Vertebral Column. Part of the axial skeleton Consists of 26 irregular bones 24 vertebrae, sacrum,...
-
Upload
mark-attwood -
Category
Documents
-
view
223 -
download
3
Transcript of Vertebral Column. Part of the axial skeleton Consists of 26 irregular bones 24 vertebrae, sacrum,...
Vertebral Column
• Part of the axial skeleton
• Consists of 26 irregular bones
• 24 vertebrae, sacrum, coccyx
• Vertebral column divisions– Cervical C1-C7– Thoracic T1-T12– Lumbar L1-L5– Sacrum S1-S5(fused)
Spinal curvatures
• Cervical and lumbar curves are secondary curves
• Develop after birth
• Thoracic and sacral curves are primary curves
• Appear during fetal development
• Overall curve of the spine is S shaped
Vertebral Anatomy
• All vertebrae have a common structural plan• Structural features are:
– Vertebral body– Vertebral arch – Vertebral foramen– Pedicles– Lamina– Articular processes, superior and inferior– Spinous process
Cervical Vertebrae
• C1-C7• Smallest vertebrae• Small vertebral body• Triangular shaped vertebral foramen• Small spinous process that is usually notched at
the end – bifid process• ALL cervical vertebrae have a transverse
foramen• C1 is called the ATLAS• C2 is called the AXIS
Thoracic Vertebrae
• T1-T12
• Larger vertebral body
• Oval vertebral foramen
• Spinous process projects posterocaudally
• T1-T8 vertebrae have superior and inferior costal facets for rib articulation
• T1-T10 have transverse costal facets for articulation of tubercles of the ribs
Lumbar Vertebrae
• L1-L5• Largest vertebrae• Large body• No articular facets on the body or
transverse processes• Triangular vertebral foramen• Short, flat spinous process• Weight bearing vertebrae
Sacrum
• Five fused sacral vertebrae• Fusion begins after puberty and is complete by
25-30 years of age• Curved dorsal surface• Special features
– Sacral canal– Median sacral crest– Sacral foramina– Lateral auricular surface to form the sacroiliac joint
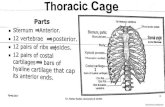
Thoracic Cage
• Consists of the – Thoracic vertebrae– Ribs, 12 pair– Sternum– Ribs 1-7 are true ribs, vertebrosternal– Ribs 8-12 are false ribs, vertebrochondrial, do
not attach directly to the sternum– Ribs 11-12 are called floating ribs, NO
connection to sternum
Sternum
• Flat bone that forms the midline of the thoracic wall
• Three components– Manubrium – articulates with the clavicles and
costal cartilages of R1– Manubrium has the jugular notch on the
superior surface– Body of sternum, articulation of ribs 2-7– Xiphoid process