Unit 5: Seventh Grade. Asexual Mitosis Only one parent cell is needed Division results in offspring...
-
Upload
dwight-ferguson -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Unit 5: Seventh Grade. Asexual Mitosis Only one parent cell is needed Division results in offspring...

Meiosis and Heredity Unit 5: Seventh Grade

There are two kinds of reproduction
Asexual• Mitosis• Only one parent cell is
needed• Division results in
offspring with a genotype identical to the parents’
Sexual• Meiosis• Two parent cells join • Sex cells• Sperm= males• Eggs = females• Offspring share traits
with traits with their parents, but are not exactly like their parents

Walter Sutton’s Discovery• In 1903, an American
graduate student named Walter Sutton made an important observation.
• While studying grasshopper cells, Sutton observed that chromosomes occurred in distinct pairs
• And that during meiosis, the chromosome pairs split, and each chromosome goes to its own cell.

Meiosis• While mitosis was
cell division for growth, meiosis is cell division for sexual reproduction.
• Meiosis happens when it’s time to reproduce an organism

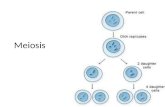
The Big Idea• There are TWO cell divisions• Mitosis has one division, but meiosis has TWO• You still have to remember PMATI, but you
have to go though it twice• Prophase-Metaphase-Anaphase-Telophase-
Interphase• Four cells are created from one.• Start with one, get four!• Each cell has only HALF the amount of DNA
needed by a cell

Meiosis happens when it’s time to reproduce an organism• The steps are very simple, when you break it
down, it’s just two PMATIs in a row.• Scientists call it Meiosis I and Meiosis II, but it’s
just two PMATIs• The interphase that happens between the two
PMATIs is very short and the DNA is not replicated• The resulting cells (sperm and eggs) have half the
number of chromosomes (23 in humans) and are referred to as haploid cells.
• This is basically like the PMATI of regular mitosis.

Meiosis I --- Almost like mitosis• Pairs of
chromosomes line up at the center of the cell and then are pulled to each side.
• The genetic material duplicates, the cell divides and two cells result

A Short Interphase• Normally, the cell
would go about its business of living during its interphase, and slowly duplicate its chromosomes getting ready for its next mitotic division
• But since this is meiosis, there is a very short interphase and division begins again!

Meiosis II is a bit different from mitosis.. • During Prophase I, a process
called crossing-over occurs.• This crossing over is an
exchange of genes.• This leads to the genes being
mixed up, and the cell is not an exact duplicate like in mitosis
• The rest of the steps (Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase) follow the patterns of mitosis and meiosis I, but instead of starting with one cell and ending with two, one cell becomes four!

Because of meiosis …• Instead of two new cells being created with equal
numbers of chromosomes like mitosis, the cell divides a second time after the first.
• Genetic material is mixed up, and different eggs/sperm from the same person have different genetic make up
• The resulting cells (sperm and eggs) have half the number of chromosomes of a normal (diploid) body cell• Haploid cells
• When a sperm fertilizes an egg, the resulting zygote (fertilized egg) receives one copy of each gene from the mother and one copy from the father. Thus, each person receives half of his/her genes from mom and the other half from dad.

Walter Sutton used his observations of meiosis, • And his understanding of Mendel’s work that
stated that an offspring receives half its genetic information from its father and the other half from its mother,
• And some creative thinking,• Sutton proposed something very important:• Genes are located on chromosomes

Meiosis and Mendel • Through his work,
Sutton was able to show that the steps of meiosis explained Mendel’s results with his pea plants.
• Meiosis explained how characteristics were inherited.
•

Sex Chromosomes• Information on
chromosomes determines many of our traits.
• Sex chromosomes carry the genes that determine gender

Gender Determination• Sex chromosomes
are described as either “X” or “Y”
• In humans, females have the genotype of XX
• Males have the genotype of XY

So how was your gender determined?
• During meiosis, only one of each of the chromosome pairs ends up in a sex cell.
• All female sex cells (eggs) have one “X” chromosome
• However, male sex cells (sperm), will have either an “X” or “Y”

Boy or Girl???????• If an egg is fertilized
by a sperm with an “X” chromosome, the offspring will be a female• Genotype: XX• Girls are X-cellent!!!
• If the egg is fertilized by a sperm with a “Y” chromosome, the offspring will be a male• Genotype XY

Sex-Linked Disorders• The Y chromosome does not
carry all of the genes an X chromosome
• Females have two X chromosomes, so they carry two copies of each gene carried on the X chromosome.
• This makes a backup gene available if one becomes damaged.
• Males only have one copy of the X chromosome
• They have no back up!

Sex-Linked Disorders• Examples:• Color Blindness• Hemophilia• Baldness
• The genes for certain disorders are carried on the X chromosome.
• These disorders are called sex-linked disorders.
• Because the gene for such disorders is recessive, males are more likely to be affected

Genetic Counseling• Many genetic disorders can be traced through a
family tree.• If a couple is worried that they might pass a
disease to their children, they may consult a genetic counselor.
• These counselors often make use of a diagram called a pedigree, which is a tool for tracing a trait through generations of a family.
• By making this pedigree, a counselor can often predict if a person is a carrier of a hereditary disease.

Cystic Fibrosis Pedigree

Selective Breeding• In selective breeding,
organisms with desirable characteristics are mated.
• Plants and animals are often selectively bred for higher food quality.
• Dogs, cats and other pets are also commonly bred selectively.
• http://pbskids.org/dragonflytv/games/game_dogbreeding.html