W xxD R RHHCR R505VC - The Plant Cell€¦ · 05/08/2016 · Supplemental Data. Belda-Palazon et...
Transcript of W xxD R RHHCR R505VC - The Plant Cell€¦ · 05/08/2016 · Supplemental Data. Belda-Palazon et...

Supplemental Data. Belda-Palazon et al. (2016). Plant Cell. 10.1105/tpc.16.00178
BA
W452xxD R473RHHCR R505VC
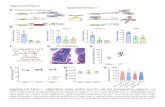
Supplemental Figure 1. Identification and Modeling of the FYVE Domain in At1g20110/FYVE1/FREE1.
(A) Amino acid sequence alignment of the FYVE1 C-terminal region (residues 390-601) with the FYVE domain of human EEA1. The Protein Databank (PDB) accesion number for the EEA1 FYVE domain is 1joc. The amino acid sequence and secondary structure alignment was generated with ESPrit software (http://espript.ibcp.fr/). The predicted secondary structure of the FYVE domain in At1g20110 is depicted according to the structure of EEA1 and using PSIPRED software (http://bioinf.cs.ucl.ac.uk/).(B) Modelling of FYVE domain binding to PI3P-enriched membranes according to the crystal structure of the human EEA1 FYVE domain. Zinc atoms of the RING finger are labeled in grey. The inositol backbone is shown in green and phosphorus atoms are shown as orange.
1

Supplemental Data. Belda-Palazon et al. (2016). Plant Cell. 10.1105/tpc.16.00178
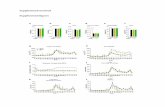
Intrinsic disorder profile
Supplemental Figure 2. Analysis of FYVE1 Using PSIPRED and DISOPRED2 Prediction Servers Reveals the Presence of an IDR in the N-terminal Region of the Protein. The FYVE1 amino acid sequence was used as a query in http://bioinf.cs.ucl.ac.uk/. Amino acids in FYVE1 are considered disordered when the blue line is above the grey dashed line, that is the confidence score is higher than 0.5. The orange line shows the confidence of protein binding site prediction within disordered regions. 2

Supplemental Data. Belda-Palazon et al. (2016). Plant Cell. 10.1105/tpc.16.00178
CAR1-YFPN/YFPC-PYR1 YFPC-PYR1 + YFPN-RSL1 RFP-TMD23-Ub MergedBA
YFPC-PYR1 + CAR1-YFPNRFP-FYVE1
YFPC-PYL4 + CAR1-YFPN
**
**
*Merged
RP =0.65 RS=0.60
Supplemental Figure 3. Interaction of PYR1 and CAR1 Generates Punctate/Globular Structures near the Plasma Membrane that Co-localize with RFP-FYVE1.
(A) BiFC interaction of CAR1 and PYR1 and co-expression of RFP-FYVE1. The photographs show confocal images of transiently transformed tobaccoepidermal cells co-expressing CAR1-YFPN/YFPC-PYR1 interacting proteins and RFP-FYVE1. Asterisks indicate the presence of CAR1-PYR1 in membranecomplexes that co-localize with FYVE1. Bar=30 m.(B) Co-expression of Receptor-RSL1 or Receptorr-CAR complexes with the vacuolar marker RFP-TMD23-Ub. Z-scan of confocal images of transiently
f N S C /C N C /transformed tobacco epidermal cells co-expressing either YFPN-RSL1 or CAR1/CAR4-YFPN and YFPC-PYR1/PYL4 plus RFP-TMD23-Ub. The RFP-TMD23-Ub marker decorates the vacuole and reveals the presence of Receptor-RSL1 complexes in vacuole, whereas CAR1-PYR1 or CAR1-PYL4 complexes werenot found in the vacuole when co-expressed with RFP-TMD23-Ub. Plants were incubated in darkness for 4 h in order to promote stabilization of fluorescentprotein-tagged vacuolar marker. Bars=30 µm.
3

A
Supplemental Data. Belda-Palazon et al. (2016). Plant Cell. 10.1105/tpc.16.00178
BiFC
FYVE1-YFPN
YFPC-Vps23A
B
Supplemental Figure 4. In Planta Interaction of FYVE1 and Vps23A and Colocalization of FYVE1 and ARA7 in BY-2 Cells.
(A) BIFC interaction of FYVE1 and Vps23A. Epifluorescence confocal images of transiently transformed tobacco epidermal cells co-expressingFYVE1-YFPN and YFPC-Vps23A. Co-localization of FYVE1 with the ESCRT-I Vps23 is observed in globular-shaped structures. Right panelh d t il f th BiFC fl t i l B 20 Mshows a detail of the BiFC fluorescent signal. Bars =20 M.
(B) Co-expression of FYVE1 and ARA7 in BY-2 cells. Plant cells were co-transformed with the indicated gene constructs and the cells wereprocessed, imaged and analyzed by CLSM as described in methods. GFP-FYVE1 and RFP-ARA7 co-localize both in punctuate and globular-shaped structures. Bar=10 m.
4

hA GFP-PYL5 FM4-64 Merged GFP-PYL5 MergedLysoTRedCB GFP-PYL4 LTRed Merged
Supplemental Data. Belda-Palazon et al. (2016). Plant Cell. 10.1105/tpc.16.00178
µM B
FA, 1
h
µM W
M 1
h
µM W
M 1
h
50
33
D
33
Was
h ou
t 2h Con
A, 2
h
D
ock
idi
0.5
µM
Mo
Supplemental Figure 5. GFP-PYL5 Accumulates in BFA Bodies and Both GFP-PYL4 and GFP-PYL5 Can Be Found in Lytic Compartments.
(A) Wm treatment induces accumulation of GFP-PYL4 in lytic compartments stained by the acidophilic probe LysoTrackerRed (1 µM for 1h ). Arrows show the presence of GFP-PYL4 into lytic compartments of the late endocytic pathway. All bars = 10 µm. (B) GFP PYL5 l t i BFA b di GFP PYL5 l li i BFA t t ith th
Moc
k
(B) GFP-PYL5 accumulates in BFA bodies. GFP-PYL5 colocalizes in BFA compartments with the endocytic tracer FM4-64. CLSM of root epidermal cells from Arabidopsis transgenic lines expressing GFP-PYL5. Four-d-old seedlings were labeled with 4 µM FM4-64 for 10 min, followed by 50 µM BFA treatment for 1 h. After washing out in MS medium for 2h, GFP-PYL5 redistributes and it appears localized mostly in nucleus and cytosol. Arrows mark BFA bodies. Bars = 10 µm. (C) Wm treatment induces accumulation of GFP-PYL5 in lytic compartments stained by the acidophilic ( ) y p y pprobe LysoTrackerRed (1 µM for 1h ). Arrows show the presence of GFP-PYL5 into lytic compartments of the late endocytic pathway. Bars = 10 µm. (D) Concanamycin A treatment (0.5 mM for 2 h) induces accumulation of GFP-PYL5 into vacuole, which was stained by the acidophilic probe LysoTrackerRed (1 µM for 1h ). Arrows show the presence of GFP-PYL5 in vacuole lumen of root epidermal cells. Bars = 10 µm.
5

Supplemental Data. Belda-Palazon et al. (2016). Plant Cell. 10.1105/tpc.16.00178
hGFP-PYL6 FM4-64 MergeA
h
GFP-PYL6 MergeLysoTracker
Red B50
µM
BFA
, 1
3 µM
WM
, 1h
5h
33
Was
h ou
t 2 Supplemental Figure 6. GFP-PYL6 Accumulates in BFA Bodies and Lytic Compartments.
(A) GFP-PYL6 colocalizes in BFA compartments with the endocytic tracer FM4-64. CLSMof root epidermal cells from Arabidopsis transgenic lines expressing GFP-PYL6. Four-d-old seedlings were labeled with 4 µM FM4-64 for 10 min, followed by 50 µM BFAtreatment for 1 h. After washing out in MS medium for 2h, GFP-PYL6 redistributes. Arrows
k BFA b di B 10mark BFA bodies. Bars = 10 µm.(B) Wm treatment induces accumulation of GFP-PYL6 in lytic compartments stained by theacidophilic probe LysoTrackerRed (1 µM for 1h ). Arrows show the presence of GFP-PYL5into lytic compartments of the late endocytic pathway. Bars = 10 µm.
Moc
k
6

Supplemental Data. Belda-Palazon et al. (2016). Plant Cell. 10.1105/tpc.16.00178
1
1,2
VE1
mR
NA
0 4
0,6
0,8
ress
ion
of F
YV
F436 and R535F1185 and RnoStop
0
0,2
0,4
Rel
ativ
eex
pr
SAIL_516_E05 SALK_205349fyve1-1/free1 (pst18264/15-1960 Riken)
fyve1-3 fyve1-4
0Col-0 fyve1-1(+/-) fyve1-3 fyve1-4
_
RnoStopF1185
1 1078 1258 1490 1777 1927 2184 2509 2948
y e / ee (pst 8 6 / 5 960 e )
fyve1-2
F436 R535
R267F450
2386Q139Stop
Supplemental Figure 7. Diagram of FYVE1 and Location of the Primers used for qRT-PCR Analysis of FYVE1 mRNA expression. The mRNAs were prepared from 10-d-old seedlings of Col-0 wt, fyve1-1 heterozygous (+/-) individuals, fyve1-3 and fyve1-4 homozygous mutants. Data are averages ± SD from three independent experiments. Expression of actin-8 was used to normalize data. Primers used for PCR amplifcation were F1185 + RnoStop (yellow arrows), for Col-0, fyve1-3 and fyve1-4 genotypes, or F436 R535 (red arrows), for Col-0 and fyve1-1(+/-). Primers F450 and R267 were used for genotyping of fyve1-3 (blue arrows).
7

fyve1-1 (+/-)Col fyve1-3 fyve1-4ASupplemental Data. Belda-Palazon et al. (2016). Plant Cell. 10.1105/tpc.16.00178
M4-
64, 3
h
root
4 µM
F
coty
ledo
n
fyve1-1 (+/-)Col fyve1-3 fyve1-4BCECF-AM BCECF-AM BCECF-AM BCECF-AMDIC DIC DIC DIC
B
Z-sc
anZ
nder
ing
JS
urfa
cere
nw
ithIm
age
Supplemental Figure 8. Altered Vacuolar Morphology in fyve1 Alleles.
(A) FM4-64 staining of (+/-) fyve1-1, fyve1-3 and fyve1-4 alleles reveals altered vacuolar morphology both in root meristem and cotyledonepidermal cells. Bars = 10 m.(B) BCECF-AM staining reveals tubular-like structures in vacuoles of (+/-) fyve1-1, fyve1-3 and fyve1-4. DIC, differential interferencecontrast. Bars = 10 m for Z-scan and 5 m for 3D reconstruction.
8

Supplemental Data. Belda-Palazon et al. (2016). Plant Cell. 10.1105/tpc.16.00178
FREE1 DEX-RNAi/GFP-PYL4pr
essi
on
1,5
2HA-PYL4
A B
-DEX
Rel
ativ
eex
p
0
0,5
1
Col fyve1-3
+DEX
y
expr
essi
on
1
1,5
2GFP-PYL4
Rel
ativ
ee
0
0,5
1
-DEX +DEX
Supplemental Figure 9. Analysis of HA-PYL4 and GFP-PYL4 mRNA Expression and CLSM Imaging of GFP-PYL4.
(A) Accumulation of HA-PYL4 or GFP-PYL4 mRNA is not significantlñy altered in fyve1-3 or FREE1 DEX-RNAi plants, respectively. Data areaverages ±SD from three independent experiments. Expression of actin-8 was used to normalize data.g p p p(B) CLSM imaging of GFP-PYL4 in FREE1 DEX-RNAi plants treated with 10 M Dexamethasone (DEX). Higher fluorescence of GFP-PYL4 wasobserved in FREE1 DEX-RNAi plants treated with 10 M Dexamethasone (DEX), which suggests enhanced accumulation of GFP-PYL4. DEX-inducible RNAi lines were crossed with plants expressing GFP-PYL4. The resulting F2 seedlings were visualized by CLSM after mock or DEXtreatment in darkness for 6 h. Bars = 10 m
9

Supplemental Data. Belda-Palazon et al. (2016). Plant Cell. 10.1105/tpc.16.00178
Supplemental Table 1. List of Oligonucleotides Used in this Work.
FYVE1/FREE1 amplifications:
FNcoIFYVE ACCATGGAACAGGGAGATTACAATTCGRnoStopFYVE ATGTGCGCTAACGAGGAAAGGRStop1184FYVE TCAGGTGGTGTAACTATTTGATTGRStopFYVE TCAATGTGCGCTAACGAGGAAAGG
Genotyping fyve 1-3 (SAIL 516 E05)Genotyping fyve 1 3 (SAIL_516_E05)Fp450FYVE tccgagtttgctacgtcatctR267FYVE AGTGAAGGAAGGAGCTGAAGGLB3SAIL: TAGCATCTGAATTTCATAACCAATCTCGATACAC
Genotyping fyve 1-4 (SALK_205349)F1185FYVE AACACCCTTCTGGACACTGTGACGF1185FYVE AACACCCTTCTGGACACTGTGACGRnoStopFYVE ATGTGCGCTAACGAGGAAAGGnewpROK2: GCCGATTTCGGAACCACCATC
Genotyping heterozygous fyve1-1/free1 (pst18264/15-1960 RIKEN BRC) Ds5-2A TCCGTTCCGTTTTCGTTTTTTACRnoStopFYVE ATGTGCGCTAACGAGGAAAGG
F436FYVE (qRT-PCR) TATTACTCACCGTATGATCAGCATCR535FYVE (qRT-PCR) ATGAATAAGGCGCGGGATTAG
TAP constructFattBPYL4: AAAAAGCAGGCTCCACC ATGGTTGCCGTTCACCGTCC RPYL4StopattB: agaaagctgggtc TCACAGAGACATCTTCTTCTTGattB1_FWD: GGGGACAAGTTTGTACAAAAAAGCAGGCT
B2 REV GGGGACCACTTTGTACAAGAAAGCTGGGTattB2_REV: GGGGACCACTTTGTACAAGAAAGCTGGGT
10