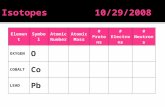
ElementSymbol Atomic Number Atomic Mass # Protons # Electrons # Neutrons OXYGEN O COBALT Co LEAD Pb.
Wake-up 1.Explain the relationship between the following: atomic number, mass number, protons,...
-
Upload
albert-horton -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
0
Transcript of Wake-up 1.Explain the relationship between the following: atomic number, mass number, protons,...
Wake-up
1. Explain the relationship between the following: atomic number, mass number, protons, neutrons, and electrons.
2. How do you find the number of electrons of an element?
3. How do you find the number of neutrons of an element?
Examine the information of hydrogen below and answer the following questions. Do not
round the mass number!
What is an ISOTOPE?• Isotope = atoms that have the same number of
PROTONS but different number of NEUTRONS.• Chemically alike but with varying mass numbers
Examine the mass number of the various elements on the periodic table. Very few are even. This is
due to isotopes. The mass number is better known as the Atomic Mass or Atomic Unit. This number represents the AVERAGE mass of all the naturally
occurring isotopes of an element.
Relative Abundance
The abundance isotopes of an element as naturally found on a planet (%)
Relative abundance of elements on
Earth’s surface
In other words, all the isotopes of the same element (atom) have the SAME
but DIFFERENT
Atomic Number (p+ and e-)
Mass Number (specifically n0)
Calculating Average Atomic Mass #1
You have a box containing two sizes of marbles.
• 25% of the marbles have a mass of 2.0 g.
• 75% of the marbles have a mass of 3.0 g.
Calculate the average weight of the marble.
Example #2: Rubidium has two common isotopes, 85Rb and 87Rb. If the abundance of 85Rb
is 72.2% and the abundance of 87Rb is 27.8%, what is the average atomic mass of rubidium?