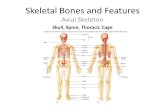
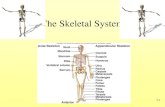
Unit 5: The Skeletal System Ch. 7. General Organization 206 bones* Axial Skeleton – down the...
-
Upload
annabel-carpenter -
Category
Documents
-
view
226 -
download
1
Transcript of Unit 5: The Skeletal System Ch. 7. General Organization 206 bones* Axial Skeleton – down the...
General OrganizationGeneral Organization206 bones*206 bones*
Axial Skeleton – down Axial Skeleton – down the centerthe center
Skull Skull Cranium – 8Cranium – 8 Facial – 14Facial – 14 Middle Ear - 6Middle Ear - 6
Vertebral ColumnVertebral Column Cervical – 7Cervical – 7 Thoracic – 12Thoracic – 12 Lumbar – 5Lumbar – 5 Sacrum, CoccyxSacrum, Coccyx
Thoracic Cage Thoracic Cage 12 pairs12 pairs
7 true ribs7 true ribs 5 False 5 False
RibsRibs 2 2
floatinfloatingg ribs ribs
Appendicular Skeleton – the appendagesAppendicular Skeleton – the appendages Pectoral GirdlePectoral Girdle
Scapula – 2Scapula – 2 Clavicle – 2Clavicle – 2
Upper LimbsUpper Limbs Humerus – 2Humerus – 2 Radius – 2Radius – 2 Ulna – 2Ulna – 2 Carpals – 16Carpals – 16 Metacarpals – 10Metacarpals – 10 Phalanges – 28Phalanges – 28
Pelvic GirdlePelvic Girdle Coxal – 2Coxal – 2
Lower LimbsLower Limbs Femur – 2Femur – 2 Patella – 2Patella – 2 Tibia – 2Tibia – 2 Fibula – 2Fibula – 2 Tarsals – 14Tarsals – 14 Metatarsal 10Metatarsal 10 Phalanges - 28Phalanges - 28
Types of BonesTypes of Bones Long – cartoon boneLong – cartoon bone
Expanded endsExpanded ends Longer than wideLonger than wide Humerus, femur, finger bones Humerus, femur, finger bones
Short – boxy or cube-likeShort – boxy or cube-like Carpals, tarsalsCarpals, tarsals
Flat – platelikeFlat – platelike Ribs, scapula, sternumRibs, scapula, sternum
Irregular – variety of shapesIrregular – variety of shapes Vertebrae, many facial bonesVertebrae, many facial bones
Sesamoid – found in joints for stabilitySesamoid – found in joints for stability Patella (knee cap)Patella (knee cap)
Wormian (sutural) – extra bones in skull where Wormian (sutural) – extra bones in skull where cranial bones meetcranial bones meet
Bone Structure:Bone Structure: Macroscopic Structure – Long boneMacroscopic Structure – Long bone
Epiphyses – expanded endsEpiphyses – expanded ends Articular Cartilge – hyaline; protection in jointsArticular Cartilge – hyaline; protection in joints
Diaphysis – shaftDiaphysis – shaft Medullary Cavity – hollow portion containing marrowMedullary Cavity – hollow portion containing marrow Periosteum – outer coveringPeriosteum – outer covering Endosteum – inner coveringEndosteum – inner covering
Types of boneTypes of bone Compact – dense for strengthCompact – dense for strength
outerouter OsteonsOsteons
Spongy – light, airySpongy – light, airy innerinner Reduce weightReduce weight TrabeculaeTrabeculae
Bone Structure:Bone Structure: Microscopic – CompactMicroscopic – Compact
Osteon – Repeating unitOsteon – Repeating unit BullseyeBullseye
Osteonic (Haversion Canal)Osteonic (Haversion Canal) CentralCentral Blood vessels, nervesBlood vessels, nerves
Lamellae – concentric circles of matrixLamellae – concentric circles of matrix Osteocytes – mature bone cellsOsteocytes – mature bone cells
LacunaeLacunae CanaliculiCanaliculi
Transverse (perforating/ Volkmann’s) CanalTransverse (perforating/ Volkmann’s) Canal Connects osteonic canalsConnects osteonic canals
Bone Structure:Bone Structure:
Spongy - cancellousSpongy - cancellous Trabeculae – bony platesTrabeculae – bony plates
Osteocytes found hereOsteocytes found here
Bone Growth and Bone Growth and DevelopmentDevelopment
Skeletal Formation AnimationSkeletal Formation Animation OssificationOssification – formation of bone – formation of bone
OsteoblastOsteoblast – deposit solid mineral matrix – deposit solid mineral matrix Turn into Turn into osteoclastsosteoclasts – mature bone cells – mature bone cells
Endochondral Bone FormationEndochondral Bone Formation Most common; arise from hyaline cartilageMost common; arise from hyaline cartilage Periosteum forms; deposit bone underneath – Periosteum forms; deposit bone underneath –
outside of bone firstoutside of bone first Primary ossification center – center of Primary ossification center – center of
diaphysisdiaphysis Ossification moves towards endsOssification moves towards ends
Secondary Ossification Center – EpiphysesSecondary Ossification Center – Epiphyses Mainly spongy bone developsMainly spongy bone develops
Bone Growth and Bone Growth and DevelopmentDevelopment
Epiphyseal Disk – growth plateEpiphyseal Disk – growth plate Area between the two ossification centers that Area between the two ossification centers that
remains cartilageremains cartilage Does not ossifiy until adulthoodDoes not ossifiy until adulthood 4 layers of cells 4 layers of cells
Cartilage cells continue to divide, mature, ossify and dieCartilage cells continue to divide, mature, ossify and die Move toward ends of boneMove toward ends of bone
Intramembranous Ossification – bone Intramembranous Ossification – bone formation between two sheets of connective formation between two sheets of connective tissuetissue Generally in flat bones of skullGenerally in flat bones of skull
Factors Affecting Bone GrowthFactors Affecting Bone Growth Diet – what you eatDiet – what you eat
Minerals such as calcium, phosphatesMinerals such as calcium, phosphates Vitamin D – needed for proper absorption of calciumVitamin D – needed for proper absorption of calcium
Rickets/ osteomalacia – lack of vit. D; soft bonesRickets/ osteomalacia – lack of vit. D; soft bones Dehydrocholesterol – inactive form; activated by sunlight in the Dehydrocholesterol – inactive form; activated by sunlight in the
skinskin Vitamin A & CVitamin A & C
Vit. A – bone resorptionVit. A – bone resorption Lack causes retardation in developmentLack causes retardation in development
Vit. C – collagen synthesisVit. C – collagen synthesis Hormones – chemical messengers from glandsHormones – chemical messengers from glands
Human Growth Hormone – pituitary; stimulates growth of Human Growth Hormone – pituitary; stimulates growth of epiphyseal diskepiphyseal disk
Dwarfism, gigantism, achondroplasia, acromegalyDwarfism, gigantism, achondroplasia, acromegaly Thyroid hormone – thyroid; replace cartilage with boneThyroid hormone – thyroid; replace cartilage with bone Male and Female Sex HormonesMale and Female Sex Hormones
Physical Stress – exercisePhysical Stress – exercise Tug of tendons cause bones to thicken and strengthenTug of tendons cause bones to thicken and strengthen
Skeletal Functions:Skeletal Functions: Support and ProtectionSupport and Protection Body Movement – lever actionsBody Movement – lever actions
11stst class – EF, F, RF class – EF, F, RF TricepsTriceps
22ndnd class – F, RF, EF class – F, RF, EF MandibleMandible
33rdrd Class – F, EF, RF Class – F, EF, RF BicepBicep
Blood Cell Formation – HematopoiesisBlood Cell Formation – Hematopoiesis Marrow – hematopoietic tissueMarrow – hematopoietic tissue
Found in medullary cavity of long bones (young); Found in medullary cavity of long bones (young); spongy bone spaces (older)spongy bone spaces (older)
Red – blood cell formationRed – blood cell formation Yellow – fat storageYellow – fat storage
Can be converted back and forth as neededCan be converted back and forth as needed
Skeletal Functions:Skeletal Functions: Hemocytoblast – blood stem cellHemocytoblast – blood stem cell
Erythrocyte – red blood cellErythrocyte – red blood cell Leukocyte – white blood cellLeukocyte – white blood cell Thrombocyte – plateletThrombocyte – platelet
Inorganic Salt StorageInorganic Salt Storage Electrolytes needed for a variety of Electrolytes needed for a variety of
physiological functionsphysiological functions CaCa++++ needed for nerve impulse conduction, skeletal needed for nerve impulse conduction, skeletal
muscle contractionmuscle contraction Negative FeedbackNegative Feedback
Blood Ca levels too high: Thyroid releases Calcitonin Blood Ca levels too high: Thyroid releases Calcitonin osteoblast activity; deposit calcium in bone osteoblast activity; deposit calcium in bone
Blood Ca levels too low: Parathyroid release Blood Ca levels too low: Parathyroid release parathyroid hormone parathyroid hormone Osteoclast activity; dissolve Osteoclast activity; dissolve bone, release minerals into bloodbone, release minerals into blood