UNIT 9: Introduction to DNA Lecture 4: DNA Modeling and ...modeling... · KIPP NYC College Prep...
Transcript of UNIT 9: Introduction to DNA Lecture 4: DNA Modeling and ...modeling... · KIPP NYC College Prep...

Work hard. Be nice. 100% EVERYDAY.
Name: _______________________________ Period: _______ Date: ___________________ KIPP NYC College Prep Genetics and Biotech
UNIT 9: Introduction to DNA Lecture 4: DNA Modeling and Intro to Replication
By the end of today, you will have an answer to:
How can 1 strand of DNA serve as a template for replication?
Do Now! 1) Label the following missing pieces on the DNA model.
2) Draw 1 nucleotide in the space below: Introduction: In 1953, using x-ray diffraction studies obtained by Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins, James Watson and Francis Crick proposed a model to explain the structure of DNA. In this model, each DNA molecule consists of two strands twisted about one another to form a double helix. These strands are quite long and are twisted, coiled and packed tightly in cells or in the chromosomes in cells that have nuclei. DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) is the basic hereditary material in all cells and contains all the information necessary to make proteins. In this Lab-Aids® kit, you will be assembling a small portion of a DNA model in order to understand the components that make up this very important molecule.

Work hard. Be nice. 100% EVERYDAY.
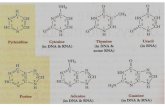
These bases are connected in the center of the molecule by weak chemical bonds called hydrogen bonds. (These are the same kind of bonds that hold liquid water or ice molecules together.) Hydrogen bonds are forces that link a hydrogen atom of one nitrogen base to an oxygen or nitrogen atom of the other base. A base is a chemical species that receives a proton, as it has an available pair of electrons. The unique feature of this molecule is the manner in which the two chains are held to each other. Each rung consists of a single-ring nitrogen base called a pyrimidine linked to a double-ringed nitrogen base called a purine. Adenine (double ring nitrogen base called a purine base) is always linked with thymine (a single ring nitrogen base called a pyrimidine. Guanine (double ring purine base) is always linked to cytosine (a single ring nitrogen pyrimidine base). An important part of the Watson-Crick model is this base-pairing rule: Adenine bases (orange) are only paired with Thymine bases (green) Guanine bases (yellow) are only paired with Cytosine bases (blue) The order in which they occur in the ladder makes up the genetic code of a living thing. Procedure: Familiarize yourself with each of the following components of the 3 chemical groups and the hydrogen bond:

Work hard. Be nice. 100% EVERYDAY.
1. Construct a ladder by first joining the sugar and phosphate groups to make the sides of the ladder (see a). Place a white tube on the north and south posts of the sugar unit. Make two sides each with 8 sugar units and the phosphate groups (white tubes). Each post on the sugar unit represents a covalent bond. 3. To complete the three-dimensional “double-helix”, gently twist the ladder until it resembles the following illustration (e.) Twist the model until it resembles (f). It will retain this shape. 4. Join your model to others in your class to make a large DNA molecule.
2. Next construct the nitrogen bases making sure you follow
the base-pairing rule. (see b) (AT or TA) Attach orange
and green tubes with the hydrogen bond (white rod). Then
(CG or GC) Attach blue and yellow tubes with hydrogen
bonds. Attach each pair of tubes to east post of the sugar
unit if left side (west post if right side) of ladder.
See illustration below and construct your model using the
same combinations or code. (As in illustration d).
Study the diagram of a segment of the DNA. Note that the
guanine (yellow tube) is always linked to cytosine (blue tube).
Thymine (green tube) is always connected to adenine (orange tube).
While only certain pairs of nitrogen based nucleotides can be linked to
one another, the order of the combinations of these pairs occur in
many different arrangements or sequences. These combinations or
sequences determine the characteristics of living things, the genetic
code. This is why DNA testing is widely used to identify individuals
in criminal cases and also identifying pathogens, when diagnosing
diseases.

Work hard. Be nice. 100% EVERYDAY.
Name: _______________________________ Period: _______ Date: ___________________ KIPP NYC College Prep Genetics and Biotech Classwork 9.4 DNA Modeling and intro to replication 10 points
1. What is the relationship between a nucleotide and a molecule of nucleic acid?
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
2. In the replication of DNA, what kind of molecule bonds with an unpaired cytosine nucleotide? ______________________________________________________ What pairs with adenine? ______________________________________________________
3. What substances form the uprights or sides of the DNA ladder?
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
4. What are hydrogen bonds?
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
How are they important in the replication of DNA?
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
5. Why must the quality and quantity of DNA in cells remain the same from generation to generation? _______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
6. What is a scientific model and in what ways is it useful? _______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________

Work hard. Be nice. 100% EVERYDAY.
Name: _______________________________ Period: _______ Date: ___________________ KIPP NYC College Prep Genetics and Biotech
Homework 9.4 DNA Modeling and Intro to Replication 10 points

Work hard. Be nice. 100% EVERYDAY.
Analysis:
1) What are the “rungs”
to the DNA molecule?
2) What do the sugars
bond to?
3) What do the
phosphates bond to?
4) What do hydrogen
bonds do?