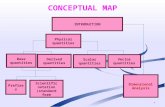
Vectors. Vector and Scalar quantities Scalar quantities have size or magnitude, but a direction is...
-
Upload
joleen-bradford -
Category
Documents
-
view
225 -
download
2
Transcript of Vectors. Vector and Scalar quantities Scalar quantities have size or magnitude, but a direction is...
Vector and Scalar quantities
• Scalar quantities have size or magnitude, but a direction is not specified.
(temperature, mass, speed, etc.)
• Vector quantities have magnitude and a specific direction (velocity, acceleration, etc.)
One way to find a resultant could be to draw the situation to scale on paper (such as 50 m = 1 cm).
Measuring the length of the vector pointing from the tail of the first vector to the head the second vector, and then, multiplying by the scale .
For example if line (c) is 3.0 cm the distance would be 150 meters. This is the displacement.
pg81 Physics Serway /Faugh (Holt)
Using Pythagorean theorem to find a resultants magnitude.
A toy car is moving directly across a moving walkway. As the car moves in the y direction, the walkway moves in the x direction.
• We can look at the diagram as a triangle. Therefore we can solve this by using the Pythagorean theorem.