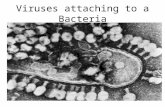
Viruses
-
Upload
germane-blevins -
Category
Documents
-
view
28 -
download
1
description
Transcript of Viruses
StandardsStandard 1: Cells CLE 3216.1.6 Describe the relationship between
bacteria, protists, and viruses and their host cells
Prokaryotes
Viruses NOT living (don’t meet all requirements)
Ex: Don’t grow and develop Needs a host to survive Cannot carry out cellular functions
Core of DNA or RNA surrounded by protein coat
Reproduce only by infecting living cells
Viral DiseasesViruses that cause disease attack and
destroy cellsCannot be treated with antibiotics
(maybe over the counter medicines)Vaccines work if used before virus is
contracted
Virus Structure Core filled with genetic
material inside Capsid =protein coat Proteins attach to cell
“tricking” it into letting the virus in
Viral genes are copied Host cell dies Bacterophage = virus
that only infects bacteria
Classification of Viruses
Have RNA vs DNA as their genomeDouble stranded vs Single strandedLinear vs Circular
Viral Infection 2 viral infection processes:1. Lytic infection - host cell bursts2. Lysogenic infection - virus remains
inactive inside of host for periods of time
Lytic Infection Virus DNA is injected
into host cell Cell begins to copy
virus DNA, then make virus proteins
Virus proteins break down host cell and uses it to copy more viruses
Cell finally bursts (lyses)
Lysogenic Infection Virus DNA is injected
into host cell’s DNA DNA is replicated with
included viral DNA Cell does not lyse -
virus remains inactive for period of time
Then enters lytic cycle when inactivation is over
Retrovirus Virus with RNA as
genetic material Retro = backwards Copies RNA into
DNA instead of DNA to RNA
Ex: AIDS
Emerging DiseaseIllness caused by new or reappearing
agents that typically exist in animal populations
Ex: Ebolo virus