidneys and associated structures
g. Lymphatic system—consists of lymph organs and vessels that play a role in the immune response
h. Reproductive system—consists of ovaries, testes and other reproductive structures that I am too embarrassed to recite
Body Cavities17

Thoracic cavity
bounded by ribs, diaphragm and lower part of neck
Abdominal cavity
18

From diaphragm to upper part of pelvis and body wall Includes, liver, kidneys, stomach, pancreas, intestines and kidneys
Cranial cavity
Includes mouth, nasal cavities, and auditory cavities
Spinal cavity
Pelvic cavity
Homeostasis
19

Examples: o Body temperature stays at around 37 °Co Blood pH is maintained at a constant level of 7.4o Blood pressure stays fairly constant
Regulation of homeostasis is achieved by hormones as well as by the nervous system that uses a negative feedback control
Negative Feedback Control Of Homeostasis
Has 2 major parts—__________ and a __________ ________ The sensor detects a change in the internal conditions of the body
and the control centre directs a change to restore conditions to normal
Thus, the control centre has negated the initial stimulus that activated the sensor—hence the name “negative feedback control”
For example, blood pressure regulation
20

When blood pressure is high, baroreceptors in major artery of neck sense it (__________)
Baroreceptor sends signal to the brain stem (________________)
This lower blood pressure tells the baroreceptors in the arteries that the blood pressure is not high anymore so no message goes back to the control centre to make any more changes to blood pressure—i.e. negative feedback.
21

Controlling Body Temperature
Example of fluctuating feedback control
Cooling Body Temperature Below Normal
Receptor in __________________ (structure in brain) senses temperature change of blood
errector pili muscles become erect trapping layer of insulating air if further blood temperature drop, nerve impulses sent to muscles
→ shivering → raises body temperature
Overheating of Body
sweat glands also activated → evaporation of sweat
22

Positive Feedback Control Of Homeostasis
less common than Negative Feedback control discussed above in childbirth, stretching of the smooth muscles of the uterus
causes increased production of the hormone oxytocin which increases the rate of uterine muscle contractions causing even more oxytocin to be released and so this continues until the baby is born
23