Water Resources and Use in Starke County€¦ · Grovertown Ober Winona Ora Bass Station Aldine...
Transcript of Water Resources and Use in Starke County€¦ · Grovertown Ober Winona Ora Bass Station Aldine...
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧#̧
#̧#̧̧#
#̧̧#
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧̧#̧#̧#
#̧
#̧#̧̧#̧#̧##̧
#̧#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧̧#
#̧
#̧
#̧#̧#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧̧#̧#
#̧#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧̧#
#̧
#̧̧#
#̧
#̧
#̧̧#̧#̧#̧#
#̧̧#̧#
#̧̧#̧#
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧#̧̧#
#̧
#̧#̧̧#̧#
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧ #̧
#̧
#̧#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧#̧̧##̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧̧#
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧ #̧
#̧#̧
#̧̧#̧#̧#
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧̧#
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧#̧
#̧
#̧#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧̧#̧#
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧
#̧̧#̧#̧#
#̧
#̧
#̧
"S
"S
"S
"S
"S
"S
"S
"S
"S
"S
"S
"S
Tippecanoe Riv er
Kankakee River
Yellow River
BassLake
Fulto
nPu
laski
Jasp
erP u
laski
Jasp
erSt
arke
LaPo
rtePo
rter
LaPo
rteSta
rke
LaPo
rteSt
. Jos
eph
Mars
hall
Stark
eMa
rshall
St. J
osep
h
PulaskiStarke
StarkeSt. Joseph
KingsfordHeights
Knox
La Crosse
NorthJudson
Walkerton
Wanatah
Source: Esri, DigitalGlobe, GeoEye, i-cubed, USDA, USGS, AEX, Getmapping, Aerogrid, IGN, IGP, swisstopo, and the GIS User Community
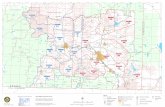
Water Resourcesand Use in
Starke CountyData Sources: U.S. Geological Survey and Indiana Department of Natural Resources
0 2 41MilesN
Major LakesInterstateCounty
"S City
River7Q2 Flow (MGD)
<10 MGD10 - 50 MGD50 - 100 MGD100 - 500 MGD> 500 MGD
Withdrawal LocationWELL INTAKE
#̧Industry#̧Irrigation
#̧Misc.#̧Public Supply#̧Rural Use
#̧Energy/Mining
Grovertown
Ober
Winona
Ora
Bass Station
Aldine
Toto
Brems
English Lake
Lomax
R. 5 W. R. 4 W.
R. 4 W. R. 3 W.
R. 3 W. R. 2 W.
R. 2 W. R. 1 W. R. 1 W. R. 1 E.
R. 1 W. R. 1 E.R. 2 W. R. 1 W.R. 3 W. R. 2 W.R. 4 W. R. 3 W.R. 5 W. R. 4 W.
T. 35 N.T. 34 N.
T. 34 N.T. 33 N.
T. 33 N.T. 32 N.
T. 32 N.T. 31 N.
T. 35 N.T. 34 N.
T. 34 N.T. 33 N.
T. 33 N.T. 32 N.
T. 32 N.T. 31 N.
30
SR 23
SR 23
35
35
SR 10
SR 10
SR 39
SR 8
SR 8
75-00434-PS
Kankakee River
Pine Creek
SR 10 / SR 39
Yellow River
Kankake
e Rive
r
Tippecanoe River
Yellow River
Eagle Creek
Robins Ditch
Jain Ditch
Bailey Ditch
Kline Ditch
Cox Ditch
Payne Ditch
Bogus Run
House
Ditch
County Road 500 S
County Road 400 N
County Road 700 N
County Road 800 S
County Road 500 E
County Road 200 N
County Road 300 E
Coun
ty Ro
ad 90
0 W
Coun
ty Ro
ad 10
0 W
Coun
ty Ro
ad 60
0 W
County Road 1000 E
County Road 200 S
County Road 100 ECoun
ty Ro
ad 50
0 W
County Road 100 S
Coun
ty Ro
ad 70
0 W
Coun
ty Ro
ad 30
0 W
Coun
ty Ro
ad 65
0 W
County Road 400 E
County Road 600 E
County Road 300 S
County Road 100 N
Coun
ty Ro
ad 80
0 W
County Road 800 ECoun
ty Ro
ad 10
0 W
County Road 700 S
County Road 800 S
Coun
ty Ro
ad 30
0 W
County Road 500 N
County Road 700 S
County Road 200 N
County Road 800 N
County Road 1000 E
County Road 700 E
County Road 1100 E
County Road 200 E
Coun
ty Ro
ad 11
00 W
County Road 200 E
County Road 900 E
County Road 600 E
County Road 300 E
County Road 400 S
County Road 500 N
County Road 200 S
County Road 600 N
County Road 300 N
County Road 800 E
SR 10
SR 8
35
SR 23
30
SR 39
421
Bass Lake
Yellow River
Big M
onon
Ditc
h
Kankakee Fish and Wildlife Area
Round Lake Wetland Nature Preserve
Jasper-Pulaski Fish and Wildlife Area
Koontz Lake Wetland Conservation Area
Bass Lake State Beach
Kankakee River Swampland
Bass Lake Public Access Site
5 42
3 51
7
31
6
62 4 523
1 45
7
34
8
3
6
2
2
2 1
9 8
7
6
5
8
9
1
62
8
9
7
7
4 1
9
98 78
3 1
9
8
1
9
9
1 3
4
23 456
7
2
8
4
5
18
11
30
11
31
1111
31
30
11
11
31
11
19
32
14
14
19
31
11
13
31
18
11
3027 26 25
30
31
31
20
13
12
13
29
14
26
30
22 23
32
29
32
17
12
35
13
19
16
35
34
13 15
18
28
15
35
21
12
23
32
24
25
33 36
36
24
28
33
31
30
36
14
28
13
35
34
19
1615
23
19
17
18
2526
35
36
30
23
1813
12
24
12
2220
31
10
34
21
36
27
35
18
3332
33
24
34
17
25
21
24
14
2927
16
32
22
36
28
22
22
12
23
10
17
29
14
23
18
25
33
28
36
13
25
16
26
27
3236
19 19
26
36
21
28
15
29
3633
24
27
20
27
35
29
19
33
26
12
21
34
16
27
14
14
1517
34 34
16
26
35
25
12
21
22
29
25 30
17
22
18
28
15
24
27
20
35
10
28
10
33
20
17
34
20
23
17
14
26
34
12
16
29
32
24
13
27
21
20
23
15
20
25
16
26
32
10
24
33
10
15
10
28
22
22
10
23
21
25
36
15
21
29
35
7
24
34
35
30
13
16
6
10
26
33
5
20
Bass Lake
Knox
Koontz Lake
Hamlet
North Judson
San Pierre
75-01778-IR
75-01776-IR
75-01775-IR
75-01774-RU
75-01773-IR75-01772-RU
75-01771-IR
Map generated by Scott H. DeanIDNR, Division of Water, Resource Assessment Section
Map Use and Disclaimer StatementWe request that the following agency be acknowledged in products derived from this map: Indiana Department of Natural Resources, Division of Water.This map was compiled by staff of the Indiana Department of Natural Resources, Division of Water using data believed to be reasonably accurate. However, a degree of error is inherent in all maps. This product is distributed “as is” without warranties of any kind, either expressed or implied. This map is intended for use only at the published scale.
The occurrence of bedrock aquifers depends on the original composition of the rocks and subsequent changes which influence the hydraulic properties. Post-depositional processes, which promote jointing, fracturing, and solution activity of exposed bedrock, generally increase the hydraulic conductivity (permeability) of the upper portion of bedrock aquifer systems. Because permeability in many places is greatest near the bedrock surface, bedrock units within the upper 100 feet are commonly the most productive aquifers.
In Starke County thickness of unconsolidated deposits overlying bedrock ranges from approximately 35 feet in the southwest near the Kankakee River, to as much as 212 feet in the east-central portion of the county. Most of the bedrock aquifers, therefore, are under confined conditions. In other words, the potentiometric surface (water level) in most wells completed in bedrock rises above the top of the water-bearing formation.
The yield of a bedrock aquifer depends on its hydraulic characteristics and the nature of the overlying deposits. Shale and glacial till act as aquitards, restricting recharge to underlying bedrock aquifers. However, fracturing and/or jointing may occur in aquitards, which can increase recharge to the underlying aquifers. Hydraulic properties of the bedrock aquifers are highly variable.
The susceptibility of bedrock aquifer systems to surface contamination is largely dependent on the type and thickness of the overlying sediments. Because the bedrock aquifer systems have complex fracturing systems, once a contaminant has been introduced into a bedrock aquifer system, it will be difficult to track and remediate.
Two bedrock aquifer systems are identified for Starke County. They are the Devonian and Mississippian Coldwater, Ellsworth and Antrim Shales; and the Silurian and Devonian Carbonates. Approximately 10 percent of all field located wells in Starke County are completed in bedrock.
In Starke County only the Ellsworth and Antrim Shale subcrops in the Coldwater, Ellsworth and Antrim Shales Aquifer System. The Ellsworth Shale is comprised of alternating beds of gray-green to brownish black shale. The Antrim Shale is typically described as brownish-black shale. However, in some places the lower portion of the Antrim Shale may contain some limestone. The subcrop area for the Antrim Shale includes most of central Starke County and the subcrop area for the Ellsworth shale includes the northwestern part of the county. In general, reported thickness of the Antrim and Ellsworth shales in the subcrop area ranges from 10 to 129 feet. Few wells utilize the Coldwater, Ellsworth and Antrim Shales Aquifer System. Shale is commonly considered an aquitard and therefore, the system is an extremely limited groundwater resource. In Starke County, most domestic wells either produce from the overlying unconsolidated deposits or penetrate through the shale in favor of the underlying Silurian and Devonian Carbonates. However, a few wells report capacities up to 10 gallons per minute (gpm). Reported depth to bedrock generally ranges from 35 to 153 feet. It is likely that these wells are under the influence of overlying sands and gravels. Because the permeability of shale materials is considered low, susceptibility to contamination introduced at or near the surface is low. However, areas where outwash deposits directly overly fractured bedrock are at moderate to high risk to contamination.
The Silurian and Devonian Carbonates Aquifer System subcrops along the southeastern and south-central portions of Starke County. The system includes Devonian age carbonate units of the Muscatatuck Group. Total thickness of the Devonian bedrock generally ranges from about 85 to 150 feet. Few wells are reported in the Silurian and Devonian Carbonates Aquifer System. However, in some isolated areas drillers bypass the unconsolidated resources and utilize the underlying bedrock aquifer. Depth to the bedrock surface is approximately 150 feet, although most wells that reportedly use the system penetrate through the overlying Ellsworth and Antrim shales outside the subcrop area. The Silurian and Devonian Carbonates Aquifer System is capable of meeting the needs of domestic and some high-capacity users. Total well depths range from 80 to 301 feet. Domestic yields generally range from 1 to 45 gpm with static water levels from 6 to 36 feet. There are 8 registered significant groundwater withdrawal facilities (10 wells) utilizing the Silurian and Devonian Carbonates Aquifer System with reported yields of individual wells ranging from 90 to 850 gpm. Much of the Silurian and Devonian Carbonates Aquifer System in Starke County is overlain by sands and gravels with intermittent clay deposits. These areas are generally considered at moderate to high risk to contamination. However, most wells completed in this aquifer system are outside the subcrop area and penetrate through the overlying Ellsworth and Antrim shales. These areas are at moderate to low risk to contamination.
Division of Water Aquifer Systems Map 75-B
Mitchell E. Daniels, Jr., GovernorDepartment of Natural Resources
Robert E. Carter, Jr., Director
Location Map
BEDROCK AQUIFER SYSTEMS OF STARKE COUNTY, INDIANA
This map was created from several existing shapefiles. Township and Range Lines of Indiana (line shapefile, 20020621), Land Survey Lines of Indiana (polygon shapefile, 20020621) and County Boundaries of Indiana (polygon shapefile, 20020621), were all from the Indiana Geological Survey and based on a 1:24,000 scale, except the Bedrock Geology of Indiana (polygon shapefile, 20020318), which was at a 1:500,000 scale. Draft road shapefiles, System1 and System2 (line shapefiles, 2003), were from the Indiana Department of Transportation and based on a 1:24,000 scale. Populated Areas in Indiana 2000 (polygon shapefile, 20021000) was from the U.S. Census Bureau and based on a 1:100,000 scale. Streams27 (line shapefile, 20000420 was from the Center for Advanced Applications in GIS at Purdue University.
Bedrock Aquifer Systems of Starke County, Indianaby
Randal D. MaierDivision of Water, Resource Assessment Section
October 2010
Devonian and Mississippian -- Coldwater, Ellsworth,and Antrim Shales Aquifer System
Silurian and Devonian Carbonates Aquifer System
Registered Significant Ground-water Withdrawal Facility
EXPLANATION
State Managed Property
Municipal Boundary
State Road & US HighwayCounty RoadStream
Lake & River
1 0 10.5 Mile
1 0 10.5 Kilometer
Grovertown
Ober
Winona
Ora
Bass Station
Aldine
Toto
Brems
English Lake
Lomax
R. 5 W. R. 4 W.
R. 4 W. R. 3 W.
R. 3 W. R. 2 W.
R. 2 W. R. 1 W. R. 1 W. R. 1 E.
R. 1 W. R. 1 E.R. 2 W. R. 1 W.R. 3 W. R. 2 W.R. 4 W. R. 3 W.R. 5 W. R. 4 W.
T. 35 N.T. 34 N.
T. 34 N.T. 33 N.
T. 33 N.T. 32 N.
T. 32 N.T. 31 N.
T. 35 N.T. 34 N.
T. 34 N.T. 33 N.
T. 33 N.T. 32 N.
T. 32 N.T. 31 N.
35
35
30
SR 8
SR 8
SR 10
SR 10
SR 23
SR 23
SR 39
Kankakee River
SR 10 / SR 39
Yellow River
Kankake
e Rive
r
Tippecanoe River
Yellow River
Robins Ditch
Jain Ditch
Bailey Ditch
Cox Ditch
Kline Ditch
Payne Ditch
Bogus Run
House
Ditch
County Road 500 S
County Road 400 N
County Road 700 N
County Road 800 S
County Road 500 E
County Road 200 N
County Road 300 E
Coun
ty Ro
ad 90
0 W
Coun
ty Ro
ad 10
0 W
Coun
ty Ro
ad 60
0 W
County Road 1000 E
County Road 200 S
County Road 100 E
Coun
ty Ro
ad 50
0 W
County Road 100 S
Coun
ty Ro
ad 70
0 W
Coun
ty Ro
ad 30
0 W
Coun
ty Ro
ad 65
0 W
County Road 400 E
County Road 600 E
County Road 300 S
County Road 100 N
Coun
ty Ro
ad 80
0 W
County Road 800 ECoun
ty Ro
ad 10
0 W
County Road 700 S
County Road 800 S
Coun
ty Ro
ad 30
0 W
County Road 500 N
County Road 700 S
County Road 200 N
County Road 800 N
County Road 700 E
County Road 1100 E
County Road 200 E
Coun
ty Ro
ad 11
00 W
County Road 200 E
County Road 900 E
County Road 600 E
County Road 300 E
County Road 400 S
County Road 500 N
County Road 200 S
County Road 600 N
County Road 300 N
County Road 800 E
SR 10
SR 8
35
SR 23
30
SR 39
421Bass Lake
Yellow River
Pine Creek
Eagle Creek
Big M
onon
Ditc
hKankakee
Fish and Wildlife Area
Round Lake Wetland Nature Preserve
Jasper-Pulaski Fish and Wildlife Area
Koontz Lake Wetland Conservation Area
Bass Lake State Beach
Kankakee River Swampland
Bass Lake Public Access Site
5 42
3 51
7
31
6
62 4 523
1 45
7
34
8
3
6
2
2
2 1
9 8
7
6
5
8
9
1
62
8
9
7
7
4 1
9
98 78
3 1
9
8
1
9
9
1 3
4
23 456
7
2
8
4
5
18
11
30
11
31
1111
31
30
11
11
31
11
19
32
14
14
19
31
11
13
31
18
11
3027 26 25
30
31
31
20
13
12
13
29
14
26
30
22 23
32
29
32
17
12
35
13
19
16
35
34
13 15
18
28
15
35
21
12
23
32
24
25
33 36
36
24
28
33
31
30
36
14
28
13
35
34
19
1615
23
19
17
18
2526
35
36
30
23
1813
12
24
12
2220
31
10
34
21
36
27
35
18
3332
33
24
34
17
25
21
24
14
2927
16
32
22
36
28
22
22
12
23
10
17
29
14
23
18
25
33
28
36
13
25
16
26
27
3236
19 19
26
36
21
28
15
29
3633
24
27
20
27
35
29
19
33
26
12
21
34
16
27
14
14
1517
34 34
16
26
35
25
12
21
22
29
2530
17
22
18
28
15
24
27
20
35
10
28
10
33
20
17
34
20
23
17
14
26
34
12
16
29
32
24
13
27
21
20
23
15
20
25
16
26
32
10
24
33
10
15
10
28
22
22
10
23
21
25
36
15
21
29
35
7
24
34
35
30
13
16
6
10
26
33
5
20
Bass Lake
Knox
Koontz Lake
Hamlet
North Judson
San Pierre
75-04818-IR
75-04817-IR
75-04501-IR
75-04364-IR
75-04336-IR
75-04298-RU
75-04175-RU
75-03467-IR
75-03357-IR
75-03248-IR
75-03196-IR
75-03168-IR75-03146-IR
75-03091-IR
75-03024-MI
75-02623-IR
75-02602-IR
75-02597-IR
75-02459-IR
75-02353-PS
75-02091-IR
75-01337-IR
75-00765-PS
75-00629-IR
75-00466-IR
75-00379-IR
75-00378-IR
75-00358-IR
75-04901-IR
75-04728-IR
75-04696-IR
75-04525-IR
75-04437-IR
75-04255-IR
75-04189-IR
75-04174-IR
75-04122-IR
75-03824-MI
75-03484-IR
75-03475-IR
75-03391-MI
75-03252-IR
75-03245-IR
75-03195-IR
75-03174-IR
75-03170-IR75-03145-IR
75-03139-IR
75-03105-IR
75-02675-IN 75-02608-IR
75-02607-IR
75-02478-IN
75-02283-IR
75-02090-IR
75-02089-IR
75-01338-IR
75-00357-IR
75-00263-PS
Map generated by Scott H. DeanIDNR, Division of Water, Resource Assessment Section
Map Use and Disclaimer StatementWe request that the following agency be acknowledged in products derived from this map: Indiana Department of Natural Resources, Division of Water.This map was compiled by staff of the Indiana Department of Natural Resources, Division of Water using data believed to be reasonably accurate. However, a degree of error is inherent in all maps. This product is distributed “as is” without warranties of any kind, either expressed or implied. This map is intended for use only at the published scale.
Five unconsolidated aquifer systems have been mapped in Starke County: the Eolian Sands; the Valparaiso Outwash Apron; the Kankakee / Plymouth Complex; the Kankakee; and the Wabash River and Tributaries Outwash System. Characteristics of the Kankakee, the Eolian Sands and the Valparaiso Outwash Apron have been described and mapped as part of the previously published regional basin study report; Water Resource Availability in the Kankakee River Basin, Indiana, IDNR, 1990. Although characteristics and descriptions of the basin study aquifer systems are generalized over large portions of northern Indiana, the descriptions of the aquifer systems have been modified here to accommodate the individuality of Starke County. Boundaries of all aquifer systems described are commonly gradational, and individual aquifers may extend across aquifer system boundaries. Thicknesses of unconsolidated sediments that overlie bedrock are quite variable in Starke County. Total thickness ranges from approximately 35 feet in the southwest near the Kankakee River, to as much as 212 feet in the east-central portion of the county. Approximately 90 percent of all located wells are completed in unconsolidated deposits. Regional estimates of aquifer susceptibility to contamination from the surface can differ considerably due to variation within geologic environments. In addition, man-made structures such as poorly constructed water wells, unplugged or improperly abandoned wells, and open excavations, can provide contaminant pathways that bypass the naturally protective clays.
The Eolian Sands Aquifer System includes portions previously mapped as part of the regional basin study report; Water Resource Availability in the Kankakee River Basin, Indiana, IDNR, 1990, and is mapped throughout the central portion of Starke County from the Town of San Pierre and continuing northeast. General characteristics of this system involve windblown (eolian) sand at the surface with, in some areas, intermittent clay beneath that separates surface deposits from the deeper aquifer resource. In some isolated areas, either the upper windblown sands are not present, or, clay that separates the upper eolian sands from the lower outwash aquifer is not present. Upper confining clay typically ranges from 1 to 50 feet thick with the overlying eolian sands generally ranging up to 30 feet thick. Wells completed in the Eolian Sands Aquifer System are typically from 50 to 105 feet deep. Aquifer thickness ranges from 7 to 40 feet. This system is capable of meeting the needs of domestic and some high-capacity users. Domestic well yields are commonly 15 to 65 gallons per minute (gpm). Static water levels range from 5 to 15 feet below surface with reports of flowing wells. There are 25 registered significant groundwater withdrawal facilities (32 wells) utilizing this system with reported yields ranging from 75 to 1500 gpm. This aquifer system is generally not very susceptible to surface contamination where intratill sand and gravel units are overlain by thick till deposits. However, areas where overlying clays are thin or absent are at moderate to high risk of contamination.
The Kankakee / Plymouth Complex Aquifer System is mapped in portions of southern Starke County. Complex multiple glacial advances resulted in a sequence of multiple, stacked, till and outwash units that are quite variable in position and thickness. Characteristics of this system may include surface sands (primarily windblown deposits that are not used as an aquifer resource) that overlie a thick clay cap with discontinuous intratill sands and gravels above the primary aquifer unit. In places the system exhibits multiple sand and gravel deposits above the primary aquifer resource that are also a potential source of groundwater. Few wells are reported in the Kankakee / Plymouth Complex. Well depths, however, generally range from 38 to 123 feet. The sand and gravel deposits vary from thin to massive and are typically discontinuous and overlain by a thick till. Total accumulative unconsolidated thicknesses above the aquifer unit are generally 10 to 108 feet of clay with the discontinuous sands and gravels typically 7 to 22 feet thick. The deeper, more productive aquifer deposits range from 5 to 64 feet thick. The Kankakee / Plymouth Complex Aquifer System is capable of meeting the needs of domestic and high-capacity users. Typical domestic yields range from 10 to 50 gpm. Static water levels commonly range from 5 to 28 feet below surface. There are 4 registered significant groundwater withdrawal facilities (5 wells) with reported yields that range from 700 to 1000 gpm. This aquifer system is not very susceptible to contamination where clay deposits overlie aquifer materials. However, in places clay deposits are thin or not present; these areas are at moderate to high risk to surface contamination.
Division of Water Aquifer Systems Map 75-A
Mitchell E. Daniels, Jr., GovernorDepartment of Natural Resources
Robert E. Carter, Jr., Director
Location Map
UNCONSOLIDATED AQUIFER SYSTEMS OF STARKE COUNTY, INDIANA
This map was created from several existing shapefiles. Township and Range Lines of Indiana (line shapefile, 20020621), Land Survey Lines of Indiana (polygon shapefile, 20020621), and County Boundaries of Indiana (polygon shapefile, 20020621), were all f rom the Indiana Geological Survey and based on a 1:24,000 scale. Draft road shapefiles, System1 and System2 (line shapefiles, 2003), were from the Indiana Department of Transportation and based on a 1:24,000 scale. Populated Areas in Indiana 2000 (pol ygon shapefile, 20021000) was from the U.S. Census Bureau and based on a 1:100,000 scale. Streams27 (line shapefile, 20000420) was from the Center for Advanced Applications in GIS at Purdue University. Managed Areas 96 (polygon shapefile, various dates) was from IDNR. Unconsolidated Aquifer Systems coverage was from IDNR (Water Resource Availability in the Kankakee River Basin, Indiana, 1990 ) (Modified, Maier 2010) and based on a 1:48,000 scale.
Registered Significant Ground-Water Withdrawal Facility
EXPLANATION
State Managed Property
Municipal Boundary
State Road & US HighwayCounty RoadStream
Lake & River
Unconsolidated Aquifer Systems of Starke County, Indianaby
Randal D. MaierDivision of Water, Resource Assessment Section
October 2010
The Valparaiso Outwash Apron Aquifer System was previously mapped as part of the regional basin study report; Water Resource Availability in the Kankakee River Basin, Indiana, IDNR, 1990. Unconsolidated deposits are associated with the southern limit of a wide band of glacially derived outwash that overlies bedrock or clay. This system is mapped along much of the northwestern part of Starke County. Total depth of wells completed in Starke County range from 17 to 148 feet with up to 94 feet of continuous aquifer sands and gravels. Where present, intermittent clay ranging from 3 to 120 feet thick separates upper outwash sands and gravels from the underlying aquifer. This system is capable of meeting the needs of domestic and high-capacity users. Domestic well yields are commonly 10 to 60 gpm with static water levels that range from 2 to 28 feet below surface. There are 25 registered significant groundwater withdrawal facilities (61 wells) utilizing this system with reported high-capacity yields ranging from 138 to 1300 gpm. This aquifer system is generally not very susceptible to surface contamination because intratill sand and gravel units are overlain by thick till deposits. However, wells that utilize the shallow sands and gravels are at moderate to high risk to surface contamination.
In Starke County the Kankakee Aquifer System is mapped in the northwestern and southwestern areas of the county and includes previously mapped portions as part of the regional basin study report; Water Resource Availability in the Kankakee River Basin, Indiana, IDNR, 1990. Few wells are reported in the Kankakee Aquifer System in Starke County. Total well depths range from 19 to 105 feet with sands and gravels up to 53 feet thick. In isolated areas some intermittent clay deposits may be present. Static water levels range from 3 to 24 feet below surface. This system is capable of meeting the needs of domestic and some high-capacity users. There are 7 registered significant groundwater withdrawal facilities (9 wells) with yields that range from 80 to 1100 gpm. The system is at moderate to high risk to contamination.
In Starke County the Wabash River and Tributaries Outwash Aquifer System includes thick, glacially derived outwash deposits along with recent alluvial deposits that cap the outwash deposits in places. The system is mapped in the southeastern part of the county along the floodplain of the Tippecanoe River. There are no domestic wells reported in this system in Starke County. However, there are 2 registered significant groundwater withdrawal facilities (3 wells) in the outwash system in Starke County. Well depths range from 60 to 90 feet below the surface with total thickness reported as continuous sand and gravel. In places, aquifer materials may be capped by silt, clay or sandy clay. Individual wells report yields ranging from 450 to 1050 gpm with static water levels of 6 and 15 feet below the surface. In nearby Pulaski County domestic wells are reported to yield 15 to 60 gpm. The Wabash River and Tributaries Outwash Aquifer System is capable of meeting the needs of domestic and high-capacity users. Areas that lack overlying clay deposits are highly susceptible to contamination. However, where overlying clay deposits are present the system is moderately susceptible to surface contamination.
Eolian Sands Aquifer System
Kankakee / Plymouth Complex Aquifer System
Wabash River and Tributaries Outwash Aquifer System
1 0 10.5 Mile
1 0 10.5 Kilometer
Kankakee Aquifer System
Valparaiso Outwash Apron Aquifer System
Grovertown
Ober
Winona
Ora
Bass Station
Aldine
Toto
Brems
English Lake
Lomax
R. 5 W. R. 4 W.
R. 4 W. R. 3 W.
R. 3 W. R. 2 W.
R. 2 W. R. 1 W. R. 1 W. R. 1 E.
R. 1 W. R. 1 E.R. 2 W. R. 1 W.R. 3 W. R. 2 W.R. 4 W. R. 3 W.R. 5 W. R. 4 W.
T . 35 N.T . 34 N.
T . 34 N.T . 33 N.
T . 33 N.T . 32 N.
T . 32 N.T . 31 N.
T . 35 N.T . 34 N.
T . 34 N.T . 33 N.
T . 33 N.T . 32 N.
T . 32 N.T . 31 N.
£¤30
¬«23
¬«23
£¤35
£¤35
¬«10
¬«10
¬«39
¬«8
¬«8
Kankakee River
¬«10
Yellow River
Kankake
e Rive
r
Tippecanoe River
Yellow River
Eagle Creek
Robins Ditch
Jain Ditch
Bailey Ditch
Kline Ditch
Cox Ditch
Bogus Run
House D
itch
Kankakee River Basin
Upper Wabash River Basin
Upper Wabash River Basin
Kankakee River Basin
670
700
690
690
710
710
680
680
680
690
700
720
Pine Creek
¬«39
CR 500 S
CR 400 N
CR 700 N
CR 800 S
CR 500 E
CR 200 NCR 300 E
CR 90
0 W
CR 10
0 W
CR 60
0 W
CR 1000 E
CR 200 S
CR 100 E
CR 50
0 W
CR 100 S
CR 70
0 W
CR 30
0 W
CR 65
0 W
CR 400 E
CR 60
0 E
CR 300 S
CR 100 N
CR 80
0 W
CR 80
0 E
CR 10
0 W
CR 700 S
CR 800 S
CR 30
0 W
CR 500 N
CR 700 S
CR 200 N
CR 800 N
CR 1000 E
CR 700 E
CR 1100 E
CR 200 E
CR 11
00 W
CR 200 E
CR 900 E
CR 600 E
CR 300 E
CR 400 S
CR 500 N
CR 200 S
CR 600 N
CR 300 N
CR 800 E
¬«10
¬«8
£¤35
¬«23
£¤30
¬«39
£¤421
Bass Lake
Big M
onon
Ditc
h
5 42
3 51
7
31
6
62 4 523
1 45
7
34
8
3
6
2
2
2 1
9 8
7
6
5
8
9
1
62
8
9
7
7
4 1
9
98 7 8
3 1
9
8
1
9
9
1 3
4
23 456
7
2
8
4
5
18
11
30
11
31
1111
31
30
11
11
31
11
19
32
14
14
19
31
11
13
31
18
11
3027 26 25
30
31
31
20
13
12
13
29
14
26
30
22 23
32
29
32
17
12
35
13
19
16
35
34
13 15
18
28
15
35
21
12
23
32
24
25
33 36
36
24
28
33
31
30
36
14
28
13
35
34
19
1615
23
19
17
18
2526
35
36
30
23
1813
12
24
12
22
20
31
10
34
21
36
27
35
18
3332
33
24
34
17
25
21
24
14
2927
16
32
22
36
28
22
22
12
23
10
17
29
14
23
18
25
33
28
36
13
25
16
26
27
3236
19 19
26
36
21
28
15
29
3633
24
27
20
27
35
29
19
33
26
12
21
34
16
27
14
14
1517
34 34
16
26
35
25
12
21
22
29
25 30
17
22
18
28
15
24
27
20
35
10
28
10
33
20
17
34
20
23
17
14
26
34
12
16
29
32
24
13
27
21
20
23
15
20
25
16
26
32
10
24
33
10
15
10
28
22
22
10
23
21
25
36
15
21
29
35
7
24
34
35
30
13
16
6
10
26
33
5
20
Bass Lake
Knox
Koontz Lake
Hamlet
North Judson
San Pierre
680
700
690
710
670
660
720
730
700
720
700
690
670
720
730
710
720
730
Kankakee Fish and Wildlife Area
Koontz Lake Nature Preserve
Kankakee Fish and Wildlife Area
Jasper-Pulaski Fish and Wildlife Area
Round Lake Wetland Nature
Preserve
Ober Savanna
Highway Prairie Managment Area
Bass Lake State Beach
Koontz Lake Dam Property
Bass Lake Public Access
Site
Ma p genera ted b y Ro b ert K. Sc hm id t a nd Jo el D. Sa nd erso nInd ia na Dep a rtm ent o f Na tura l Reso urc es,Divisio n o f Wa ter, Reso urc e Assessm ent Sec tio n
Divisio n o f Wa ter Aquifer System s Ma p 22-AMic ha el R. Penc e, Go verno r
Dep a rtm ent o f Na tura l Reso urc esRo b ert E. Ca rter, Jr., Direc to r
Location Map
POT ENT IOMET RIC SU RFACE MAP OF T HE U NCONSOL IDAT ED AQU IFERSOF ST ARKE COU NT Y, INDIANA
®
Digital Elevation Model of Starke County, Indiana
Potentiometric Surface Map of the Unconsolidated Aquifersof Starke County, Indiana
b yRo b ert K. Sc hm id t
Divisio n o f Wa ter, Reso urc e Assessm ent Sec tio n
Feb rua ry 2013
T his m a p wa s c rea ted fro m severa l existing sha p efiles. T o wnship a nd Ra nge L ines o f Ind ia na (line sha p efile, 20020621), L a nd Survey L ines o f Ind ia na (p o lygo n sha p efile, 20020621), a nd Co unty Bo und a ries o f Ind ia na (p o lygo n sha p efile, 20020621), were a ll fro m the Ind ia na Geo lo gic a l Survey a nd b a sed o n a 1:24,000 sc a le. Dra ft ro a d sha p efiles, System 1 a nd System 2 (line sha p efiles, 2003), were fro m the Ind ia na Dep a rtm ent o f T ra nsp o rta tio n a nd b a sed o n a 1:24,000 sc a le. Po p ula ted Area s in Ind ia na 2000 (p o lygo n sha p efile, 20021000) wa s fro m the U .S. Census Burea u a nd b a sed o n a 1:100,000 sc a le. Hyd ro gra p hy, Strea m s (NHD) (line sha p efile, 20081218), Rivers (NHD) (p o lygo n sha p efile, 20081218), L a kes (NHD) (p o lygo n sha p efile, 20081218) wa s fro m the U .S. Geo lo gic a l Survey a nd the U .S. Enviro nm enta l Pro tec tio n Agenc y, a nd b a sed o n a 1:24,000 sc a le. Ma na ged L a nd s IDNR IN (p o lygo n sha p efile, 20100920) wa s fro m the Ind ia na Dep a rtm ent o f Na tura l Reso urc es a nd b a sed o n a 1:24,000 sc a le. Digita l Eleva tio n Mo d el im a ge is d erived fro m the Ind ia na Ortho /L iDAR Sta tewid e Co llec tio n Pro gra m (2011). Po tentio m etric Surfa c e Ma p o f the U nc o nso lid a ted Aquifers o f Sta rke Co unty, Ind ia na (line sha p efiles, Sc hm id t, 2013) wa s b a sed o n a 1:24,000 sc a le.
Sta rke Co unty, Ind ia na is lo c a ted in the no rthwest sec tio n o f the sta te. T he so uthwestern a nd so uthea stern p o rtio ns o f the c o unty a re situa ted within the U p p er Wa b a sh River Ba sin with the rem a ining p a rts lo c a ted in the Ka nka kee River Ba sin.T he Po tentio m etric Surfa c e Ma p (PSM) o f the unc o nso lid a ted a quifers o f Sta rke Co unty wa s m a p p ed b y c o nto uring the eleva tio ns o f a p p ro xim a tely 870 sta tic wa ter-levels rep o rted o n well rec o rd s rec eived p rim a rily o ver a 50 yea r p erio d . T hese wells a re c o m p leted in a quifers a t va rio us d ep ths, a nd typ ic a lly, und er c o nfined c o nd itio ns (b o und ed b y im p erm ea b le la yers a b o ve a nd b elo w the wa ter b ea ring fo rm a tio n). Ho wever, so m e wells were c o m p leted und er unc o nfined (no t b o und ed b y im p erm ea b le la yers) settings. T he p o tentio m etric surfa c e is a m ea sure o f the p ressure o n wa ter in a wa ter b ea ring fo rm a tio n. Wa ter in a n unc o nfined a quifer is a t a tm o sp heric p ressure a nd will no t rise in a well a b o ve the to p o f the wa ter b ea ring fo rm a tio n, in c o ntra st to wa ter in a c o nfined a quifer whic h is und er hyd ro sta tic p ressure a nd will rise in a well a b o ve the to p o f the wa ter b ea ring fo rm a tio n.Sta tic wa ter-level m ea surem ents in ind ivid ua l wells used to c o nstruc t c o unty PSM’s a re ind ic a tive o f the wa ter-level a t the tim e o f well c o m p letio n. T he gro und wa ter level within a n a quifer c o nsta ntly fluc tua tes in resp o nse to ra infa ll, eva p o tra nsp ira tio n, gro und wa ter m o vem ent, a nd gro und wa ter p um p a ge. T herefo re, m ea sured sta tic wa ter-levels in a n a rea m a y d iffer d ue to lo c a l o r sea so na l va ria tio ns. Bec a use fluc tua tio ns in gro und wa ter a re typ ic a lly sm a ll, sta tic wa ter-levels c a n b e used to c o nstruc t a genera lized PSM. Gro und wa ter flo w is na tura lly fro m a rea s o f rec ha rge to wa rd a rea s o f d isc ha rge. As a genera l rule, b ut c erta inly no t a lwa ys, gro und wa ter flo w a p p ro xim a tes the o verlying to p o gra p hy a nd intersec ts the la nd surfa c e a t m a jo r strea m s.U niversa l T ra nsverse Merc a to r (U T M) c o o rd ina tes fo r the wa ter wells were either p hysic a lly o b ta ined in the field , d eterm ined thro ugh a d d ress geo c o d ing, o r rep o rted o n wa ter well rec o rd s; ho wever, the lo c a tio n o f the m a jo rity o f the wa ter well rec o rd s used to m a ke the PSM were no t field verified . Eleva tio n d a ta were either o b ta ined fro m to p o gra p hic m a p s o r a d igita l eleva tio n m o d el. Qua lity c o ntro l/qua lity a ssura nc e p ro c ed ures were utilized to refine o r rem o ve d a ta where erro rs were rea d ily a p p a rent.U nc o nso lid a ted sta tic wa ter levels in Sta rke Co unty ra nge fro m a high o f 738 feet m ea n sea level (m sl) in the no rthea stern sec tio n o f the c o unty, to a lo w o f 652 feet m sl in the so uthwestern p o rtio n. Gro und wa ter flo w d irec tio n in the Ka nka kee River Ba sin is to the West to wa rd the Ka nka kee River, a nd genera lly to the so uth to wa rd the T ip p ec a no e River within the U p p er Wa b a sh River Ba sin.T he c o unty PSM c a n b e used to d efine the regio na l gro und wa ter flo w p a th a nd to id entify signific a nt a rea s o f gro und wa ter rec ha rge a nd d isc ha rge. Co unty PSM’s rep resent o vera ll regio na l c ha ra c teristic s a nd a re no t intend ed to b e a sub stitute fo r site-sp ec ific stud ies. 1 0 10.5 Mile
1 0 10.5 Kilo m eter
Map Use and Disclaimer StatementWe request tha t the fo llo wing a genc y b e a c kno wled ged in p ro d uc ts d erived fro m this m a p : Ind ia na Dep a rtm ent o f Na tura l Reso urc es, Divisio n o f Wa ter.T his m a p wa s c o m p iled b y sta ff o f the Ind ia na Dep a rtm ent o f Na tura l Reso urc es, Divisio n o f Wa ter using d a ta b elieved to b e rea so na b ly a c c ura te. Ho wever, a d egree o f erro r is inherent in a ll m a p s. T his p ro d uc t is d istrib uted “a s is” witho ut wa rra nties o f a ny kind , either exp ressed o r im p lied . T his m a p is intend ed fo r use o nly a t the p ub lished sc a le.
EXPLANATION
Sta te Ma na ged Pro p erty
Munic ip a l Bo und a ry
U S Highwa y
Co unty Ro a dStrea m
L a ke & River
Sta te Ro a d¬«8
£¤35
L ine o f equa l eleva tio n, in feet a b o ve m ea n sea levelPo tentio m etric Co nto ur interva l 10 feetBa sin Bo und a ry
700
Elevation (feet)781
658


















![CROMATOGRAFIA - people.unica.it · CROMATOGRAFIA DOTT. JOANNA IZABELA LACHOWICZ . RISOLUZIONE DELLA COLONNA R= ΔZ ½(W A +W B) R= 2ΔZ (W A +W B) R= 2[(t R) B – (t R) A] (W A +W](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/5f61cc816b14e4658d17962b/cromatografia-cromatografia-dott-joanna-izabela-lachowicz-risoluzione-della.jpg)




