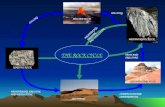
Weathering and Erosion. Student Objectives Analyze effects of regional deposition and weathering...
-
Upload
aldous-price -
Category
Documents
-
view
222 -
download
1
Transcript of Weathering and Erosion. Student Objectives Analyze effects of regional deposition and weathering...
Student Objectives Student Objectives
Analyze effects of regional deposition and Analyze effects of regional deposition and weathering weathering
Definitions Definitions
Weathering- mechanical or chemical surfaces Weathering- mechanical or chemical surfaces processes that break rocks into smaller pieces processes that break rocks into smaller pieces
Types of Weathering Types of Weathering
MechanicalMechanical Breaks materials down Breaks materials down Same properties as the Same properties as the
original material just original material just changes in sizechanges in size
Example: Example: Gravel becoming smaller Gravel becoming smaller
Chemical Chemical Breaks materials down Breaks materials down Change of properties, Change of properties,
material becomes a material becomes a totally new substance totally new substance
Example: Example: Iron rusting Iron rusting
What type of weathering is this: What type of weathering is this: mechanical or chemical? mechanical or chemical?
Definition Definition Erosion- process in which surface materials Erosion- process in which surface materials
are worn away and transported from one place are worn away and transported from one place to another by agents such as gravity, water, to another by agents such as gravity, water, wind, and glaciers wind, and glaciers
Definitions Definitions
Deposition- dropping of sediments that occur Deposition- dropping of sediments that occur when an agent of erosion such as gravity, when an agent of erosion such as gravity, wind, or water loses its energy and can no wind, or water loses its energy and can no longer carry its load longer carry its load
Erosion and WeatheringErosion and Weathering
Video Narration/ Video Narration/
Question and Answering Question and Answering
Student Objectives Student Objectives
Define the differences between Define the differences between weatheringweathering and and erosionerosion
List the agents of erosionList the agents of erosion Define Define physical weatheringphysical weathering, , chemical chemical
weatheringweathering, and , and erosionerosion Describe how Describe how windwind, , waterwater, , ice,ice, and and gravity gravity
affect the surface of earthaffect the surface of earth
The forces of nature not only build up the land The forces of nature not only build up the land but also wear it down. These major processes but also wear it down. These major processes are _________ ____________, are _________ ____________, __________weathering, and __________. __________weathering, and __________.
_______, _______, ______ and even _______ _______, _______, ______ and even _______ and ___________ all play their part in turning and ___________ all play their part in turning the mightiest mountains into the tiniest grains the mightiest mountains into the tiniest grains of sand. of sand.
physical weatheringphysical weatheringchemicalchemical erosion erosion
Water wind iceWater wind ice plantsplantsanimalsanimals
________ ___________ is the actual ________ ___________ is the actual breaking breaking downdown of rock by the action of natural forces, of rock by the action of natural forces, such as water, wind, ice, plants and animals.such as water, wind, ice, plants and animals.
The most common cause of physical weathering The most common cause of physical weathering is due to constant ________ and _______ of is due to constant ________ and _______ of water in and around rocks. water in and around rocks.
Physical weatheringPhysical weathering
freezing meltingfreezing melting
________ ___________ causes changes in the ________ ___________ causes changes in the rocks from the rocks from the reaction of different chemicalsreaction of different chemicals on the surface of the rocks.on the surface of the rocks.
The most common example of chemical The most common example of chemical weathering is called ____________. _______is weathering is called ____________. _______is an example of oxidation. an example of oxidation.
________ changes into oxidized iron (rust). ________ changes into oxidized iron (rust).
Fe + O Fe O Fe + O Fe O
Chemical weatheringChemical weathering
oxidation Rustoxidation Rust
IronIron
3 2 2 33 2 2 3 Iron + Oxygen RustIron + Oxygen Rust
________, a plant that covers rocks, is an ________, a plant that covers rocks, is an example of chemical weathering. This plant example of chemical weathering. This plant secretes a mild acid, _____________, that eats secretes a mild acid, _____________, that eats away or dissolves the surface of rocks.away or dissolves the surface of rocks.
LichenLichen
Carbonic acidCarbonic acid
________ is the process of ___________, ________ is the process of ___________, __________, or ____________ away __________, or ____________ away weathered rock material.weathered rock material.
Water, wind, ice, and gravity all serve in eroding- Water, wind, ice, and gravity all serve in eroding- ____________ weathered material greater ____________ weathered material greater distances, but _________ is the most significant distances, but _________ is the most significant force of erosion.force of erosion.
ErosionErosion washingwashingblowing carryingblowing carrying
transportingtransportingwaterwater
What are 3 ways water erosion can happen?What are 3 ways water erosion can happen?
________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Lifting rocks, grinding rocks, dissolving rocks Lifting rocks, grinding rocks, dissolving rocks
__________, huge sheets or mountains of __________, huge sheets or mountains of ice that melt after a ice age or during ice that melt after a ice age or during global warming leave behind ice-carved global warming leave behind ice-carved valleys. valleys.
Yosemite Valley Yosemite Valley
GlaciersGlaciers
____________ causes tiny grains of sand to ____________ causes tiny grains of sand to be carried causing polishing and be carried causing polishing and reshaping.reshaping.
Sand dunes Sand dunes
Wind erosion Wind erosion