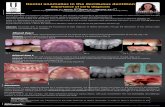
· Web viewDentigerous cyst is the most common cyst found in oral cavity. It is always better to...
Transcript of · Web viewDentigerous cyst is the most common cyst found in oral cavity. It is always better to...

ABSTRACT. Dentigerous cyst is the most common cyst found in oral cavity. It is always better
to be conservative in managing this problem in children because dentition is yet to complete in
them. The case here describes the technique of marsupialization in which extraction of the
grossly carious deciduous 1st molar was done and window was created through the extracted
socket to decompress the lesion.
KeyWords. Dentigerous cyst, Marsupialization, deciduous dentition
INTRODUCTION
Dentigerous cysts are the most common developmental odontogenic cysts. Studies reveal that
dentigerous cyst constitute more than a quarter of all jaw cysts. They are usually derived from
the epithelial remnants of tooth forming organs1. They develop around the crown of an unerupted
tooth by expansion of the follicle when fluid collects or a space is created between the reduced
enamel epithelium and the enamel of an impacted tooth. It predominates during the 2nd – 3rd
decades of life2. Most commonly dentigerous cyst involves mandibular 3rd molar followed by
maxillary canine. These patients usually complain of painless slow growing swelling involving
the affected area which is very firm on palpation indicating cortical expansion. The classic
treatment for dentigerous cysts is enucleation and extraction of the involved tooth3. It is always
better to be conservative in managing this problem in children because dentition is yet to
complete in them. Children have a great regenerative potential and tooth with incomplete root
development maintain the eruptive strength4. In such circumstances, therefore, marsupialization
or decompression should be tried as a major therapy.5,6
CASE REPORT

This work was conducted in accordance with bioethical concerns. Written informed consents
were obtained from the child’s parents for all examinations and for the treatment modality
adopted.
A boy aged 10 years was referred to the department of Pedodontics who was accompanied by his
parents who complained about facial asymmetry and presence of decayed teeth. No history of
systemic pathologies or previous trauma in the affected area was reported. The boy presented an
important facial asymmetry with slight expansion of paranasal region and upper lip on the right
side. Intraoral exam revealed compressible and painless expansion of buccal cortical plates of the
alveolar ridge extending from deciduous canine to 1st deciduous molar on right side of maxilla.
(Figure1) Dentition was mixed, carious lesion was present with respect to maxillary 1st
deciduous molar on right side. The radiographic findings (OPG) revealed a radiolucent area,
measuring approximately 18 mm in its largest diameter, with sclerotic margins pushing the
premolars and canines. (Fig2) Premolars were completely overlapping each other.
Carious deciduous 1st molar was extracted and aspiration of the lesion fluid was done which
revealed a serous and bloody liquid content. (Fig 3a) The clinical diagnosis of dentigerous cyst
was concluded allowing the beginning of an initial treatment with marsupialization in the case of
the cyst that involved the maxillary teeth. The cyst cavity was packed with sterile iodoform
gauze to achieve hemostasis and to prevent hematoma formation. (Fig3b) The iodoform gauze
was changed on every third day. After 1 month the OPG was repeated and it was clearly visible
that the premolars started migrating mesially and the canine moved distally (Fig4). Follow up
radiographs were repeated after 3 months, 6 months and after 1year. (Fig 5a,b) Ist premolars
started erupting on both sides (fig 6). After 1 year of clinical and radiographic follow-up, there

were no signs of recurrence of the lesion. To relieve the crowding, the patient was referred to the
department of orthodontics for further treatment.
Discussion
Benn and Altini7 discussed the genesis of the dentigerous cysts and proposed two different
processes for cystic degeneration of the reduced epithelium of enamel organ of an included
tooth. The first phenomenon is usually associated to the compression promoted by tooth eruption
at the pericoronary follicle, which induces fluid accumulation between this tissue and tooth
crown. The other mechanism is associated to an apical inflammation in the primary predecessor
whose cytokines, stimulates cystic degeneration of the permanent tooth follicle. The case
described at this paper was probably associated with inflammatory processes caused by caries in
the primary dentition. Biopsy is an essential and fundamental diagnostic element for the
treatment7 since dentigerous cyst shares features with many other lesions such as
ameloblastomas, odontogenic keratocyst, adenomatoid odontogenic tumor, which can
simultaneously occur with this cyst8. For the treatment purpose many different surgical
therapeutic modalities have been applied to treat dentigerous cysts. Among them,
Marsupialization is more conservative method than enucleation of the entire cyst in cases of
large lesions and when the permanent teeth involved have eruptive potential8. This should be
considered as the first line of management in children with dentigerous cyst. The main
advantages of marsupialization or decompression for the treatment of dentigerous cyst are the
stimulus for bone formation after the decrease of cystic pressure. The communication with oral
secretions increases the inflammatory process and both macrophages and lymphocytes from
inflammation release growth factors that enhance bone formation9-11. Another Major advantage
of this procedure is loss of viable permanent tooth buds can be prevented11. The patients should

be followed up carefully by performing radiological imaging every 6 months in order to keep an
eye on potential recurrence. The lack of patient's cooperation in cleaning the pathological cavity
and the need for periodic follow-up visits represent few disadvantages.
In this case, only marsupialization led to successful eruption of the permanent tooth along with
complete ossification of the bony defects in 15 months. The patient comes from a nearby area
and is being supervised regularly. There is no sign or symptom of developing ameloblastoma or
other malignancy in the area since the last 2 years. The successful preservation and eruption of
the affected teeth in this present investigation may be attributed to the active growth potential
and remodeling of bone in children unlike in adults where jaw growth is completed.
Conclusion
Treatment of dentigerous cyst through conservative therapy is preferable in children.
Marsupialization and decompression are very low invasive techniques that could easily be
conducted by any dentist familiar with basic surgical procedures, in order to treat the pathology
and to preserve the teeth involved.
Acknowledgement
Authors are grateful to the child and his parents who were always ready to cooperate and used to
come for regular visits.
References.
1)Amin ZA., Amran M., Khairudin. Removal of extensive maxillary dentigerous cyst via a
CaldwellLuc procedure. Arch Orofac Sci 2008;3(2):4851.
2)Mervin S and Paul SM. Cysts of the Oral Cavity and Maxillofacial Regions. 4th ed. Blackwell
Munksgaard Publishers; c2007. 228p

3)Manoela C, Danilo BD, AntônioMM, MaríliaGO, Miguel GA. Conservative treatment of the
dentigerous cyst: report of two cases. Braz. J. Oral Sci. vol.12 no.1 Piracicaba Jan./Mar. 2013.
4.Picciotti M, Divece L, Parrini S, Pettini M, Lorenzini G. Replantation of tooth involved in
dentigerous cyst: a case report. Eur J Paediatr Dent. 2012; 13: 349-51.
5 Kumar R, Singh RK, Pandey RK, Mohammad S, Ram H. Inflammatory dentigerous cyst in a
ten-year-old child. Natl J Maxillofac Surg. 2012; 3: 80-3.
6 Marwah N, Bishen KA, Prabha V, Goenka P. A conservative approach in the management of
inflammatory dentigerous cyst in transitional dentition: a case report. Eur J Paediatr Dent. 2012;
13: 349-51
7.Benn A, Altini M. Dentigerous cysts of inflammatory origin. A clinicopathologic study. Oral
Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1996; 81: 203-9.
8 Hyomoto M, Kawakami M, Inoue M, Kirita T. Clinical conditions for eruption of maxillary
canines and mandibular premolars associated with dentigerous cysts. Am J Orthod Dentofac
Orthop. 2003; 124: 515-20.
9. Gervasio AM, Silva DA, Taketomi EA, Souza CJ, Sung SS, Loyola AM. Levels of GM-
CSF, IL-3, and IL-6 in fluid and tissue from human radicular cysts. J Dent Res. 2005; 81: 64-8.
10. Takagi S, Koyama S. Guided eruption of an impacted second premolar associated with a
dentigerous cyst in the maxillary sinus of a 6-year-old child. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1999; 56:
237-45.

11. Miyawaki S, Hyomoto M, Tsubauchi J. Eruption speed and rate of angulation change of a
cyst-associated mandibular second premolar after marsupialization of a dentigerous cyst. Am J
Orthod Dentofac Orthop. 1999; 116: 578-84.
Pics..
Fig 1 Fig 2
Fig 3a Fig 3b

Fig 4
Fig 5a Fig 5b
Fig 6