We need to understand the basic process of transport across a plasma membrane. We are learning... ...
-
Upload
gordon-pitts -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
2
Transcript of We need to understand the basic process of transport across a plasma membrane. We are learning... ...
LEARNING GOALS:
We need to understand the basic process of transport across a plasma membrane.
We are learning ... That the cell has a semi-permeable
membrane To understand the difference between
passive and active transport
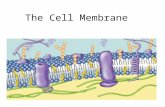
CELL MEMBRANE Controls what goes in and out of the cell
Cell membrane is composed of different structures:
Phospholipid bilayerProtein ChannelsCarbohydratesCholesterol
Together these structures make up the Fluid Mosaic Model
THE CELL MEMBRANE IS SEMI-PERMEABLE
The cell membrane selects substances to enter and leave the cell (semi-permeable)
What is entering? Water and uncharged molecules
(E.g. O2, CO2)
What is leaving? Water and waste (E.g. Fatty Acids)
FEATURES OF THE CELL MEMBRANE
Phospholipid Bilayer:holds components of the cell together
Proteins:transport specific substances across
membrane and aids in signaling
Cholesterol:keeps fluidity of the cell membrane
Carbohydrates:identifies molecules entering the cell
TRANSPORTSubstances can be transported across cell
membrane in 2 different ways:
1. PASSIVE TRANSPORT requires no energy Substances travel from high to low
concentration
2. ACTIVE TRANSPORT requires energy Substances travel from low to high
concentration
PASSIVE TRANSPORT: SIMPLE DIFFUSION
Movement of molecules from a region of high to low concentration
No energy needed
Stops when the concentration of particles are equal everywhere EQUILIBRIUM
Small molecules travel across the phospholipid bilayer in this fashion
I
FACTORS THAT AFFECT SIMPLE DIFFUSION
1. TEMPERATURE: Molecules move faster and reach
equilibrium quicker
2. CONCENTRATION: The bigger difference in concentration, the
faster the rate of diffusion
3. SIZE OF MOLECULE: Smaller molecules diffuse faster than
large molecules
PASSIVE TRANPORT:FACILITATED DIFFUSION
Diffusion with the aid of membrane proteins
Proteins are very selective:
Bind to an identified molecule and transport it across the cell membrane
(ex. Na+ and Cl-Ions)
Energy not needed
DIFFUSION OF WATER:OSMOSIS
The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane
Occurs when water concentrations differ on either side of the cell membrane
Water moves to ensure that the concentration of water is equal on both sides of the cell membrane EQUILIBRIUM
TYPES OF SOLUTIONS:There are three different types of
solutions:
1. ISOTONIC SOLUTION2. HYPERTONIC SOLUTION3. HYPOTONIC SOLUTION
ISOTONIC SOLUTIONSCONDITIONS:equal concentration
inside and out
WATER MOVEMENT: water molecules go in
and out of the cell at the same rate
No net movement
CELL SIZE: stays the same
HYPERTONIC SOLUTIONCONDITIONS:The solution has a
higher concentration of solute than inside the cell
WATER MOVEMENT: Water will move out of the cell
CELL SIZE: cells will shrink and shrivel
HYPOTONIC SOLUTIONCONDITIONS:The solution has a lower
concentration of solute than inside of the cell
WATER MOVEMENT:Water will move inside
the cell
CELL SIZE:expands and swells
ANIMATIONShttp://www.northland.cc.mn.us/biology/biology1111/animations/passive1.swf
http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire/content/chp05/0502001.html
http://biology-animations.blogspot.com/2011/06/cell-membrane-passive-transport.html
http://www.teachersdomain.org/asset/tdc02_int_membraneweb/