Urinary Bladder, Irrational Fear of Peeing in Public, Bladder Shy, Shy Bladder Help, Public Phobia
Urinary bladder
-
Upload
praveen-nagula -
Category
Documents
-
view
5.409 -
download
5
Transcript of Urinary bladder

04/18/20231
URINARY BLADDER
BY Dr.NAGULA PRAVEEN

04/18/2023 2
Case scenarios
1. A 45 year old male came to ED few hours after sustaining a fall from the steps and injured his spine—MRI spine showed the cord compression at T11, T12,L1—on examination the patient had paraplegia, areflexia,hypotonia.incontinence of bowel and bladder.

04/18/2023 3
2. A 35 yr old female k/c/o multiple sclerosis came with bladder complaints—cystometrogram showed uninhibited contractions of the bladder,detrusor is hyperactive,dysynergia present--?
3.A 55 yr old female,had prolapse of uterus and incontinence of urine while coughing and sneezing.she had h/o vaginal deliveries at home and perineal injury due to delivery.no treatment taken.

04/18/2023 4
4. a 45 yr old ,grossly pallor,k/c/ TB,cachetic patient was found to be incontinent before he could reach the toilets.cystometrogram revealed normal bladder function.
5.A 43 yr old female suffering from frequent UTI presented with incontinence of urine before reaching the toilet.nocturnal wetting present.

04/18/2023 5
6. a 65 yr old case of BOO came with complaints of frequent passage of urine,patient giving history of pressure over the abdominal muscles while voiding but voiding is incomplete—USG showed high residual volume.

04/18/2023 6
Review of cases
1.overflow incontinence---spinal shock ,UMN lesion
2.reflex neurogenic bladder,spastic as sacral nerves are intact.cortical inhibition is lost.UMN
3.stress incontinence. 4.functional incontinence. 5.urge incontinence. 6. atonic bladder due to BOO.

04/18/2023 7
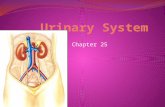
Anatomy
immediately behind the pelvic bones Empty bladder within pelvis. pyramidal in shape when empty. Ovoid when filled with urine. Parts—apex, base,neck,superior
surface ,two inferolateral surfaces. Epithelium-transitional---plastic

04/18/2023 8
Apex connected to the umbilicus by median umbilical ligament—remnant of urachus.
Superolateral angle joined by ureters. Inferior angle gives rise to urethra. Base or posterior surface is triangular. Vas deferens on the posterior surface of
bladder.. Peritoneal covering is peeled off the
lower part of anterior abdominal wall,as the bladder fills,lies in direct contact with anterior abdominal wall.

04/18/2023 9
held in position by puboprostatic ligaments.
Mucous membrane -rugae –disappear when filled.
Trigone-smooth,firmly adherent to the underlying muscular wall.
Between ureters is called as interureteric ridge.
Ureters enter obliquely. Muscle of the bladder-smooth muscle-
detrusor. Sphincter vesicae at neck of bladder.

04/18/2023 10

04/18/2023 11

04/18/2023 12

04/18/2023 13

04/18/2023 14
Blood supply,lymphatic drianage
Superior and inferior vesical arteries----internal iliac arteries
Vesical venous plexus---prostatic plexus –internal iliac vein
Internal and external iliac lymph nodes

04/18/2023 15
sphincters
Assure continence In male ,internal sphincter prevents the
reflux of semen from urethra during ejaculation.
to relax during micturition. Int. sphincter-sphincter vesicae-sym-
adrenergic Ext,sphincter –sphincter urethrae-
int.pudendal nerve

04/18/2023 16
Nerve supply Inferior hypogastric plexuses. Sympathetic post ganglionic fibres
from L1,L2 via hypogasrtic plexuses Parsympathetic preganglionic fibers
from S2,S3,S4---inferior hypogastric plexuses—bladder wall—synapse with post ganglionic fibres
Afferent sensory fibres---pelvic sphlanchnic nerves—CNS
Some afferent—sympathetic—hypogastric plexus—L1,L2

04/18/2023 17

04/18/2023 18

04/18/2023 19

04/18/2023 20
BLADDER FUNCTION
Storage and intermittent evacuation of urine are served by three structural components –bladder itself,detrusor ,functional internal sphincter composed of smooth muscle,striated external sphincter or urogenital diaphragm .

04/18/2023 21
Detrusor muscle innervation
DETRUSOR CENTER S2,S3,S4 ofspinal cord intermediolateral columns of gray matter pre ganglionic fibers synapse in parasympathetic ganglia within the bladder wall short post ganglionic fibers end on ----muscarnic acetylcholine receptors of muscle fibers.
Cause contraction of bladder. Antagonised by atropine—5mg

04/18/2023 22
Sympathetic fibers interomediolateral nerve cells of T10,T11,T12 preganglionic fibers pass via inferior sphlanchnic nerves,inferior mesenteric ganglia-----hypogastric nerve---beta adrenergic receptors in dome of bladder,alpha adrenergic to internal sphincter and trigone
Filling phase of urine. Causes relaxation of bladder. Relaxation of sphincter.

04/18/2023 23
Anterolateral horns of S2,S3,S4----densely packed group of somatomotor neurons—(nucleus of onuf)—pudendal nerves---External urethral and anal sphincter are composed of striated muscle fibers.
Ventrolateral part —innervate external urethral sphincter
Mediodorsal part--- anal sphincter Respond to nicotinic effects of Ach.

04/18/2023 24
Urethra,external sphincter –afferent fibers---pudendal nerves—sacral segments of spinal cord---higher centers
Impulses for reflex activities Sensation of bladder fullness Some go through hypogastric plexus---
transverse lesions of the cord as high as T 12 report vague discomfort of urethra.

04/18/2023 25
Special feature of Detrusor muscle
Unlike striated muscle ,detrusor muscle is capable of some contractions,imperfect at best due to its postganglionic system—after complete transection of the sacral segments of spinal cord.
Do not empty the bladder completely. Dysynergia of detrusor and external
sphincter muscles---as coordination occur at supraspinal levels.

04/18/2023 26
Micturition center lies in locus cereleus. Medial region—triggers micturition. Lateral region—continence. Afferents from sacral segments Efferents ---reticulospinal tracts in the lateral
funiculi of the spinal cord ---cells of onuf—sacral segments.
Fibers from motor cortex—corticospinal tracts—AHC-external sphincter.
Mid brain tegmentum are inhibitory Pontine tegmentum are facilitatory From cortico spinal tract is inhibitory.

04/18/2023 27
Normal micturition
Possible only when the spinal segments.,together with their afferent and efferent nerve fibers,are connected with so called micturition centers in the pontomesencephalic tegmentum.

04/18/2023 28
The act of micturition is both reflex and voluntary.
Normal person on voiding 1.voluntary relaxation of the perineum 2.increased tension of the abdominal
wall 3.slow contraction of the detrusor 4.opening the internal sphincter 5.relaxation of the external sphincter. Detrusor contraction is spinal stretch
reflex

04/18/2023 29
Assisted by abdominal muscle contraction –raises intrabdominal pressure—external pressure on bladder
It is a simple reflex in young children,inhibited by crebral cortex in adults—corticospinal tracts –S2,S3,S4
Voluntary control of micturition –sphincter urethrae contraction—2-3 yr of life.

04/18/2023 30
The abdominal muscles have no power to initiate micturition except when the detrusor muscle is not functioning normally.
The voluntary restraint of micturition is a cerebral affair—arise from frontal lobes
Integration of detrusor and external sphincteric function depends mainly on the descending pathway from the dorsolateral pontine tegmentum.

04/18/2023 31
Increased blood flow was detected in the right pontine tegmentum,periaqueductal region,hypothalamus,and right inferior frontal cortex
Subjects prevented from voiding with full bladder-right ventral pontine tegmentum
Pontine centers involved in in voiding.

04/18/2023 32
LESIONS—BLADDER FUNCTION

04/18/2023 33
1.Loss of complete cord below T12

04/18/2023 34
Trauma,myelodysplasias,tumor,venous angioma,necrotizing myelitis.
Bladder is paralysed No awareness of fullness of bladder. Overflow incontinence Voiding by crede manuevre—lower
abdominal compression and straining Saddle anesthesia. Anal sphincter and colon are affected. Abolition of bulbocavernous reflexes,anal
reflex Cystometrogram low pressure and no
emptying contractions.

04/18/2023 35
2.disease of the sacral motor neurons in the spinal gray matter,the anterior roots ,peripheral nerves

04/18/2023 36
Ex—lumbar meningomyelocele,tethered cord syndrome.
LMN paralysis of the bladder Paralyzed bladder.—tone is lost. Voluntary intiation of micturition is lost.
—loss of cortical fibres Bladder distends as urine accumulates
until there is overflow in continence. Sacral and bladder sensation are
intact. It is ATONIC bladder.

04/18/2023 37

04/18/2023 38
3.interupption of sensory afferents from the bladder
in diabetes and tabes dorsalis motor fibers are unaltered. primary sensory bladder paralysis both afferents and efferents are
affected small fibers-diabetes. Guillain barre syndrome..

04/18/2023 39
4.upper spinal cord lesions: Reflex neurogenic bladder (spastic) Multiple sclerosis,traumatic
myelopathy Syringomyelia,myelitis,spondylosis,AV
M,tropical spastic paraperesis. Sudden onset—spinal shock Urine accumulates—distended—
overflows As spinal shock resolves—unable to
inhibit the bladder—urgency,precipitant micturition,incontinence result.

04/18/2023 40

04/18/2023 41
Intiationof voluntary micturition is impaired and bladder capacity is reduced
Bladder sensation upon sensory tracts Preservation of bulbocavernous and anal
reflexes Uninhibited contractions of bladder in
relation to low volume of urine If the lesion develops slowly—no flaccid
stage,incontinence worsen with time In case of cervical cord injury there is
persistent hypotonicity.

04/18/2023 42
5.mixed type of neurogenic bladder Multiple sclerosis Tethered cord syndrome, Multiple level lesions Combination of sensory motor,spastic bladder
paralysis
6.stretch injury of the bladder Anatomic obstruction of bladder neck Repeated voluntary retention of urine Repeated overdistention leads to
decompensation—atonia,hypotonia Emptying contractions are inadequate. Large residual volume even after the crede
manuevre

04/18/2023 43
7.frontal lobe incontinence Confused mental state Ignores the desire to void Subsequent incontinence Supranuclear type of hyperactivity and
precipitant evacuation Posterior part of superior frontal
gyrus,anterior cingulate gyrus No warning signs of fullness—
suddenly wet Waking hours. 8. nocturnal incontinence enuresis- Delay in acquiring inhibition of micturition

04/18/2023 44
Urge incontinence

04/18/2023 45
URGE INCONTINENCE Reduced bladder capacity Excessive and inappropriate detrusor
contraction. Decreased cortical inhibition –cerebral
infarction,alzheimers disease,brain tumor,parkinsons disease.
Bladder irritation—trigonitis,post radiation fibrosis.
Outflow tract obstruction . Frequent episodes of urgency
Moderate to large volumes Nocturnal wetting

04/18/2023 46
Sphincter /pelvic incompetence
MC form of urinary incontinence Pelvic floor laxity-ageing,vaginal
deliveries,direct perineal injury cystocele prostatic surgery
Partial denervation. Incontinence at times of straining –
coughing,laughing,sneezing.lifting Small to moderate volume of urine Very infrequent night time leakage Little post voidal residual .

04/18/2023 47

04/18/2023 48

04/18/2023 49
Reflex incontinence Spinal cord damage above sacral cord level Detrusor spasticity Functional outflow obstruction Unable to sense the need to void Spinal cord injury is most common Day and night time with equal frequency Without warning or precipitating stress Moderate volumes Frequent voiding Perineal sensation reduced Sacral reflexes intact

04/18/2023 50
Functional incontinence
Physical and mental disabilty Urinary tract is intact Sedatives may exacerbate the
condition Frontal lobe dysfunction

04/18/2023 51
WORK UP History—precipitants Timing Frequency Volume of urine loss Warning symptoms Intactness of perineal and bladder
sensations Diary of events and contributing factors Medications—anticholinergics,alpha
adrenergics,b blockers

04/18/2023 52
Physical examination
Gen examination Suprapubic palpation Percussion of bladder after voiding Per rectal-prostate enlargement Valsalva manuevre Stress incontinence when bladder is full Vaginal atrophy Bulbocavernous reflex’ Anal sphincter tone

04/18/2023 53
Lab analysis Urinalyiss BUN Creatinine Glucose USG Cystometrogram Stress tests2gm of wetting Cotton swab test Marshall and bonney test Urethroscopy

04/18/2023 54

04/18/2023 55
CYSTOMETROGRAM

04/18/2023 56
Therapy
Flaccid paralysis—bethanechol Spastic paralysis—
propantheline,oxybutinin Intermittent self catheterisation Chronic antibiotic therapy Vitamin C 1000mg/day Sacral stimulator

04/18/2023 57
summary
incontinence detrusor features
Detrusor instability Unstable detrusor Frequent episodesNocturnal wettingSmall post voidal residualIntact reflexesNormal sensation
Stress incontinence Inadequate sphincter
Upon strainingSmall to moderate volumesRarely at nightSmall post voidal
Reflex incontinence Autonomous bladder
No warning or pptDuring day and nightModerate volumeReflexes intactLoss of control and sensation
Overflow incontinence
Distended bladderLoss of reflexesPost voidal residual
Functional incontinence
Inability to reach toilet due to illness

04/18/2023 58
TAKE HOME MESSAGE Stress incontinence is a feature of elderly. Urge Incontinence in case of chronic trigonitis Functional incontinence in case of severel ill
patients. Cystometrogram is important for evaluation. Self catheterisation by the patient to be
encouraged. USG showing residual volume over 20 ml—
neurogenic bladder. Every case of incontinence check for sacral
area for sensations,bulbocavernous reflex,anal sphincter tone by PR

04/18/2023 59
REFERENCES
SNELLS ANATOMY PRIMARY CARE MEDICINE HARRISONS 17 TH ED ADAM AND VICTORS’ PRICIPLES OF
NEUROLOGY SEVENTH ED.

04/18/2023 60
Thank you