Urochordata
description
Transcript of Urochordata

• Urochordata

Marine animals, live in all seas from shore to depth
Suspension feeders Adult sessile, solitary or colonial Only larva with notochord resembles vertebrates Figures: Class Ascidiacea (sea squirts)

Adult: Thick tunic protects animal and
attaches the base of the body to the substratum
Water incurrent (branchial) siphon stigmata of the branchial basket atrial cavity excurrent (atrial) siphon
Finger-like sensory tentacles surround the incurrent siphon to test the size of food particles
Endostyle (ventral groove) in branchial basket produces mucus that traps food particles. Cilia move mucus towards the gut. Undigested food passes out through the anus
Heart with two large vessels that connect to smaller vessels in pharyngeal basket. Direction of pumping alternates every few beats. From: Hickman et al. 2011

Larva:
Possesses all five chordate characteristics.
An acellular tunic covers the larva, and at the anterior end of the body the epidermis forms adhesive papillae under the tunic
At the end of its planktonic existence, the larva attaches with its adhesive papillae to substratum and undergoes metamorphosis
From: Hickman et al. 2011

Metamorphosis: The notochord, dorsal nerve cord and tail muscles are resorbed. All
that remains of the nerve cord is a ganglion.
The pharynx enlarges and the individual starts feeding for the first time
From: Hickman et al. 2011

Cephalochordata (lancelets) Small (length 3-7 cm), laterally compressed, hence name lancelet
Marine, sandy bottoms of coastal temperate or tropical waters, 29 species
Previously called Amphioxus now by priority Branchiostoma. The name “amphioxus” is still used as a common name for this group
From: Hickman et al. 2011

Shows the five diagnostic characteristics of chordates: dorsal notochord, hollow nerve cord above notochord, pharyngeal slits, endostyle, postanal tail. The notochord stretches from the tail up into the head, hence the name cephalochordates
Suspension feeder: Water mouth pharyngeal slits atrium atriopore
Food trapped in mucus (from endostyle) lining the pharynx intestine. Small particles hepatic cecum phagocytosis and intracellular digestion. Undigested food anus. Food movement by cilia not muscles.
Segmented slanted trunk musculature
Segmental spinal nerve roots.
From: Hickman et al. 2011

Closed circulatory system. Flow pattern similar to fish: Ventral aorta up through branchial arteries paired dorsal aortas unpaired dorsal aorta. No heart but bulbilli at pharyngeal arches.
No erythrocytes or hemoglobin only distribution of nutrients.
Respiration over body surface (laterally compressed)
Sexes separate, gametes atrium atriopore fertilization outside
From: Kardong 2009

Principles of systematics

Linnean Taxonomy
From: Hickman et al. 2011

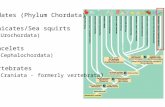
Cladogram of living Chordates
From: Hickman et al. 2011

monophyly, paraphyly, polyphyly
From: Hickman et al. 2011

Cladogram of living Chordates
From: Hickman et al. 2011

Radiata Bilateria
Acoelomate Pseudocoelomate Coelomate
Protostomes Deuterostomes
From: Kardong 2009
From Kardong 1998